中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 716-719.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2431
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
创伤性神经瘤模型的构建及评价
汪 靖1,2,鲁长风2,彭 江2,朱 晨3,许文静2,程晓清2,方 杰2,朱亚琼2,赵燕旭2,蒋 雯2,徐宏光1,王 玉2
- 1皖南医学院第一附属医院(弋矶山医院)脊柱外科,安徽省芜湖市 241001;2解放军总医院骨科研究所,北京市再生医学重点实验室,全军战创伤重点实验室,北京市 100853;3中国科学技术大学附属第一医院 安徽省合肥市 230000
Establishment and evaluation of traumatic neuroma model
Wang Jing1, 2, Lu Changfeng2, Peng Jiang2, Zhu Chen3, Xu Wenjing2, Cheng Xiaoqing2, Fang Jie2, Zhu Yaqiong2, Zhao Yanxu2, Jiang Wen2, Xu Hongguang1, Wang Yu2
- 1Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wannan Medical College (Yijishan Hospital); 2Institute of Orthopaedics of PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, the Key Laboratory of National Military Warfare; 3the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China
摘要:
文题释义:
神经瘤:1811年Odier首先提出神经瘤的概念,周围神经受到创伤后,神经纤维断裂,神经轴突在变性的基础上开始再生,在神经纤维的再生过程中,两断端组织增生过多,断端再生的轴突因瘢痕障碍,不能成功长入远端神经中,近端轴突和胞体在内源性神经生长因子及其靶器官分泌的神经生长因子的刺激和诱导下,持续在障碍物上向各个方向出芽生长、卷曲、甚至反折、相互缠绕,加之期间的纤维结缔组织生长、增生,并逐渐增长形成以纤维结缔组织为主的假性神经瘤。
神经纤维瘤病:为常染色体显性遗传病,是基因缺陷使神经嵴细胞发育异常导致多系统损害。创伤性神经瘤需与肥大性瘢痕及神经纤维瘤鉴别,后两者也可在外伤后发生,但组织学显示增生组织主要为胶原和成纤维细胞,无神经组织改变。
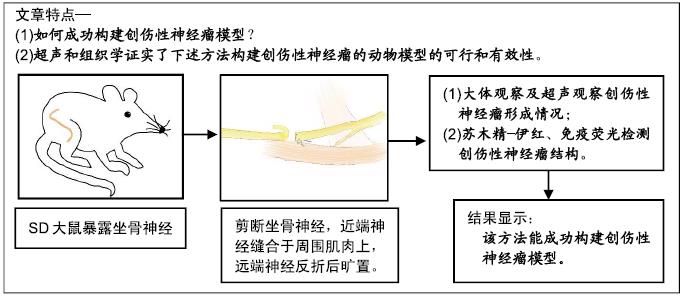
背景:创伤性神经瘤是周围神经损伤的常见并发症,国内外通过创伤性神经瘤模型进行周围神经修复、再生的基础研究较少见。
目的:建立创伤性神经瘤模型并进行鉴定。
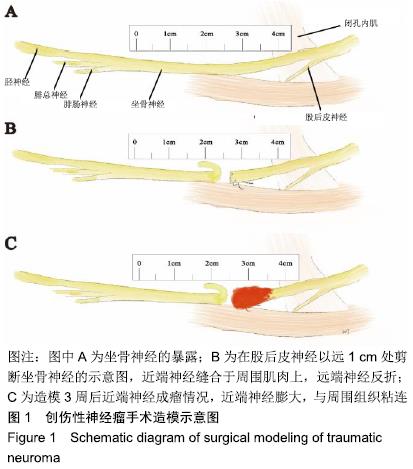
方法:实验方案经中国人民解放军总医院动物实验伦理委员会批准。选择15只8周健康SD大鼠,显微镜下暴露坐骨神经,用显微剪剪断股后皮神经以远1 cm处的坐骨神经,11-0显微线将神经近端缝合于周围肌肉上,远端神经反折后旷置,3周后使用超声和组织学验证神经瘤是否形成。
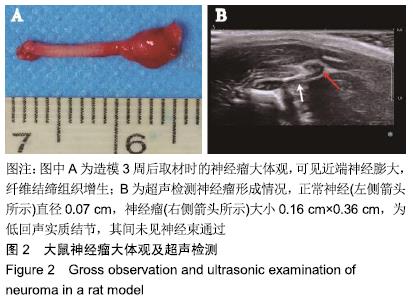
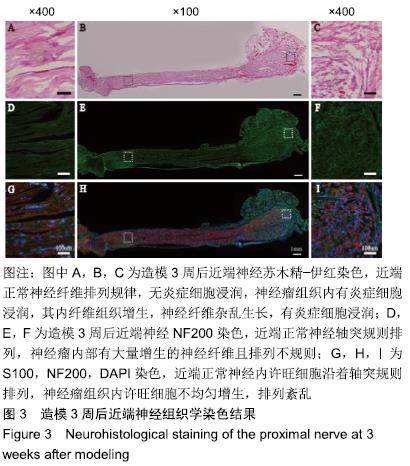
结果与结论:①造模3周后,超声可见近端神经明显梭形膨大,为一低回声实质结节,不伴回声;②大体观察可观察到近端神经膨大,质稍硬,纤维结缔组织增生,与周围组织粘连;③苏木精-伊红染色可见瘤体内纤维组织增生,神经纤维杂乱生长,免疫荧光染色(S100、NF200)可见瘤体内许旺细胞和神经轴突不规则增生;④结果表明:实验成功构建了创伤性神经瘤模型。ORCID: 0000-0002-3134-5488(汪靖);0000-0002-4517-734X(鲁长风)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: