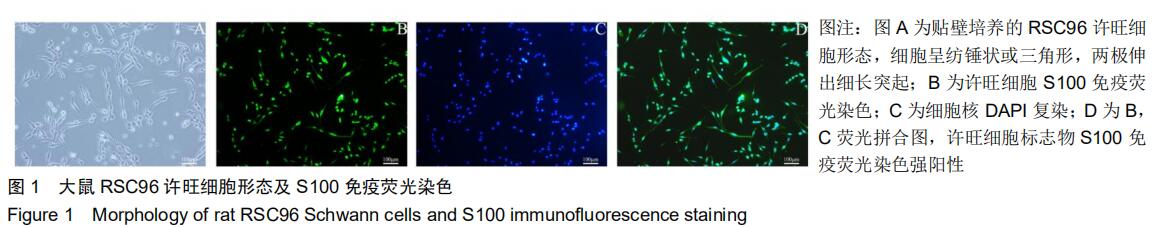
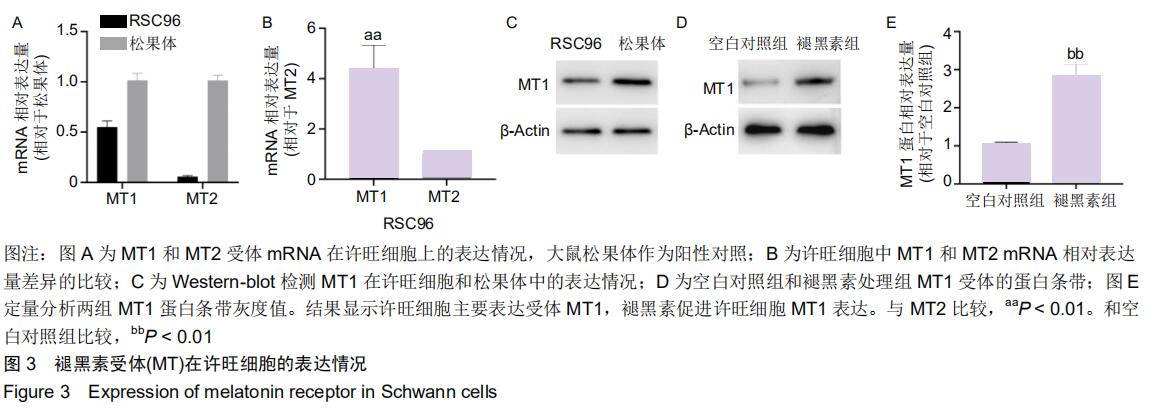
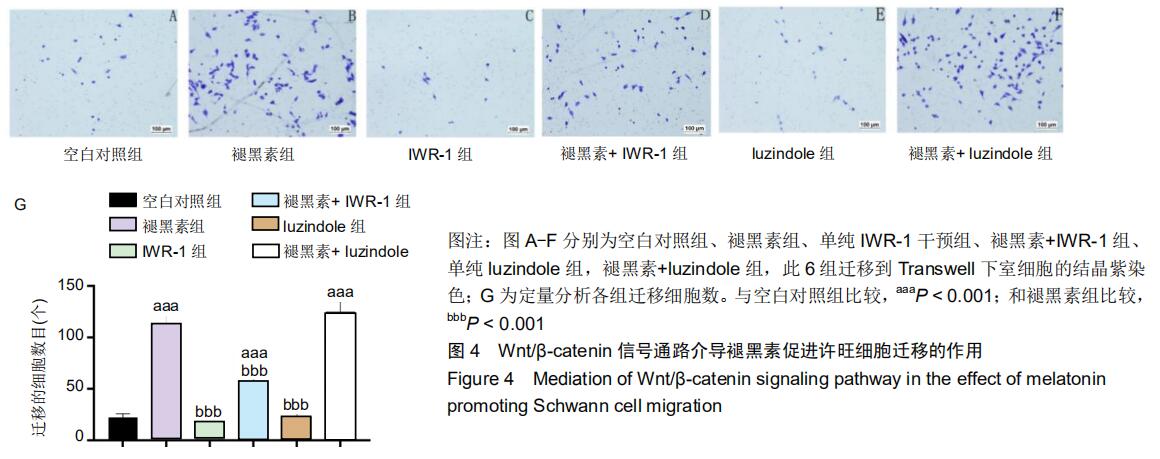
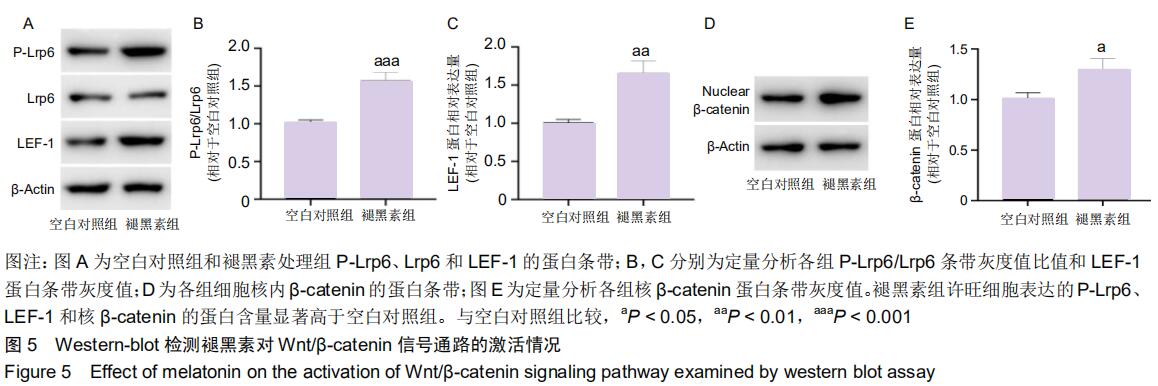
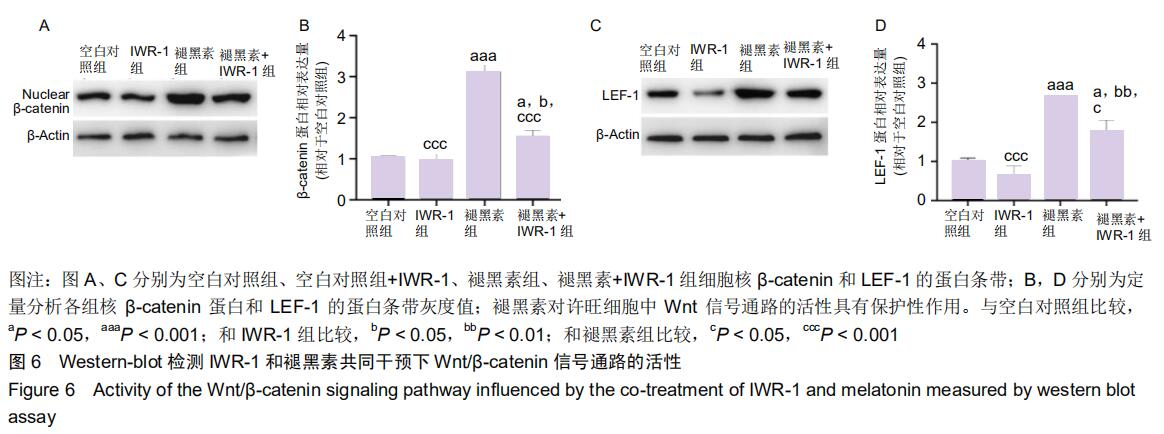
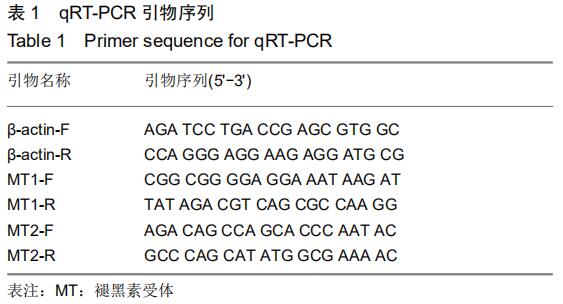
|
[1] QIAN Y, HAN Q, ZHAO X, et al. 3D melatonin nerve scaffold reduces oxidative stress and inflammation and increases autophagy in peripheral nerve regeneration. J Pineal Res. 2018;65(4):e12516.
[2] TRICAUD N, PARK HT. Wallerian demyelination: chronicle of a cellular cataclysm. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(22):4049-4057.
[3] WONG KM, BABETTO E, BEIROWSKI B. Axon degeneration: make the Schwann cell great again. Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(4):518-524.
[4] 高伟,邵水金,胡琳娜,等.许旺细胞在周围神经损伤修复中的作用及其可能分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(36):6825-6827.
[5] YU F, WENG J, YUAN Y, et al. Wnt5a Affects Schwann Cell Proliferation and Regeneration via Wnt/c-Jun and PTEN Signaling Pathway. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(21): 2623-2625.
[6] SHEFA U, JUNG J. Comparative study of microarray and experimental data on Schwann cells in peripheral nerve degeneration and regeneration: big data analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(6):1099-1104.
[7] HSU C, HUANG H, WU P, et al. Sesame oil improves functional recovery by attenuating nerve oxidative stress in a mouse model of acute peripheral nerve injury: role of Nrf-2. J Nutr Biochem. 2016;38:102-106.
[8] KAYA Y, SARIKCIOĞLU L, ASLAN M, et al. Comparison of the beneficial effect of melatonin on recovery after cut and crush sciatic nerve injury: a combined study using functional, electrophysiological, biochemical, and electron microscopic analyses. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013;29(3):389-401.
[9] GÜL S, CELIK SE, KALAYCI M, et al. Dose-dependent neuroprotective effects of melatonin on experimental spinal cord injury in rats. Surg Neurol. 2005;64(4):355-361.
[10] TORDJMAN S, CHOKRON S, DELORME R, et al. Melatonin: pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(3):434-443.
[11] CUTANDO A, ANEIROS-FERNÁNDEZ J, LÓPEZ-VALVERDE A, et al. A new perspective in Oral health: potential importance and actions of melatonin receptors MT1, MT2, MT3, and RZR/ROR in the oral cavity. Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56(10):944-950.
[12] CHEN BH, PARK JH, LEE YL, et al. Melatonin improves vascular cognitive impairment induced by ischemic stroke by remyelination via activation of ERK1/2 signaling and restoration of glutamatergic synapses in the gerbil hippocampus. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:687-697.
[13] TURGUT M, KAPLAN S. Effects of melatonin on peripheral nerve regeneration. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2011;5(2):100-108.
[14] SAYAN H, OZACMAK VH, Ozen OA, et al. Beneficial effects of melatonin on reperfusion injury in rat sciatic nerve. J Pineal Res. 2004;37(3):143-148.
[15] Edizer DT, Donmez Z, Gul M, et al. Effects of Melatonin and Dexamethasone on Facial Nerve Neurorrhaphy. J Int Adv Otol. 2019;15(1):43-50.
[16] CHIANG RP, HUANG C, TSAI Y. Melatonin reduces median nerve injury-induced mechanical hypersensitivity via inhibition of microglial p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in rat cuneate nucleus. J Pineal Res. 2013;54(2):232-244.
[17] SALEHI M, NASERI-NOSAR M, EBRAHIMI-BAROUGH S, et al. Polyurethane/Gelatin Nanofibrils Neural Guidance Conduit Containing Platelet-Rich Plasma and Melatonin for Transplantation of Schwann Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018; 38(3):703-713.
[18] CHANG H, LIU C, HSU W, et al. Proliferative effects of melatonin on Schwann cells: implication for nerve regeneration following peripheral nerve injury. J Pineal Res. 2014;56(3):322-332.
[19] TIONG YL, NG KY, KOH RY, et al. Melatonin Prevents Oxidative Stress-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis in High Glucose-Treated Schwann Cells via Upregulation of Bcl2, NF-κB, mTOR, Wnt Signalling Pathways. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(7):198.
[20] GUTIERREZ-CUESTA J, TAJES M, JIMÉNEZ A, et al. Evaluation of potential pro-survival pathways regulated by melatonin in a murine senescence model. J Pineal Res. 2008;45(4):497-505.
[21] SHEN Z, ZHOU Z, GAO S, et al. Melatonin Inhibits Neural Cell Apoptosis and Promotes Locomotor Recovery via Activation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway After Spinal Cord Injury. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(8):2336-2343.
[22] HU F, YAN Y, WANG C, et al. Article Effect and Mechanism of Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides on Human Fibroblasts and Skin Wound Healing in Mice. Chin J Integr Med. 2019; 25(3):203-209.
[23] LIAO B, CHEN R, LIN F, et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTTIP promotes endothelial cell proliferation and migration via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(3):2797-2805.
[24] WANG Y, CHEN H, ZHANG H. Kaempferol promotes proliferation, migration and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells via up-regulation of microRNA-101. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1050-1056.
[25] GALANO A, TAN DX, REITER RJ. On the free radical scavenging activities of melatonin's metabolites, AFMK and AMK. J Pineal Res. 2013;54(3):245-257.
[26] LIU D, WEI N, MAN H, et al. The MT2 receptor stimulates axonogenesis and enhances synaptic transmission by activating Akt signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(4): 583-596.
[27] LIU L, HOFFMAN GE, FEI X, et al. Delayed rectifier outward K+ current mediates the migration of rat cerebellar granule cells stimulated by melatonin. J Neurochem. 2007;102(2): 333-344.
[28] LEE S, JUNG YH, OH SY, et al. Melatonin enhances the human mesenchymal stem cells motility via melatonin receptor 2 coupling with Gαq in skin wound healing. J Pineal Res. 2014;57(4):393-407.
[29] CHAO C, CHEN P, CHIOU P, et al. Melatonin suppresses lung cancer metastasis by inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through targeting to Twist. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019;133(5):709-722.
[30] KEPKA M, SZWEJSER E, PIJANOWSKI L, et al. A role for melatonin in maintaining the pro- and anti-inflammatory balance by influencing leukocyte migration and apoptosis in carp. Dev Comp Immunol. 2015;53(1):179-190.
[31] LUCHETTI F, CANONICO B, BARTOLINI D, et al. Melatonin regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation: a review. J Pineal Res. 2014;56(4):382-397.
[32] MORTEZAEE K, PASBAKHSH P, RAGERDI KASHANI I, et al. Melatonin Pretreatment Enhances the Homing of Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Following Transplantation in a Rat Model of Liver Fibrosis. Iran Biomed J. 2016;20(4):207-216.
[33] CEREZO AB, HORNEDO-ORTEGA R, ÁLVAREZ-FERNÁNDEZ MA, et al. Inhibition of VEGF-Induced VEGFR-2 Activation and HUVEC Migration by Melatonin and Other Bioactive Indolic Compounds. Nutrients. 2017;9(3):249.
[34] LIU Z, ZOU D, YANG X, et al. Melatonin inhibits colon cancer RKO cell migration by downregulating Rho‑associated protein kinase expression via the p38/MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(6):9383-9392.
[35] YE X, QIU Y, GAO Y, et al. A Subtle Network Mediating Axon Guidance: Intrinsic Dynamic Structure of Growth Cone, Attractive and Repulsive Molecular Cues, and the Intermediate Role of Signaling Pathways. Neural Plast. 2019;2019:1719829.
[36] LV J, SUN X, MA J, et al. Netrin-1 induces the migration of Schwann cells via p38 MAPK and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway mediated by the UNC5B receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464(1):263-268.
[37] GUO WL, QI ZP, YU L, et al. Melatonin combined with chondroitin sulfate ABC promotes nerve regeneration after root-avulsion brachial plexus injury. Neural Regen Res. 2019; 14(2):328-338.
[38] LI X, LI Z, WANG J, et al. Wnt4 signaling mediates protective effects of melatonin on new bone formation in an inflammatory environment. FASEB J. 2019;33(9): 10126-10139.
[39] LIU L, WANG T, YANG X, et al. MTNR1B loss promotes chordoma recurrence by abrogating melatonin-mediated β-catenin signaling repression. J Pineal Res. 2019;67(2): e12588.
[40] HAN B, ZHAO J, WANG W, et al. Cdc42 Promotes Schwann Cell Proliferation and Migration Through Wnt/β-Catenin and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway After Sciatic Nerve Injury. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(5):1317-1324.
[41] WHITEHEAD MJ, MCGONIGAL R, WILLISON HJ, et al. Heparanase attenuates axon degeneration following sciatic nerve transection. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):5219.
[42] TAWK M, MAKOUKJI J, BELLE M, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is an essential and direct driver of myelin gene expression and myelinogenesis. J Neurosci. 2011;31(10): 3729-3742.
[43] KILIC U, YILMAZ B, UGUR M, et al. Evidence that membrane-bound G protein-coupled melatonin receptors MT1 and MT2 are not involved in the neuroprotective effects of melatonin in focal cerebral ischemia. J Pineal Res. 2012; 52(2):228-235.
|