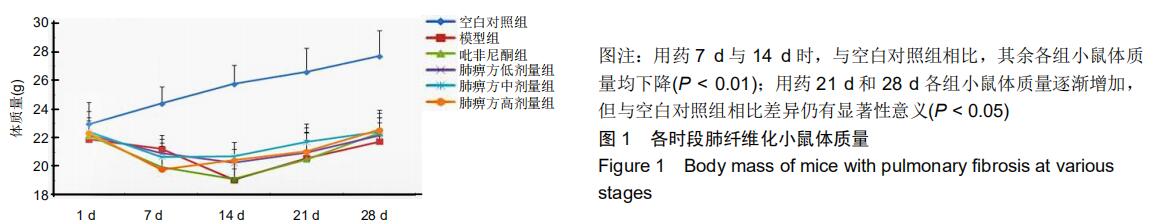
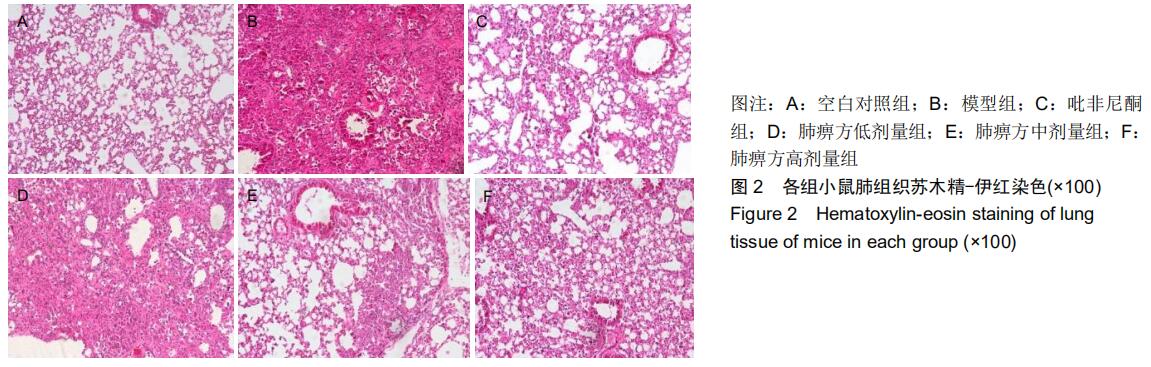
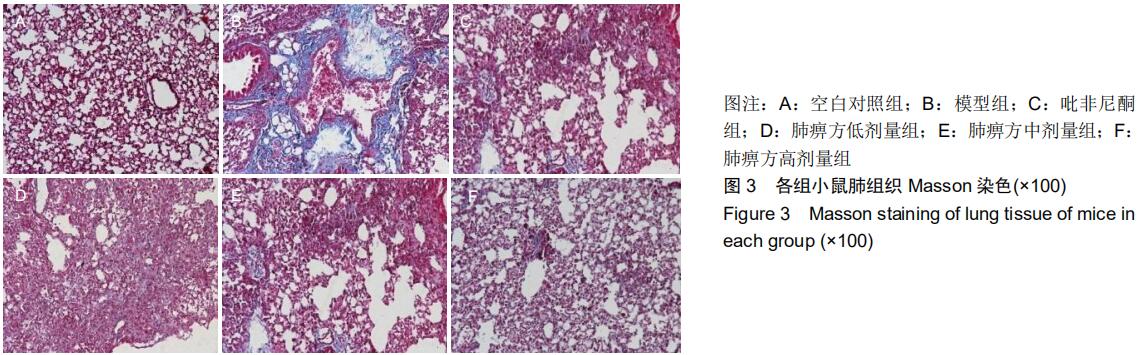
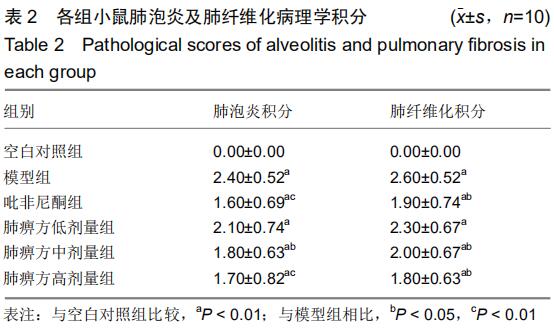
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (31): 5038-5043.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2112
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
肺痹方干预肺纤维化模型小鼠细胞外基质转化的机制
程 雪1,方 泓2,张运克1,吴银根2
- 1河南中医药大学,河南省郑州市 450046;2上海中医药大学附属龙华医院,上海市 200032
Interventional mechanism of Feibi prescription on extracellular matrix transformation in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis
Cheng Xue1, Fang Hong2, Zhang Yunke1, Wu Yingen2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
摘要:

文题释义:
细胞外基质:肺组织的细胞外基质与肺纤维化关系最为密切,肺组织损伤修复过程中细胞外基质成分首先填补损伤肺组织,当其过度沉积时可形成肺间质纤维化,此外细胞外基质与炎症也有密切关系,因此研究细胞外基质形成对于认识肺纤维化的发病机制及诊断、防治具有重要意义。
博来霉素:是一类糖苷类抗生素,临床上用于多种肿瘤的治疗,具有可致机体发生明显肺间质纤维化的毒副作用,故多用于肺纤维化动物模型的制备,其作用机制是诱导肌成纤维细胞的异常增生,过量胶原纤维堆积,最终导致肺纤维化的形成。
背景:肺组织损伤修复过程中,细胞外基质成分首先填补损伤肺组织,当其过度沉积时可形成肺间质纤维化。
目的:探讨肺痹方对博莱霉素致肺纤维化小鼠细胞外基质转化的干预作用。
方法:将60只C57BL/6雄性小鼠随机分为空白对照组、模型组、吡非尼酮组、肺痹方低剂量组、肺痹方中剂量组、肺痹方高剂量组,每组10只。除空白对照组外,其余5组腹腔注射博莱霉素[7.5 mg/(kg·d)]建立肺纤维化模型,连续注射10 d。造模后第1天各药物组灌胃给药[51.43 mg/(kg·d)]吡非尼酮,6.43,12.86, 25.72 mg/(kg·d)肺痹方],连续给药28 d。用药28 d后取肺组织,采用苏木精-伊红染色和Masson染色观察小鼠肺组织的形态学变化,ELISA法检测血清中转化生长因子β1、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,Western blot法检测肺组织中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原的表达。
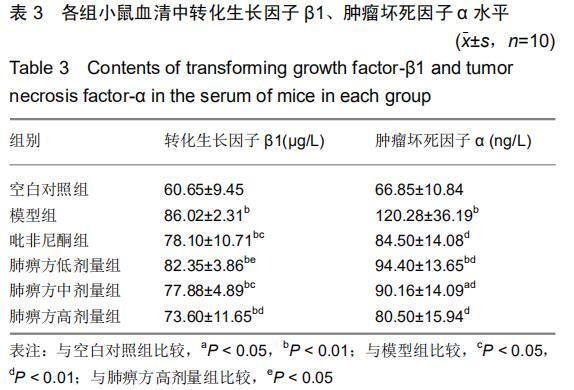
结果与结论:①与空白对照组相比,各组小鼠血清转化生长因子β1水平显著升高(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,吡非尼酮组、肺痹方中剂量组、肺痹方高剂量组血清转化生长因子β1水平显著降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),肺痹方高剂量组降低最明显;②与模型组相比,用药各组血清肿瘤坏死因子α水平明显降低(P < 0.01),用药各组之间两两比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③与空白对照组相比,各组α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达均不同程度增高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);肺痹方高剂量组α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达低于肺痹方低、中剂量组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④与空白对照组相比,模型组、肺痹方低剂量组Ⅰ型胶原表达增高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与模型组相比,肺痹方中、高剂量组Ⅰ型胶原表达降低(P < 0.05);⑤与空白对照组相比,各组Ⅲ型胶原表达均不同程度增高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);肺痹方中、高剂量组以及吡非尼酮组Ⅲ型胶原表达明显低于肺痹方低剂量组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);⑥结果表明,肺痹方可以减轻肺纤维化,抑制博来霉素诱导的肺纤维化小鼠细胞外基质转化,其机制可能与下调血清中转化生长因子β1、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,抑制肺组织中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原表达有关。
ORCID: 0000-0002-9170-7217(程雪)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: