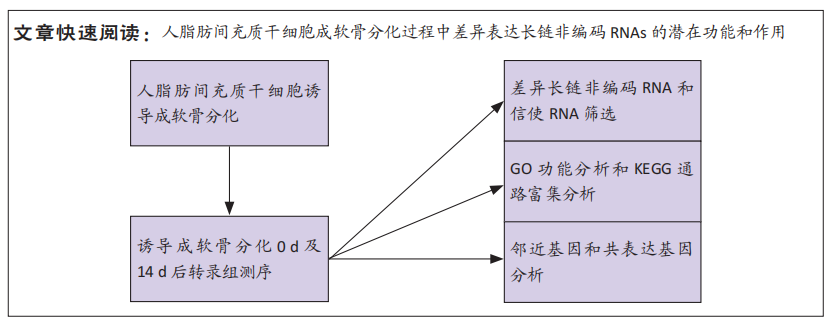
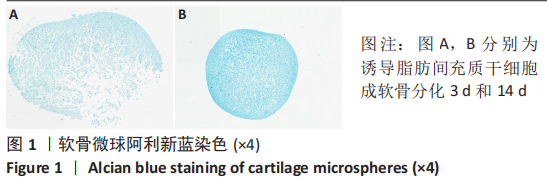
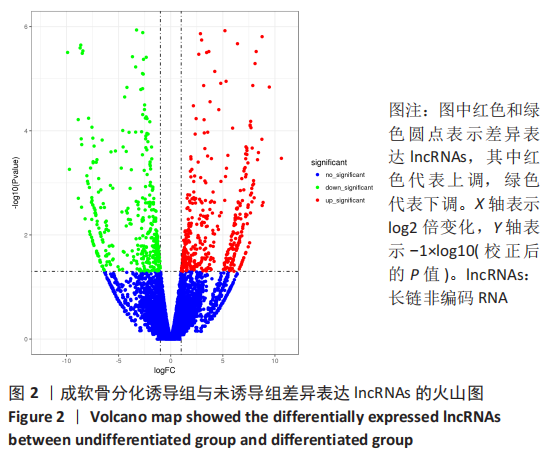
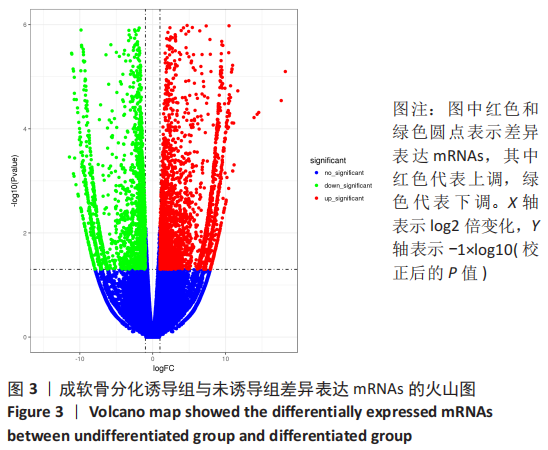
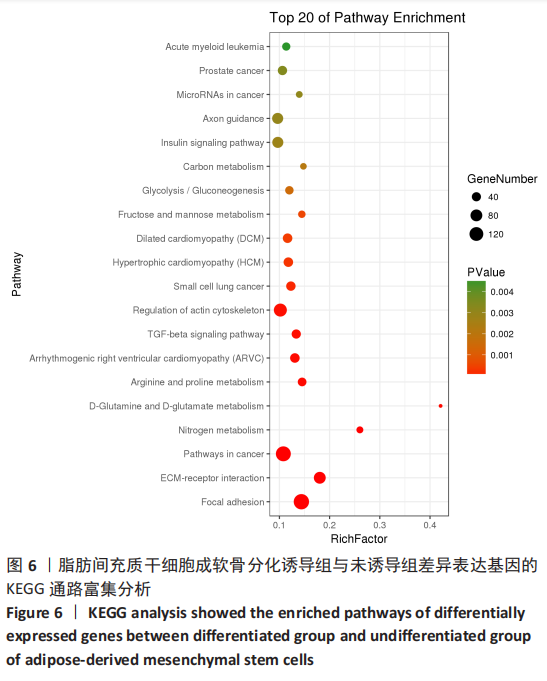
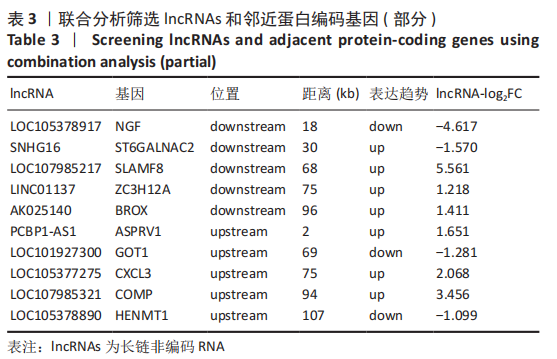
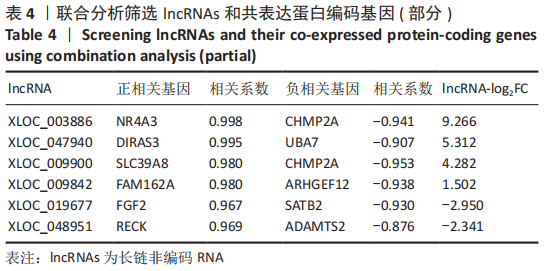
[1] BORRELLI J JR, OLSON SA, GODBOUT C, et al. Understanding Articular Cartilage Injury and Potential Treatments. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 6:S6-S12.
[2] ANDERSSON JK, HAGERT E, BRITTBERG M. Cartilage Injuries and Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis in the Wrist: A Review. Cartilage. 2021; 13(1_suppl):156S-168S.
[3] ZHAO X, HU DA, WU D, et al. Applications of Biocompatible Scaffold Materials in Stem Cell-Based Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:603444.
[4] MENDE W, GÖTZL R, KUBO Y, et al. The Role of Adipose Stem Cells in Bone Regeneration and Bone Tissue Engineering. Cells. 2021;10(5):975.
[5] SHI YY, NACAMULI RP, SALIM A, et al. The osteogenic potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal cells is maintained with aging. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116(6):1686-1696.
[6] PUISSANT B, BARREAU C, BOURIN P, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells: comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Br J Haematol. 2005;129(1):118-129.
[7] MAZINI L, ROCHETTE L, AMINE M, et al. Regenerative Capacity of Adipose Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs), Comparison with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2523.
[8] KOPP F, MENDELL JT. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2018;172(3):393-407.
[9] RANSOHOFF JD, WEI Y, KHAVARI PA. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(3): 143-157.
[10] SUN H, PENG G, NING X, et al. Emerging roles of long noncoding RNA in chondrogenesis, osteogenesis, and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(1):16-30.
[11] HUYNH NP, GLOSS CC, LORENTZ J, et al. Long non-coding RNA GRASLND enhances chondrogenesis via suppression of the interferon type II signaling pathway. Elife. 2020;9:e49558.
[12] YANG Q, HAN Y, LIU P, et al. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells by Regulating GDF5 and p38/JNK Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:701.
[13] XU Y, DUAN L, LIU S, et al. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00707 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation in osteoarthritis by serving as a sponge for microRNA-199-3p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):11137-11145.
[14] BUNNELL BA, FLAAT M, GAGLIARDI C, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods. 2008;45(2):115-120.
[15] 李聪聪,姚楠,黄丹娥,等.人髌下脂肪垫干细胞的鉴定及成软骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19):2976-2981.
[16] ZHANG Z, KANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Expression of microRNAs during chondrogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1638-1646.
[17] ZHANG Z, HUANG G, MAO G, et al. Characterization of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(3):1411-1420.
[18] LI H, ZHAO X, WEN X, et al. Inhibition of miR-490-5p Promotes Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Chondrogenesis and Protects Chondrocytes via the PITPNM1/PI3K/AKT Axis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:573221.
[19] STATELLO L, GUO CJ, CHEN LL, et al. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2): 96-118.
[20] URLIĆ I, IVKOVIĆ A. Cell Sources for Cartilage Repair-Biological and Clinical Perspective. Cells. 2021;10(9):2496.
[21] PANG HL, ZHAO QQ, MA Y, et al. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Participates in the Regulation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Cartilage Differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:2139814.
[22] MICHIGAMI T. Current understanding on the molecular basis of chondrogenesis. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014;23(1):1-8.
[23] 彭旭,张晓梅,魏诗航,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨及骨分化:Wnt5a/PCP信号通路作用的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(51):7717-7723.
[24] 刘宽,吴兴. Hedgehog信号调控骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨细胞分化:调控方式及其串话机制尚待研究[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(37):6040-6045.
[25] ZHOU D, GAN L, PENG Y,et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Fate. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:8876265.
[26] DYKES IM, EMANUELI C. Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-coding RNA. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017;15(3):177-186.
[27] WANG L, LI Z, LI Z, et al. Long noncoding RNAs expression signatures in chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;456(1):459-464.
[28] CAO Z, HUANG S, LI J, et al. Long noncoding RNA expression profiles in chondrogenic and hypertrophic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017;17(6):739-749.
[29] SOMOZA RA, WELTER JF, CORREA D, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: challenges and unfulfilled expectations. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(6):596-608.
[30] SHIN H, LEE MN, CHOUNG JS, et al. Focal Adhesion Assembly Induces Phenotypic Changes and Dedifferentiation in Chondrocytes. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(8):1822-1831.
[31] YU H, LIU Y, YANG X, et al. Strontium ranelate promotes chondrogenesis through inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):296.
[32] MATTA C, MOBASHERI A. Regulation of chondrogenesis by protein kinase C: Emerging new roles in calcium signalling. Cell Signal. 2014; 26(5):979-1000.
[33] FISCHER J, KNOCH N, SIMS T, et al. Time-dependent contribution of BMP, FGF, IGF, and HH signaling to the proliferation of mesenchymal stroma cells during chondrogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(11):8962-8970.
[34] KOVERMANN NJ, BASOLI V, DELLA BELLA E, et al. BMP2 and TGF-β Cooperate Differently during Synovial-Derived Stem-Cell Chondrogenesis in a Dexamethasone-Dependent Manner. Cells. 2019; 8(6):636.
[35] DUAN J, SHEN T, DONG H, et al. Association of the Expression Levels of Long-Chain Noncoding RNA TUG1 and Its Gene Polymorphisms with Knee Osteoarthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021;25(2):102-110.
[36] TANG LP, DING JB, LIU ZH, et al. LncRNA TUG1 promotes osteoarthritis-induced degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-195/MMP-13 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(24):8574-8581.
[37] HAN H, LIU L. Long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-320c/MMP-13 axis in osteoarthritis. Open Life Sci. 2021;16(1):384-394.
[38] LI Z, WANG J, YANG J. TUG1 knockdown promoted viability and inhibited apoptosis and cartilage ECM degradation in chondrocytes via the miR-17-5p/FUT1 pathway in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):154.
[39] JIANG H, PANG H, WU P, et al. LncRNA SNHG5 promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in osteoarthritis by regulating miR-10a-5p/H3F3B axis. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(6):605-614.
[40] SUN Y, KANG S, PEI S, et al. MiR93-5p inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by targeting lncRNA CASC2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):26.
[41] SHI C, ZHENG W, WANG J. lncRNA-CRNDE regulates BMSC chondrogenic differentiation and promotes cartilage repair in osteoarthritis through SIRT1/SOX9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(4):1881-1890.
[42] MAO G, KANG Y, LIN R, et al. Long Non-coding RNA HOTTIP Promotes CCL3 Expression and Induces Cartilage Degradation by Sponging miR-455-3p. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:161.
[43] FENG L, YANG ZM, LI YC, et al. Linc-ROR promotes mesenchymal stem cells chondrogenesis and cartilage formation via regulating SOX9 expression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(4):568-578.
[44] CHENG W, HAO CY, ZHAO S, et al. SNHG16 promotes the progression of osteoarthritis through activating microRNA-93-5p/CCND1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(21):9222-9229.
[45] FAN H, DING L, YANG Y. lncRNA SNHG16 promotes the occurrence of osteoarthritis by sponging miR‑373‑3p. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(2):117.
[46] ZHU J, YU W, WANG Y, et al. lncRNAs: function and mechanism in cartilage development, degeneration, and regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):344.
[47] MA C, WU L, SONG L, et al. The pro-inflammatory effect of NR4A3 in osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1):930-940.
[48] SONG J, KIM D, LEE CH, et al. MicroRNA-488 regulates zinc transporter SLC39A8/ZIP8 during pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20(1):31.
[49] KIM JH, JEON J, SHIN M, et al. Regulation of the catabolic cascade in osteoarthritis by the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis. Cell. 2014;156(4):730-743.
[50] ELLMAN MB, YAN D, AHMADINIA K, et al. Fibroblast growth factor control of cartilage homeostasis. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(4):735-742.
[51] VAN LENT PL, SPAN PN, SLOETJES AW, et al. Expression and localisation of the new metalloproteinase inhibitor RECK (reversion inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs) in inflamed synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(3): 368-374.
[52] KIMURA T, OKADA A, YATABE T, et al. RECK is up-regulated and involved in chondrocyte cloning in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(6):2858-2867. |