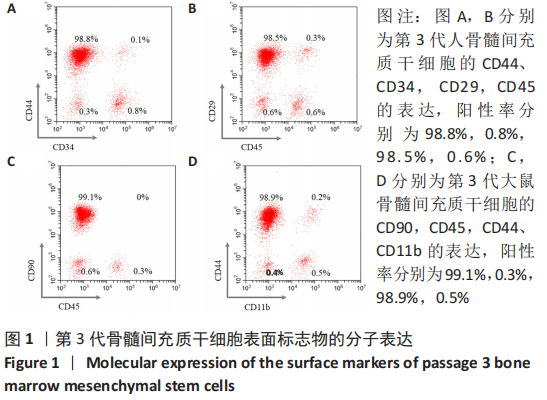
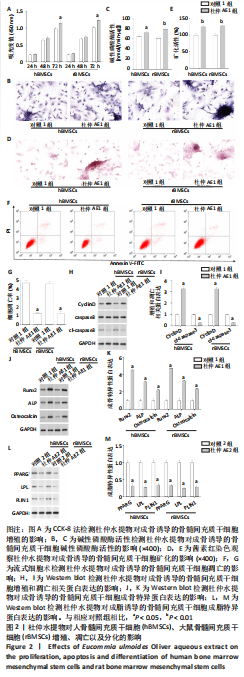
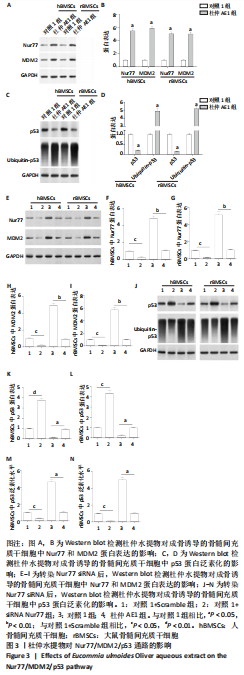
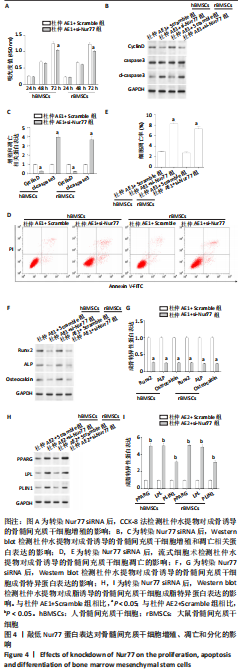
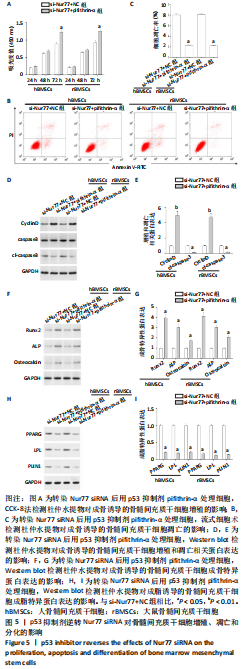
[1] MAITRA B, SZEKELY E, GJINI K, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells support unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cells and suppress T-cell activation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004;33(6):597-604.
[2] LIN Z, HE H, WANG M, et al. MicroRNA-130a controls bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation towards the osteoblastic and adipogenic fate. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(6):e12688.
[3] HSU MN, HUANG KL, YU FJ, et al. Coactivation of Endogenous Wnt10b and Foxc2 by CRISPR Activation Enhances BMSC Osteogenesis and Promotes Calvarial Bone Regeneration. Mol Ther. 2020;28(2):441-451.
[4] 高宏伟,李玉萍,李守超.杜仲的化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].中医药信息,2021,38(6):73-81.
[5] 赵继荣,杨涛,赵宁,等.杜仲诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化防治骨质疏松症相关信号通路研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2020,26(12):1868-1872.
[6] SASA K, YOSHIMURA K, YAMADA A, et al. Monocarboxylate transporter-1 promotes osteoblast differentiation via suppression of p53, a negative regulator of osteoblast differentiation. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):10579.
[7] 余瑾,黄亚琴,杨劲.DNA损伤修复基因XPC缺失导致间充质干细胞早衰的初步研究[J].中国临床研究,2018,31(7):865-869.
[8] MOLL UM, MARCHENKO N, ZHANG XK. p53 and Nur77/TR3 - transcription factors that directly target mitochondria for cell death induction. Oncogene. 2006;25(34):4725-4743.
[9] ZHAO J, WU J, XU B, et al. Kaempferol promotes bone formation in part via the mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(6):5197-5207.
[10] LI Y, HU W, HAN G, et al. Involvement of bone morphogenetic protein-related pathways in the effect of aucubin on the promotion of osteoblast differentiation in MG63 cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2018; 283:51-58.
[11] YUAN Z, MIN J, ZHAO Y, et al. Quercetin rescued TNF-alpha-induced impairments in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and improved osteoporosis in rats. Am J Transl Res. 2018; 10(12):4313-4321.
[12] 林奇生,邹学农,曾瑞芬,等.杜仲醇提取物通过RhoA/ROCK信号通路调控大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化作用研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(2):26-30.
[13] 赵亮, 陈志明. 盐炙杜仲对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢生化指标的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2019,30(3):587-588.
[14] SHRESTHA R, MOHANKUMAR K, MARTIN G, et al. Flavonoids kaempferol and quercetin are nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1, Nur77) ligands and inhibit rhabdomyosarcoma cell and tumor growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40(1):392.
[15] ZHU MQ, SUN RC. Eucommia ulmoides Oliver: A Potential Feedstock for Bioactive Products. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66(22):5433-5438.
[16] MAIJENBURG MW, GILISSEN C, MELIEF SM, et al. Nuclear receptors Nur77 and Nurr1 modulate mesenchymal stromal cell migration. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(2):228-238.
[17] CHAO LC, BENSINGER SJ, VILLANUEVA CJ, et al. Inhibition of adipocyte differentiation by Nur77, Nurr1, and Nor1. Mol Endocrinol. 2008; 22(12):2596-2608.
[18] QIN DD, YANG YF, PU ZQ, et al. NR4A1 retards adipocyte differentiation or maturation via enhancing GATA2 and p53 expression. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(10):4709-4720.
[19] NIU B, LIU J, LV B, et al. Interplay between transforming growth factor-β and Nur77 in dual regulations of inhibitor of differentiation 1 for colonic tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2809.
[20] LITH SC, DE VRIES CJM. Nuclear receptor Nur77: its role in chronic inflammatory diseases. Essays Biochem. 2021;65(6):927-939.
[21] 王建,陈华,丁聪聪.微管相关蛋白Nur77在前列腺癌转移中的作用及其机制的探讨[J].肿瘤,2018,38(2):111-119.
[22] CHOI H, MAGYAR CE, NERVINA JM, et al. Different duration of parathyroid hormone exposure distinctively regulates primary response genes Nurr1 and RANKL in osteoblasts. PLoS One. 2018; 13(12):e0208514.
[23] SCHOLTYSEK C, IPSEIZ N, BÖHM C, et al. NR4A1 Regulates Motility of Osteoclast Precursors and Serves as Target for the Modulation of Systemic Bone Turnover. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(11):2035-2047.
[24] HERRING JA, ELISON WS, TESSEM JS. Function of Nr4a Orphan Nuclear Receptors in Proliferation, Apoptosis and Fuel Utilization Across Tissues. Cells. 2019;8(11):1373.
[25] XIANG T, ZHANG S, CHENG N, et al. Oxidored-nitro domain-containing protein 1 promotes liver fibrosis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):5050-5054.
[26] MEDZIKOVIC L, VAN ROOMEN C, BAARTSCHEER A, et al. Nur77 protects against adverse cardiac remodelling by limiting neuropeptide Y signalling in the sympathoadrenal-cardiac axis. Cardiovasc Res. 2018; 114(12):1617-1628.
[27] PRINCE LR, PROSSEDA SD, HIGGINS K, et al. NR4A orphan nuclear receptor family members, NR4A2 and NR4A3, regulate neutrophil number and survival. Blood. 2017;130(8):1014-1025.
[28] NAGAOKA M, YASHIRO T, UCHIDA Y, et al. The Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR4A3 Is Involved in the Function of Dendritic Cells. J Immunol. 2017; 199(8):2958-2967.
[29] ZHENG Y, COMAILLS V, BURR R, et al. COX-2 mediates tumor-stromal prolactin signaling to initiate tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(12):5223-5232.
[30] 金富军.Bre通过增强p53蛋白的泛素化降解促进成骨分化[D].广州:暨南大学,2017.
[31] CHAABANE W, CIEŚLAR-POBUDA A, EL-GAZZAH M, et al. Human-gyrovirus-Apoptin triggers mitochondrial death pathway--Nur77 is required for apoptosis triggering. Neoplasia. 2014;16(9):679-693.
[32] ZHOU H, DU W, LI Y, et al. Effects of melatonin on fatty liver disease: The role of NR4A1/DNA-PKcs/p53 pathway, mitochondrial fission, and mitophagy. J Pineal Res. 2018;64(1):12450.
[33] JIN F, WANG Y, WANG X, et al. Bre Enhances Osteoblastic Differentiation by Promoting the Mdm2-Mediated Degradation of p53. Stem Cells. 2017;35(7):1760-1772.
|