[1] GONCALVES EM, OLIVEIRA FJ, SILVA RF, et al. Three-dimensional printed PCL-hydroxyapatite scaffolds filled with cnts for bone cell growth stimulation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016;104(6):1210-1219.
[2] 李欣. 聚己内酯基骨组织工程支架的制备和性能[J].兰州:兰州大学,2017.
[3] HUANG B, VYAS C, BYUN JJ, et al. Aligned multi-walled carbon nanotubes with nanohydroxyapatite in a 3d printed polycaprolactone scaffold stimulates osteogenic differentiation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;108:110374.
[4] 余和东,丽张,夏凌云,等.3D打印成型纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/聚己内酯三元复合支架材料的构建及表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(10):1496-1501.
[5] WANG Q, ZHANG Y, LI B, et al. Controlled dual delivery of low doses of bmp-2 and vegf in a silk fibroin-nanohydroxyapatite scaffold for vascularized bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(33):6963-6972.
[6] QI Q, YAO Y, JIA X, et al. Effects of polyethylene glycol content on the properties of a silk fibroin/nano-hydroxyapatite/polyethylene glycol electrospun scaffold. RSC Advances. 2019;9(58):33941-33948.
[7] WANG K, CHENG W, DING Z, et al. Injectable silk/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite hydrogels with vascularization capacity for bone regeneration. J Mater Sci Technol. 2021;63:172-181.
[8] SUN J, ZHANG Y, LI B, et al. Controlled release of BMP-2 from a collagen-mimetic peptide-modified silk fibroin-nanohydroxyapatite scaffold for bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(44):8770-8779.
[9] TSAI SW, HUANG SS, YU WX, et al. Collagen scaffolds containing hydroxyapatite-CaO fiber fragments for bone tissue engineering. Polymers. 2020;12(5):1174.
[10] LIU H, DU Y, YANG G, et al. Delivering proangiogenic factors from 3D-printed polycaprolactone scaffolds for vascularized bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(23):2000727.
[11] GODOY-GALLARDO M, PORTOLES-GIL N, LOPEZ-PERIAGO AM, et al. Multi-layered polydopamine coatings for the immobilization of growth factors onto highly-interconnected and bimodal PCL/HA-based scaffolds. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2020; 117:111245.
[12] 杨湘俊,陈俊宇,朱舟,等.PCL基复合骨组织工程支架研究现状及发展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2021,4(4):485-492.
[13] WANG W, OMORI M, WATARI F, et al. Novel bulk carbon nanotube materials for implant by spark plasma sintering. Dent Mater J. 2005;24(4):478-486.
[14] GEORGIA, PAGONA, NIKOS, et al. Carbon nanotubes: Materials for medicinal chemistry and biotechnological applications. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(15):1789-1798.
[15] MARRS B, ANDREWS R, RANTELL T, et al. Augmentation of acrylic bone cement with multiwall carbon nanotubes. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006; 77(2):269-276.
[16] LI X, LIU H, NIU X, et al. The use of carbon nanotubes to induce osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mscs in vitro and ectopic bone formation in vivo. Biomaterials. 2012;33(19):4818-4827.
[17] LA WG, PARK S, YOON HH, et al. Delivery of a therapeutic protein for bone regeneration from a substrate coated with graphene oxide. Small. 2013;9(23):4051-4060.
[18] CAO J, LU Y, CHEN H, et al. Bioactive poly (etheretherketone) composite containing calcium polyphosphate and multi-walled carbon nanotubes for bone repair: Mechanical property and in vitro biocompatibility. J Bioact Compat Pol. 2018;33(5):543-557.
[19] SARAVANAN S, CHAWLA A, VAIRAMANI M, et al. Scaffolds containing chitosan, gelatin and graphene oxide for bone tissue regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;104:1975-1985.
[20] HERMENEAN A, CODREANU A, HERMAN H, et al. Chitosan-graphene oxide 3d scaffolds as promising tools for bone regeneration in critical-size mouse calvarial defects. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16641.
[21] Xu X, Ray R,GU Y, et al. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single- walled carbon nanotube fragments. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126(40):12736-12737.
[22] SUN YP, ZHOU B, LIN Y, et al. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128(24):7756-7757.
[23] XIA C, ZHU S, FENG T, et al. Evolution and synthesis of carbon dots: from carbon dots to carbonized polymer dots. Adv Sci. 2019;6(23):1901316.
[24] MIAO H, WANG L, ZHUO Y, et al. Label-free fluorimetric detection of cea using carbon dots derived from tomato juice. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;86:83-89.
[25] WANG Y, MA T, MA S, et al. Fluorometric determination of the antibiotic kanamycin by aptamer-induced fret quenching and recovery between moS2 nanosheets and carbon dots. Microchim Acta. 2016;184(1):203-210.
[26] WANG X, JIANG X, ZHANG Z, et al. A fluorescence and resonance rayleigh scattering di-model probe was developed for trace k+ coupled n-doped carbon dot and aptamer. J lumin. 2019;214(C):116559-116559.
[27] SU Y, LIU S, GUAN Y, et al. Renal clearable hafnium-doped carbon dots for ct/fluorescence imaging of orthotopic liver cancer. Biomaterials. 2020;255:120110.
[28] JIANG Q, LIU L, LI Q, et al. Nir-laser-triggered gadolinium-doped carbon dots for magnetic resonance imaging, drug delivery and combined photothermal chemotherapy for triple negative breast cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):64.
[29] CHEN BB, LIU ML, HUANG CZ,et al. Recent advances of carbon dots in imaging-guided theranostics. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2021;134:116116.
[30] ZHENG M, LIU S, LI J, et al. Integrating oxaliplatin with highly luminescent carbon dots: An unprecedented theranostic agent for personalized medicine. Adv Mater. 2014;26(21):3554-3560.
[31] SUN T, ZHENG M, XIE Z, et al. Supramolecular hybrids of carbon dots with doxorubicin: synthesis, stability and cellular trafficking. Mater Chem Front. 2017;1(2):354-360.
[32] CHEN S, JIA Q, ZHENG X, et al. Pegylated carbon dot/mno2 nanohybrid: a new ph/h2o2-driven, turn-on cancer nanotheranostics. Sci China Mater. 2018;61(10):1325-1338.
[33] HUA XW, BAO YW, ZENG J, et al. Ultrasmall all-in-one nanodots formed via carbon dot-mediated and albumin-based synthesis: Multimodal imaging-guided and mild laser-enhanced cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2018;10(49):42077-42087.
[34] SUN Q, WANG Z, LIU B, et al. Self-generation of oxygen and simultaneously enhancing photodynamic therapy and mri effect: an intelligent nanoplatform to conquer tumor hypoxia for enhanced phototherapy. Chem Eng J. 2020;390:124624.
[35] PAL P, DAS B, DADHICH P, et al. Carbon nanodot impregnated fluorescent nanofibers for in vivo monitoring and accelerating full-thickness wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(32):6645-6656.
[36] OMIDI M, YADEGARI A, TAYEBI L, et al. Wound dressing application of ph-sensitive carbon dots/chitosan hydrogel. RSC Adv. 2017;7(18):10638-10649.
[37] WANG Z, LIU L, BU W, et al. Carbon dots induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition for promoting cutaneous wound healing via activation of tgf‐β/p38/snail pathway. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(43):2004886.
[38] LI P, LIU S, YANG X, et al. Low-drug resistance carbon quantum dots decorated injectable self-healing hydrogel with potent antibiofilm property and cutaneous wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2021;403:126387.
[39] BELZA J, OPLETALOVA A, POLAKOVA K, et al. Carbon dots for virus detection and therapy. Mikrochim Acta. 2021;188(12):430.
[40] QIU J, LI D, MOU X, et al. Effects of graphene quantum dots on the self-renewal and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(6):702-710.
[41] DEHGHANI A, ARDEKANI SM, HASSAN M, et al. Collagen derived carbon quantum dots for cell imaging in 3d scaffolds via two-photon spectroscopy. Carbon. 2018; 131:238-245.
[42] LU Y, LI L, LI M, et al. Zero-dimensional carbon dots enhance bone regeneration, osteosarcoma ablation, and clinical bacterial eradication. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018;29(9):2982-2993.
[43] SHAFIEI S, OMIDI M, NASEHI F, et al. Egg shell-derived calcium phosphate/carbon dot nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: fabrication and characterization. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2019;100:564-575.
[44] PENG Z, MIYANJI E H, ZHOU Y, et al. Carbon dots: Promising biomaterials for bone-specific imaging and drug delivery. Nanoscale. 2017;9(44):17533-17543.
[45] MOLAEI MJ. Carbon quantum dots and their biomedical and therapeutic applications: a review. RSC Adv. 2019;9(12):6460-6481.
[46] MANISHA H, PRIYA SWETHA PD, SHIM YB, et al. Revisiting fluorescent carbon nanodots for environmental, biomedical applications and puzzle about fluorophore impurities. Nano-Structures Nano-Objects. 2019;20(8):100391.
[47] ANSARI L, HALLAJ S, HALLAJ T, et al. Doped-carbon dots: recent advances in their biosensing, bioimaging and therapy applications. Colloid Surface B. 2021;203:111743.
[48] 郑敏,刘坤梅,苏雅,等.碳点在生物医学领域中的应用[J].发光学报,2021, 42(8):1233-1244.
[49] PENG Z, ZHAO T, ZHOU Y, et al. Bone tissue engineering via carbon-based nanomaterials. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(5):e1901495.
[50] FENG Z, ADOLFSSON KH, XU Y, et al. Carbon dot/polymer nanocomposites: From green synthesis to energy, environmental and biomedical applications. Sustain Mater Tech. 2021;29(206):00304.
[51] LIU H, CHEN J, QIAO S, et al. Carbon-based nanomaterials for bone and cartilage regeneration: a review. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(10):4718-4735.
[52] VEDHANAYAGAM M, RAJA IS, MOLKENOVA A, et al. Carbon dots-mediated fluorescent scaffolds: recent trends in image-guided tissue engineering applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5378.
[53] 李泽华,谢元栋,詹骆宁,等.碳点在组织再生支架中的应用研究进展[J].化学与生物工程,2022,39(2):6-9.
[54] FAN Z, WANG J, WANG Z, et al. One-pot synthesis of graphene/hydroxyapatite nanorod composite for tissue engineering. Carbon. 2014;66:407-416.
[55] GOGOI S, KUMAR M, MANDAL BB, et al. High performance luminescent thermosetting waterborne hyperbranched polyurethane/carbon quantum dot nanocomposite with in vitro cytocompatibility. Compos Sci Technol. 2015;118:39-46.
[56] GOGOI S, MAJI S, MISHRA D, et al. Nano-bio engineered carbon dot-peptide functionalized water dispersible hyperbranched polyurethane for bone tissue regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2017;17(3):1600271.
[57] KHAJURIA DK, KUMAR VB, GIGI D, et al. Accelerated bone regeneration by nitrogen-doped carbon dots functionalized with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2018;10(23):19373-19385.
[58] WANG B, YANG M, LIU L, et al. Osteogenic potential of zn(2+)-passivated carbon dots for bone regeneration in vivo. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(12):5414-5423.
[59] JIN N, JIN N, WANG Z, et al. Osteopromotive carbon dots promote bone regeneration through the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway. Biomater Sci. 2020; 8(10):2840-2852.
[60] GENG B, FANG F, LI P, et al. Surface charge-dependent osteogenic behaviors of edge-functionalized graphene quantum dots. Chem Eng J. 2021;417:128125.
[61] GENG B, LI P, FANG F, et al. Antibacterial and osteogenic carbon quantum dots for regeneration of bone defects infected with multidrug-resistant bacteria. Carbon. 2021;184:375-385.
[62] YANG M, MENG Y, LIU J, et al. Facile synthesis of mg2+-doped carbon dots as novel biomaterial inducing cell osteoblastic differentiation. Part Part Syst Char. 2019; 36(1):1800315.
[63] MENG Y, YANG M, LIU X, et al. Zn2+-doped carbon dots, a good biocompatibility nanomaterial applied for bio-imaging and inducing osteoblastic differentiation in vitro. NANO. 2019;14(3):1950029.
[64] HAN Y, ZHANG F, ZHANG J, et al. Bioactive carbon dots direct the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;179:1-8.
[65] SAMADIAN S, KARBALAEI A, POURMADADI M, et al. A novel alginate-gelatin microcapsule to enhance bone differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Polym Mater. 2021;4:1-8.
[66] HASSANZADEH S, ADOLFSSON KH, WU D, et al. Supramolecular assembly of biobased graphene oxide quantum dots controls the morphology of and induces mineralization on poly (epsilon-caprolactone) films. Biomacromolecules. 2016;17(1):256-261.
[67] WU D, SAMANTA A, SRIVASTAVA RK, et al. Starch-derived nanographene oxide paves the way for electrospinnable and bioactive starch scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(5):1582-1591.
[68] WU D, SAMANTA A, SRIVASTAVA RK, et al. Nano-graphene oxide functionalized bioactive poly(lactic acid) and poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanofibrous scaffolds. Materials. 2018;11(4):566.
[69] YADAV A, ERDAL NB, HAKKARAINEN M, et al. Cellulose-derived nanographene oxide reinforced macroporous scaffolds of high internal phase emulsion-templated cross-linked poly(epsilon-caprolactone). Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(2):589-596.
[70] GHORGHI M, RAFIENIA M, NASIRIAN V, et al. Electrospun captopril-loaded pcl-carbon quantum dots nanocomposite scaffold: fabrication, characterization, and in vitro studies. Polymers for Advanced Technologies. 2020;31(12):3302-3315.
[71] LU Z, LIU S, LE Y, et al. An injectable collagen-genipin-carbon dot hydrogel combined with photodynamic therapy to enhance chondrogenesis. Biomaterials. 2019;218:119190.
[72] BU W, XU X, WANG Z, et al. Ascorbic Acid-PEI carbon dots with osteogenic effects as miR-2861 carriers to effectively enhance bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2020;12(45):50287-50302.
[73] MU Q, DU G, CHEN T, et al. Suppression of human bone morphogenetic protein signaling by carboxylated single-walled carbon nanotubes. Acs Nano. 2009;3(5):1139-1144.
[74] KILIAN KA, BUGARIJA B, LAHN BT, et al. Geometric cues for directing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107(11):4872-4877.
[75] LIU DD, ZHANG JC, ZHANG Q, et al. TGF-β/BMP signaling pathway is involved in cerium-promoted osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(5):1105-1114. |
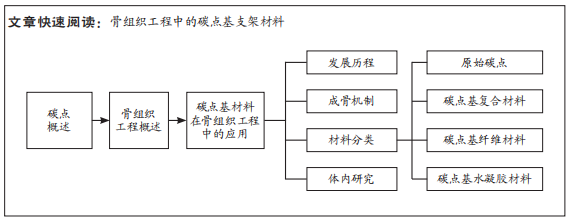
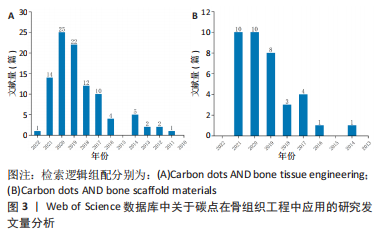
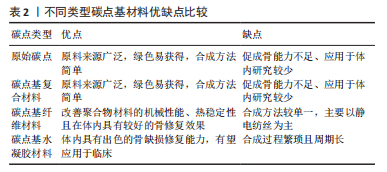
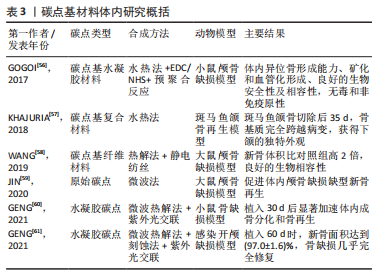

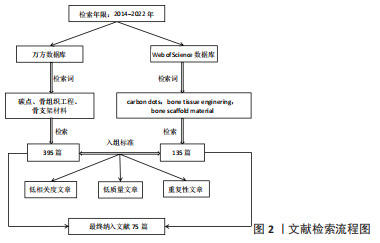
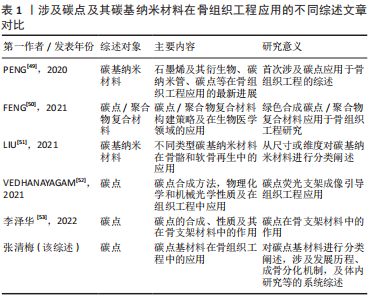 鉴于此,该综述首次将碳点基材料分为4种类型,原始碳点、碳点基复合材料、碳点基纤维材料以及碳点基水凝胶材料,并详细概述了碳点基材料的发展历程、不同类型碳点基材料的优缺点以及应用于体内外骨缺损修复的研究现状和挑战,旨在为有针对性地设计一种性能优异真正有潜力应用于临床的骨修复支架材料提供一些研究思路和实验方法上的借鉴。
鉴于此,该综述首次将碳点基材料分为4种类型,原始碳点、碳点基复合材料、碳点基纤维材料以及碳点基水凝胶材料,并详细概述了碳点基材料的发展历程、不同类型碳点基材料的优缺点以及应用于体内外骨缺损修复的研究现状和挑战,旨在为有针对性地设计一种性能优异真正有潜力应用于临床的骨修复支架材料提供一些研究思路和实验方法上的借鉴。