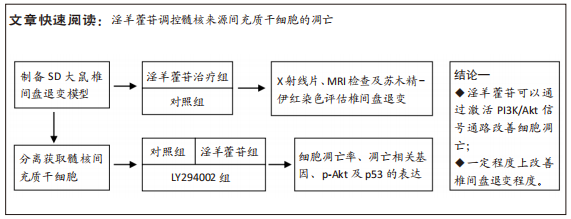
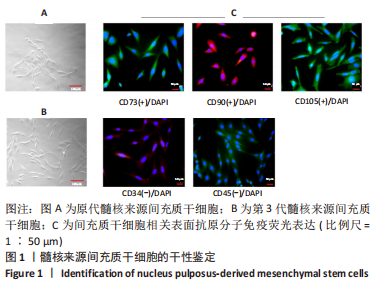
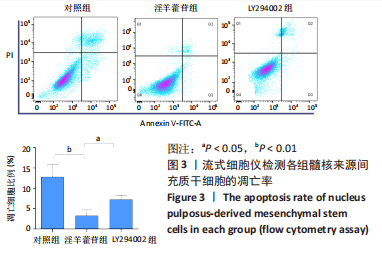
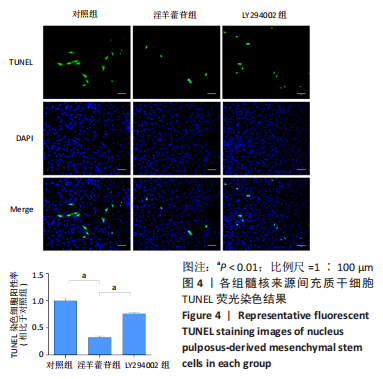
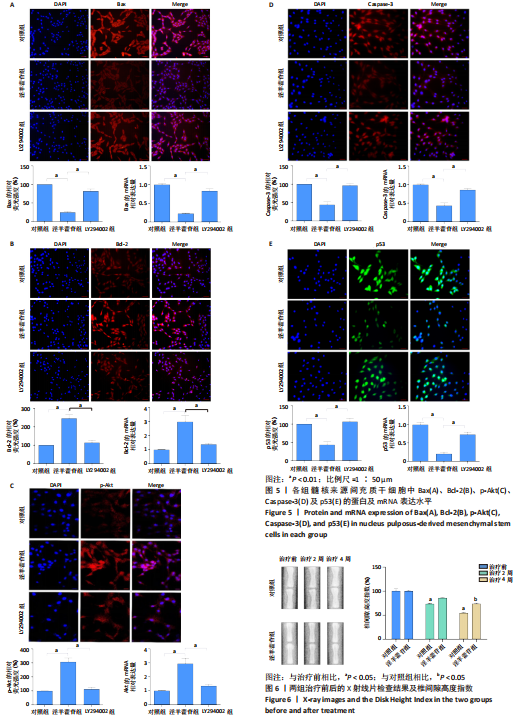
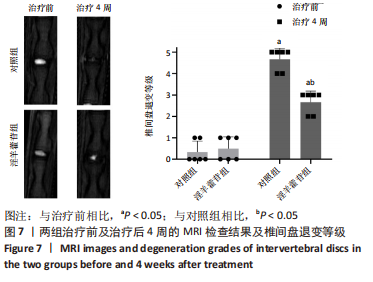
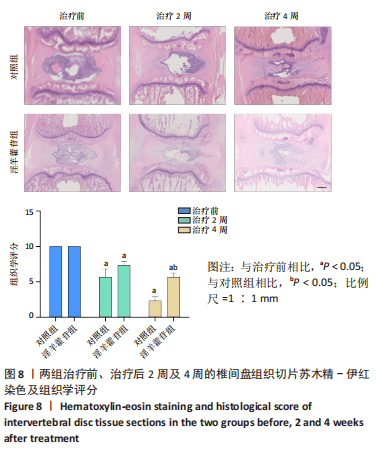
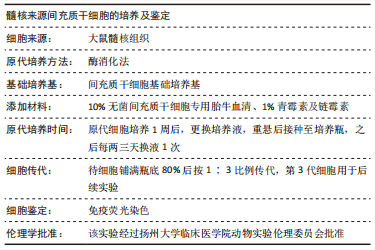
[1] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[2] VERGROESEN PP, KINGMA I, EMANUEL KS, et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(7):1057-1070.
[3] RISBUD MV, GUTTAPALLI A, TSAI TT, et al. Evidence for skeletal progenitor cells in the degenerate human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(23):2537-2544.
[4] SAKAI D, NAKAMURA Y, NAKAI T, et al. Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1264.
[5] MA K, CHEN S, LI Z, et al. Mechanisms of endogenous repair failure during intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019; 27(1):41-48.
[6] CHENG S, LI X, JIA Z, et al. The inflammatory cytokine TNF-α regulates the biological behavior of rat nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells through the NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(8):13664-13679.
[7] LIU Y, LI Y, HUANG ZN, et al. The effect of intervertebral disc degenerative change on biological characteristics of nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cell: an in vitro study in rats. Connect Tissue Res. 2019;60(4):376-388.
[8] WANG F, YANG Z, HE W, et al. Effects of icariin on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):578.
[9] YAO X, JING X, GUO J, et al. Icariin Protects Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Iron Overload Induced Dysfunction Through Mitochondrial Fusion and Fission, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:163.
[10] DENG X, CHEN S, ZHENG D, et al. Icariin Prevents H2O2-Induced Apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt Pathway in Rat Nucleus Pulposus Intervertebral Disc Cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017; 2017:2694261.
[11] CHENG X, ZHANG L, ZHANG K, et al. Circular RNA VMA21 protects against intervertebral disc degeneration through targeting miR-200c and X linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018; 77(5):770-779.
[12] WANG F, NAN LP, ZHOU SF, et al. Injectable Hydrogel Combined with Nucleus Pulposus-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Degenerative Intervertebral Disc in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:8496025.
[13] URRUTIA J, BESA P, CAMPOS M, et al. The Pfirrmann classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration: an independent inter- and intra-observer agreement assessment. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(9):2728-2733.
[14] NORCROSS JP, LESTER GE, WEINHOLD P, et al. An in vivo model of degenerative disc disease. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(1):183-188.
[15] ZHANG C, GULLBRAND SE, SCHAER TP, et al. Combined Hydrogel and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Moderate-Severity Disc Degeneration in Goats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(1-2):117-128.
[16] VADALÀ G, AMBROSIO L, RUSSO F, et al. Interaction between Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Intervertebral Disc Microenvironment: From Cell Therapy to Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019: 2376172.
[17] LI H, TAO Y, LIANG C, et al. Influence of hypoxia in the intervertebral disc on the biological behaviors of rat adipose- and nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2013;198(4): 266-277.
[18] HAN B, WANG HC, LI H, et al. Nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells in acidic conditions mimicking degenerative intervertebral discs give better performance than adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014;199(5-6):342-352.
[19] LI H, WANG J, LI F, et al. The Influence of Hyperosmolarity in the Intervertebral Disc on the Proliferation and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Nucleus Pulposus-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2018;205(3):178-188.
[20] ZHAO Y, JIA Z, HUANG S, et al. Age-Related Changes in Nucleus Pulposus Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An In Vitro Study in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:6761572.
[21] 刘摇摇,刘湘宁,田银平,等.淫羊藿苷对骨骼系统药理作用机制的研究进展[J].中药新药与临床药理,2020,31(12):1516-1520.
[22] 杨丽红,肖波,侯丽霞,等.淫羊藿苷调节细胞增殖作用的研究进展[J].医学信息,2019,32(1):33-36.
[23] 马娜,张长城,陈茜,等.淫羊藿苷延缓衰老的药理作用及分子机制研究进展[J].时珍国医国药,2018,29(11):2728-2730.
[24] 汪海滨,董晤讯,郭杨,等.淫羊藿苷对大鼠椎间盘退变的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(5):444-449.
[25] 徐永明,徐宏光,高智,等.淫羊藿素通过抑制Hedgehog信号通路保护终板软骨细胞退变[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2017, 22(4):373-380.
[26] 冯仲锴,孙永强,刘汝银,等.淫羊藿苷联合地塞米松对人髓核细胞增殖及分泌表达的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2016,26(24):11-17.
[27] CHENG YH, DONG JC, BIAN Q. Small molecules for mesenchymal stem cell fate determination. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11(12):1084-1103.
[28] 孙凯,朱立国,魏戌,等.中药复方及单体成分延缓腰椎间盘退行性病变的作用机制研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(9):2400-2408.
[29] HUA W, ZHANG Y, WU X, et al. Icariin Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammatory Response in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;23(39):6071-6078.
[30] 郭晓鹏,刘莹松,尚晖.丝素蛋白/纳米羟基磷灰石/淫羊藿苷可促进移植骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化为髓核样细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(22):3528-3534.
[31] 王峰,张文捷,冯新民,等.可注射水凝胶复合髓核间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠椎间盘退变[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(11): 1949-1952.
|