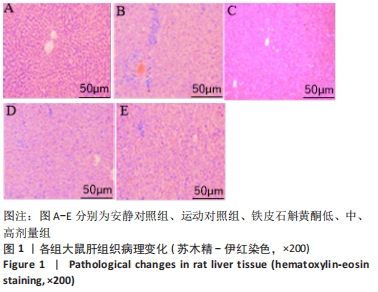
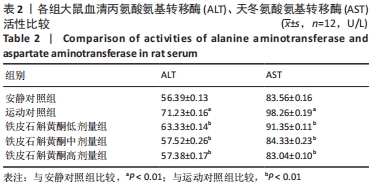
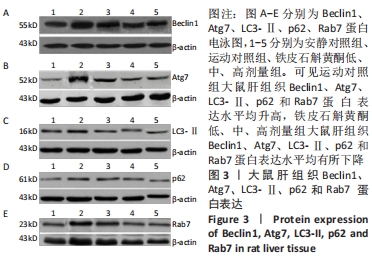
[1] ROBINSON MW, HARMON C, O’FARRELLY C. Liver immunology and its role in inflammation and homeostasis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2016;9(13): 267-276.
[2] KAWAMURA T, MURAOKA I. Exercise-induced oxidative stress and the effects of antioxidant intake from a physiological viewpoint. Antioxidants(Basel). 2018;7(9):119.
[3] LINDQVIST D , DHABHAR FS , JAMES SJ , et al. Oxidative stress, inflammation and treatment response in major depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017;76(2):197-205.
[4] FUCHS CJ, GONZALEZ JT, BEELEN M , et al. Sucrose ingestion after exhaustive exercise accelerates liver, but not muscle glycogen repletion when compared to glucose ingestion in trained athletes. J Appl Physiol. 2016;120(11):1328-1344.
[5] PINTO AP, ROCHA AL,MARAFON BB, et al.Impact of Different Physical Exercises on the Expression of Autophagy Markersin Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2635.
[6] LI S, YI Z, DENG M, et al. TSLP protects against liver I/R injury via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. JCI Insight. 2019;4(22):1-12.
[7] JADEJA RN , UPADHYAY KK , DEVKAR RV, et al. Naturally Occurring Nrf2 Activators: Potential in Treatment of Liver Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:3453926.
[8] GUNADI JW , TARAWAN VM , RAY H , et al. Different training intensities induced autophagy and histopathology appearances potentially associated with lipid metabolism in wistar rat liver. Heliyon, 2020; 6(5): e03874.
[9] PI H , LIU M , Y XI, et al. Long‐term exercise prevents hepatic steatosis: a novel role of FABP1 in regulation of autophagy‐lysosomal machinery. FASEB J. 2019;33(11):11870-11883.
[10] 封毅,黄茂康,叶建保,等.铁皮石斛提高小鼠运动能力、抗疲劳能力和免疫水平的量效关系分析[J].南方农业学报,2014,45(6): 1089-1093.
[11] 周海涛,曹建民,林强,等.铁皮石斛对运动训练大鼠物质代谢及抗运动疲劳能力的影响[J].中国药学杂志,2013,48(19):1684-1688.
[12] TANG HX, ZHAO TW, SHENG YJ, et al. Dendrobium officinale Kimuraet Migo: a review on its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and industrialization. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7436259.
[13] KIM S , JO K , BYUN BS , et al. Chemical and biological properties of puffed Dendrobium officinale extracts: Evaluation of antioxidant and anti-fatigue activities. J Funct Foods. 2020;73:104-144.
[14] 曾艺芸, 聂雪婷, 李振坚, 等. 中药石斛黄酮活性成分研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(6):197-205.
[15] BEDFORD TG, TIPTON CM, WILSON NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol, 1979;47(6):1278-1283.
[16] 闫清伟, 李亚楠, 赵娜, 等. 运动改善APP/PS1小鼠海马白质的机制研究[J]. 中国体育科技,2020,56(11):84-89.
[17] 万雪琦. 低氧运动对肥胖大鼠血脂、肝脂、肝脏脂联素mRNA以及血清AST、ALT、FFA的影响[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学,2020.
[18] 柴伟, 彭程. 有氧运动对肝脏相关生化指标的影响[J].肝脏,2019, 24(1):104-106.
[19] 郝慧祯,曹建民,曹卉,等.鼠李糖乳杆菌对一次性大强度运动小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J].运动,2018(10):154-156.
[20] 郭枫,秦虎.樟芝可缓解大鼠运动后急性肝损伤[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2017,36(10):3992-3999.
[21] NOGUEIRA JE, PASSAGLIA P, MOTA CMD, et al. Molecular hydrogen reduces acute exercise-induced inflammatory and oxidative stress status. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;129:186-193.
[22] 贾前生, 刘远洋. 黑豆多肽对超负荷训练小鼠肝细胞损伤影响的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(11):309-313.
[23] 张辉. 女贞子提取物对大强度耐力训练力竭后大鼠肝组织自由基代谢的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2018,38(6):1479-1481.
[24] 耿慧武, 李清月, 龚治忠, 等. Pb2+ 对小鼠肝脏组织GST和GSH-PX酶活力及基因表达的影响[J]. 阜阳师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020,37(4):38-43.
[25] 云冰, 禇雪菲, 王恩行, 等. 不同浓度化痰逐瘀汤在冠心病血瘀模型家兔干预中的应用效果及对GSH、SOD、T-AOC 水平的影响[J]. 四川中医,2020,38(5):90-93.
[26] 曹姣,肖国强,陈晓光.不同强度运动对肥胖大鼠肝脏氧化应激和脂联素及其受体的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(9):779-787.
[27] 贾靖.白灵菇多糖对运动小鼠氧化应激的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(2):895-901.
[28] 李敏,沈琴,王晓萍,等.单核/巨噬细胞自噬在肝病中的作用研究进展[J].药学研究,2021,40(5):319-323.
[29] 吴玲红,李红,国娇,等. 肝细胞癌组织自噬相关蛋白Beclin1和LC3B及p62表达临床意义[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志,2019,26(8):539-544.
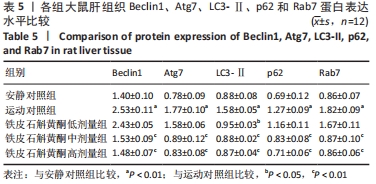
[30] 李伟,李志霞, 伍冀湘. Beclin1基因过表达对肝癌细胞生物学行为的影响机制研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2021,20(11):1124-1128.
[31] 张欣,王瑞元.大负荷运动诱导大鼠骨骼肌损伤对其自噬超微结构及Beclin1和LC3-Ⅱ/Ⅰ的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2020, 36(4):296-300+385.
[32] 安祯祥,何远利,王芳, 等.扶脾柔肝方及拆方对肝纤维化大鼠肝组织线粒体自噬相关蛋白表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2021, 9(13):1-10.
[33] 刘文锋,宋海霞,傅让. 有氧耐力运动对增龄大鼠肝细胞氧化应激和炎性因子及其AMPKα/Beclin1通路的影响[J].北京体育大学学报, 2019,42(7):145-156.
[34] GUHA P, SNYDER SH. Noncatalytic functions of IPMKare essential for activation of autophagy and liver regeneration.Autophagy. 2019;15(8):1473-1474.
[35] 张亨. Calpain-2在运动改善肝脏内质网应激中的作用及相关机制研究[D]. 上海:上海师范大学,2017.
[36] 余辕耕. 电针通过调控肝脏SIRT1/ATG7改善胰岛素抵抗的机制研究[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学,2021.
[37] 刘冠,马丽华,党裔武, 等.葡醛内酯对异烟肼和利福平所致肝损伤小鼠肝组织自噬水平的影响[J].广西医科大学学报,2021,38(6): 1101-1106.
[38] 冯芹.小鼠急性肝损伤及牛蒡子苷元保护作用的研究[D]. 南京:南京大学,2018.
[39] 沈敏燕, 胡曦, 朱静, 等. 黄连碱促进肝细胞自噬及胆固醇外流改善脂肪肝的脂质蓄积[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报,2021,46(4):421-424+430.
[40] KIM YA, KIM YS, SONG W. Autophagic response to a single bout of moderate exercise in murinekeletal muscle. J Phsiol Biochem. 2012; 68(2):229-235.
[41] JAMART C, BENOIT N, RAYMACKERS JM, et al. Autophagy-related and autophagy-regulatory genes are induced in human muscle after ultraendurance exercise. Arbeitsphysiologie. 2011;112(8):3173-3177.
[42] MARTINELLI L, BONAVENTURA MVM, AMANTINI C, et al. Effects of Prunus cerasus L. Seeds and Juice on Liver Steatosis in an Animal Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Nutrients. 2020;12(5):1308.
[43] 闫海龙, 陈乐琴, 张一民, 等. 高强度间歇性训练与中等强度持续运动对大鼠肝细胞自噬与凋亡相关因子表达的影响[J]. 山东体育学院学报,2019,35(3):71-77.
[44] 杨云昊, 庞芳, 黄思琴, 等. 电针对快速衰老小鼠肝脏自噬及脂质代谢的影响[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志,2021,5(1):1-6.
[45] 张海明, 朱志军. 自噬与p62/SQSTM1在肝缺血再灌注中的作用[J]. 生物医学转化,2021,2(1):70-74.
[46] GUNADI JW , TARAWAN VM , RAY H, et al. Different training intensities induced autophagy and histopathology appearances potentially associated with lipid metabolism in wistar rat liver. Heliyon. 2020;6(5): e03874.
[47] 王晶. 抗阻、耐力运动对肥胖小鼠肝脏自噬相关蛋白表达的影响[D]. 石家庄:河北师范大学,2018.
[48] LU Q , SHU Y , WANG L, et al. The protective effect of Veronica ciliata Fisch. Extracts on relieving oxidative stress-induced liver injury via activating AMPK/p62/Nrf2 pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;270: 113775.
[49] 金秋芳,梁国强,葛惠男,等.葛根素联合有氧运动对非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠SIRT1介导肝细胞自噬的保护作用研究[J].河北中医, 2020,42(10):1540-1546+1440.
[50] 吴安平,庆宏,全贞贞. Rab蛋白家族在神经类疾病中的作用[J].遗传,2021,43(1):16-29.
[51] 赵娜,张宪亮,夏杰,等.12周有氧跑台运动对APP/PS1小鼠海马细胞自噬活性的影响[J].体育科学,2019,39(12):43-53.
[52] WANG T, WANG L, ZHANG Y. Puerarin Restores Autophagosome-Lysosome Fusion to Alleviate Cadmium-Induced Autophagy Blockade via Restoring the Expression of Rab7 in Hepatocytes. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:632825.
[53] LIU A, WANG W, LU Z, et al. Mild hypothermia pretreatment extenuates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury through Rab7-mediated autophagosomes-lysosomes fusion- ScienceDirect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;550:15-21.
[54] LI Y, DING WX. Impaired Rab7 and dynamin2 block fat turnover by autophagy in alcoholic fatty livers. Hepatol Commun. 2017;1(6):473-476. |