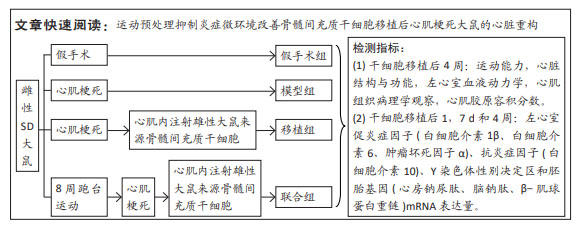
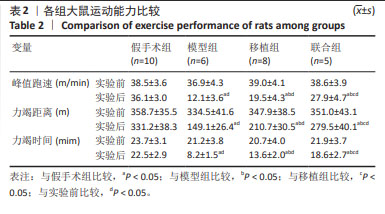
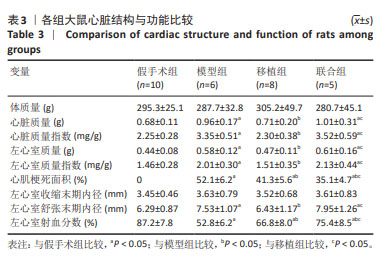
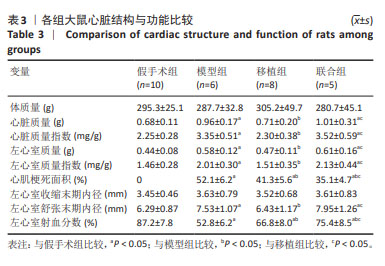
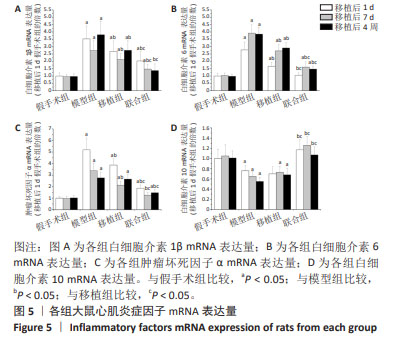
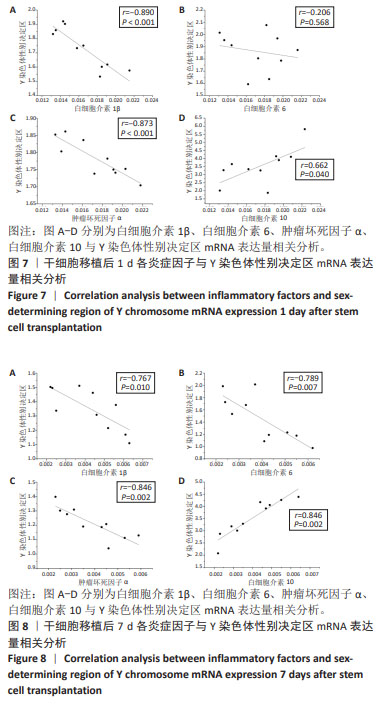
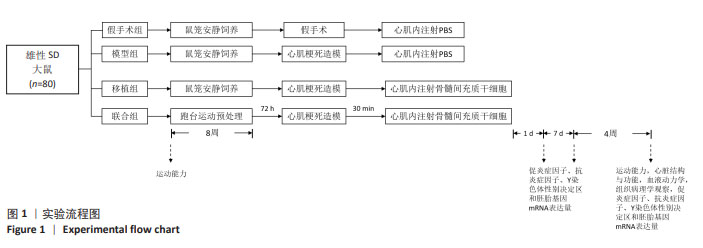
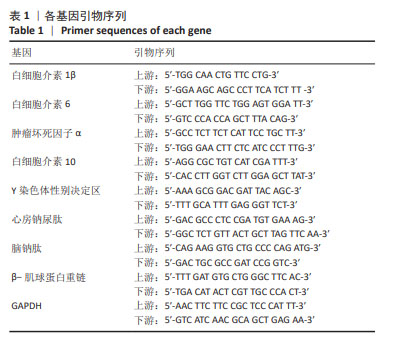
[1] 孙维兴,赵永超,赵然尊.间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死:问题、症结及新突破[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19):3103-3109.
[2] 王文华,刘洋,吕洋,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌细胞分化的研究进展[J] 华中科技大学学报(医学版),2021,50(6):811-816.
[3] YAMADA Y, MINATOGUCHI S, KANAMORI H, et al. Stem cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction - focusing on the comparison between Muse cells and mesenchymal stem cells. J Cardiol. 2022; 80(1):80-87.
[4] MENG H, CHENG W, WANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes in the treatment of myocardial infarction: a systematic review of preclinical in vivo studies. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022;15(2):317-339.
[5] HICKS MR, PYLE AD. The emergence of the stem cell niche. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33(2):112-123.
[6] KHODAYARI S, KHODAYARI H, AMIRI AZ, et al. Inflammatory microenvironment of acute myocardial infarction prevents regeneration of heart with stem cells therapy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;53(5): 887-909.
[7] LEE CC, HIRASAWA N, GARCIA KG, et al. Stem and progenitor cell microenvironment for bone regeneration and repair. Regen Med. 2019; 14(7): 693-702.
[8] LI H, HOU L. Regulation of melanocyte stem cell behavior by the niche microenvironment. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018;31(5):556-569.
[9] 黄宏,邱伟,陈民佳,等.干细胞预处理及其保护机制的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2017,12(2):138-142.
[10] QUINDRY JC, FRANKLIN BA. Exercise preconditioning as a cardioprotective phenotype. Am J Cardiol. 2021;148:8-15.
[11] CHIRICO EN, DING D, MUTHUKUMARAN G, et al. Acute aerobic exercise increases exogenously infused bone marrow cell retention in the heart. Physiol Rep. 2015; 3(10):e12566.
[12] 张艳,何瑞波,王庆博,等.不同负荷量有氧运动对肥胖大鼠骨骼肌炎症反应和胰岛素信号途径的影响及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(8):1237-1244.
[13] HAN BJ, CAO GY, JIA LY, et al. Cardioprotective effects of tetrahydropalmatine on acute myocardial infarction in rats. Am J Chin Med. 2022;50(7):1887-1904.
[14] 李鑫辉,黄淼鑫,杜建芳,等.丹参通络解毒汤联合骨髓干细胞移植对急性心肌梗死大鼠心肌纤维化的影响及其机制[J].北京中医药大学学报,2019,42(8):655-661.
[15] LAVORATO VN, DEL CARLO RJ, DA CUNHA DN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy associated with endurance exercise training: effects on the structural and functional remodeling of infarcted rat hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;90:111-119.
[16] COSMO S, FRANCISCO JC, CUNHA RC, et al. Effect of exercise associated with stem cell transplantation on ventricular function in rats after acute myocardial infarction. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2012;27(4):542-551.
[17] DOS SANTOS L, ANTONIO EL, SOUZA AF, et al. Use of afterload hemodynamic stress as a practical method for assessing cardiac performance in rats with heart failure. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010; 88(7):724-732.
[18] SANTOS AA, HELBER I, FLUMIGNAN RL, et al. Doppler echocardiographic predictors of mortality in female rats after myocardial infarction. J Card Fail. 2009;15(2):163-168.
[19] ALBAENI A, DAVIS JW, AHMAD M. Echocardiographic evaluation of the athlete’s heart. Echocardiography. 2021;38(6):1002-1016.
[20] OLDFIELD CJ, DUHAMEL TA, DHALLA NS. Mechanisms for the transition from physiological to pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;98(2):74-84.
[21] TASHIRO H, TANAKA A, ISHII H, et al. Reduced exercise capacity and clinical outcomes following acute myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels. 2020;35(8):1044-1050.
[22] SQUIRES RW, BONIKOWSKE AR. Cardiac rehabilitation for heart transplant patients: considerations for exercise training. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2022;70:40-48.
[23] NAKAMUTA JS, DANOVIZ ME, MARQUES FL, et al. Cell therapy attenuates cardiac dysfunction post myocardial infarction: effect of timing, routes of injection and a fibrin scaffold. PLoS One. 2009;4(6): e6005.
[24] 姜俣,钱海燕.间充质干细胞治疗心肌梗死的研究进展[J].基础医学与临床,2023,43(1):21-29.
[25] ZHANG H, CHEN H, WANG W, et al. Cell survival and redistribution after transplantation into damaged myocardium. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(5):1078-1082.
[26] ZHANG H, SONG P, TANG Y, et al. Injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the borderline area of infarcted myocardium: heart status and cell distribution. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;134(5):1234-1240.
[27] HANNA A, FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines as therapeutic targets in heart failure. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2020;34(6):849-863.
[28] 钟世根,骆杰,王志刚,等.超声靶向破碎微泡对心肌梗死犬心肌微环境的影响[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2017,36(11):4528-4533.
[29] PEDERSEN BK. Anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: role in diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2017;47(8):600-611.
[30] SANTOS MH, HIGUCHI MDE L, TUCCI PJ, et al. Previous exercise training increases levels of PPAR-α in long-term post-myocardial infarction in rats, which is correlated with better inflammatory response. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016;71(3):163-168.
[31] NUNES RB, ALVES JP, KESSLER LP, et al. Aerobic exercise improves the inflammatory profile correlated with cardiac remodeling and function in chronic heart failure rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013;68(6):876-882.
[32] WANG L, WEI FX, CEN JS, et al. Early administration of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist promotes survival of transplanted neural stem cells and axon myelination after spinal cord injury in rats. Brain Res. 2014;1575:87-100.
[33] SUZUKI K, MURTUZA B, BEAUCHAMP JR, et al. Role of interleukin-1beta in acute inflammation and graft death after cell transplantation to the heart. Circulation. 2004;110(11 Suppl 1):219-224.
[34] KRISHNAMURTHY P, THAL M, VERMA S, et al. Interleukin-10 deficiency impairs bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell survival and function in ischemic myocardium. Circ Res. 2011;109(11):1280-1289.
[35] BOROW KM, YAROSHINSKY A, GREENBERG B, et al. Phase 3 dream-HF trial of mesenchymal precursor cells in chronic heart failure. Circ Res. 2019;125(3):265-281. |