中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (24): 3795-3802.doi: 10.12307/2023.641
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
牛膝醇提物诱导兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化的蛋白组学分析
马笃军1,2,朱厚均2,刘乐诗2, 彭力平1,赵 静2,廖州伟1
- 1广州中医药大学第四临床医学院,广东省深圳市 518033;2广州中医药大学,广东省广州市 510006
Proteomic analysis on cartilage differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract
Ma Dujun1, 2, Zhu Houjun2, Liu Leshi2, Peng Liping1, Zhao Jing2, Liao Zhouwei1
- 1The Fourth Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese medicine, Shenzhen 518033, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangzhou University of Chinese medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
蛋白组学:是以蛋白质组为研究对象,研究细胞、组织或生物体蛋白质组成及其变化规律的科学,本质上指的是在大规模水平上研究蛋白质的特征,包括蛋白质的表达水平、翻译后的修饰、蛋白与蛋白相互作用等,由此获得在蛋白质水平上对疾病发生、细胞代谢等过程的整体而全面的认识。骨髓间充质干细胞:也称为骨髓基质成纤维细胞,是一类起源于中胚层的成体干细胞,具有自我更新及多向分化潜能,可根据所处的微环境不同,进行细胞迁移、定植、增殖与分化,其中分化潜能属于目前的研究热点,常见分化为多种间质组织,如血管、脂肪、韧带、骨骼、软骨等。
背景:前期研究发现牛膝醇提物具有诱导骨髓间充质干细胞定向软骨细胞分化的作用,但具体作用蛋白靶点和网络机制不详。
目的:观察牛膝醇提物诱导兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化的蛋白质组学分析及蛋白质相互作用网络构建。
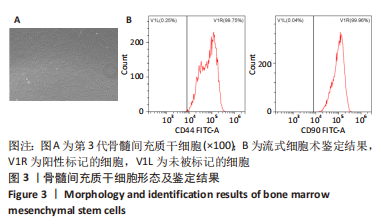
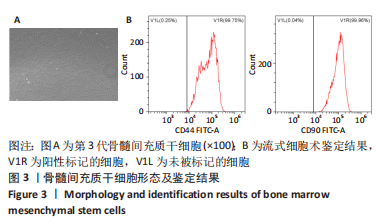
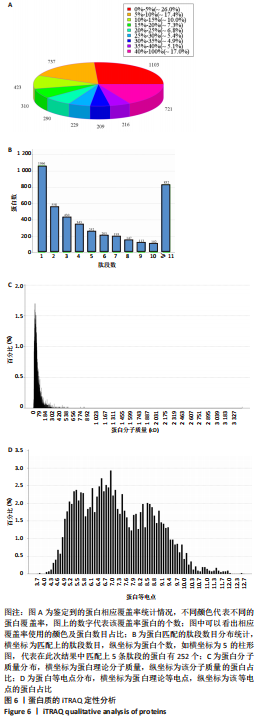
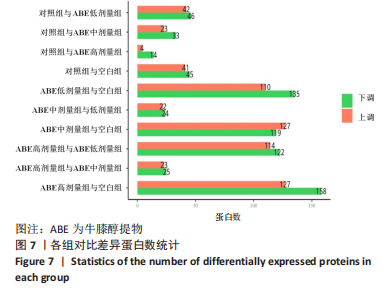
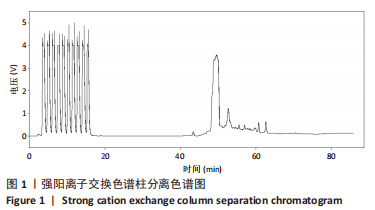
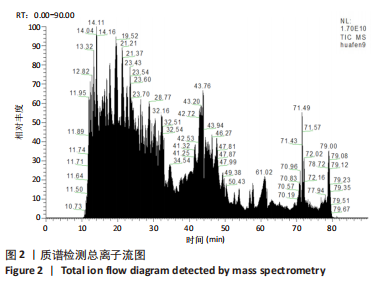
方法:采用密度梯度离心联合细胞贴壁法分离培养新西兰大白兔骨髓间充质干细胞,取第3代细胞随机分成5组:空白组、对照组、牛膝醇提物低、中、高剂量组,连续成软骨诱导培养21 d后,用qRT-PCR检测Ⅱ型胶原mRNA表达及甲苯胺蓝染色鉴定软骨细胞形成,应用绝对定量同位素标记(iTRAQ)结合双向液相色谱-串联质谱(2DLC-MS/MS)技术对各组差异表达蛋白质进行鉴定,并对差异蛋白进行GO分析、KEGG分析及蛋白质网络相互作用分析。
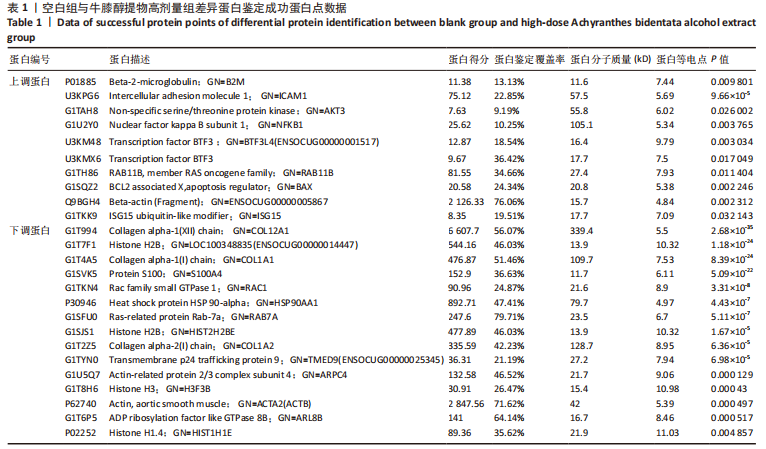
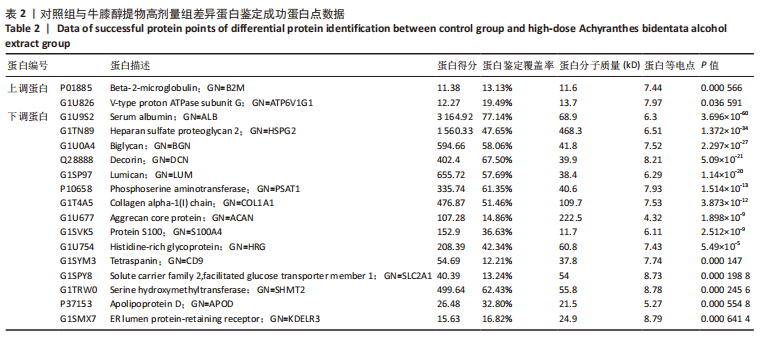
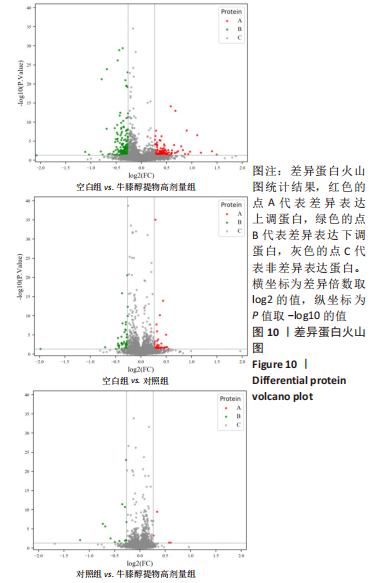
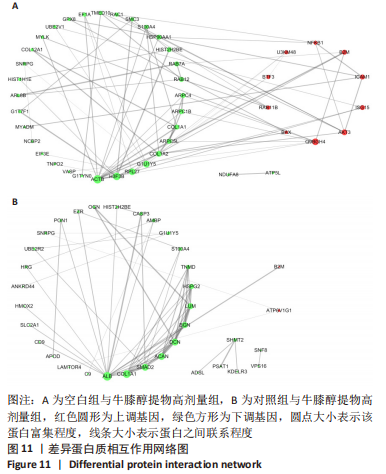
结果与结论:①qRT-PCR结果显示牛膝醇提物高剂量组较其他组Ⅱ型胶原mRNA表达明显增高(P < 0.05),牛膝醇提物高剂量组甲苯胺蓝染色阳性,蛋白组学分析共鉴定到1 354个差异蛋白点,上调蛋白633个,下调蛋白721个。②根据qRT-PCR结果对空白组、牛膝醇提物高剂量组、对照组3组差异表达蛋白进行生物信息分析。GO分析发现这些差异表达蛋白参与代谢、细胞分化、细胞周期与凋亡、炎症反应、免疫调控、氧化应激、磷酸化、泛素化、癌相关等;KEGG分析获得与骨关节病最相关的10个典型信号通路:白细胞介素17信号通路,Toll样受体信号通路,Wnt信号通路,PI3K-Akt信号通路,mTOR 信号通路,Jak-STAT信号通路,NF-kappa B信号通路,MAPK信号通路,AMPK信号通路,HIF-1信号通路;根据组间差异蛋白,使用Cytoscape3.6.0软件成功构建蛋白互作网络图。③结果表明,牛膝醇提物可以通过调控氧化、细胞周期与凋亡、细胞结构改变、细胞分化、代谢及炎症损伤等环节诱导兔骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化,具有多靶点、多中心的网络调控作用,其具体作用机制有待进一步研究。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8050-2849 (马笃军)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: