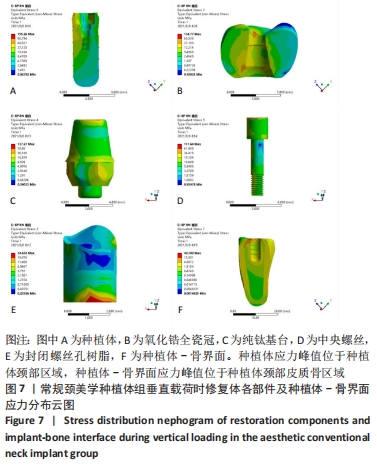
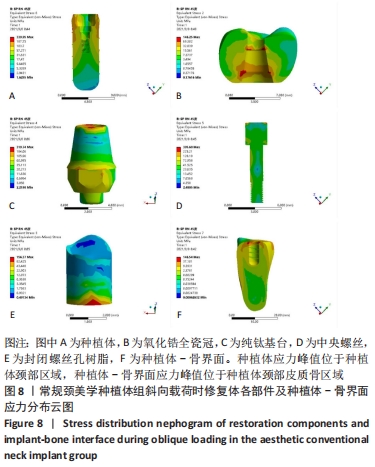
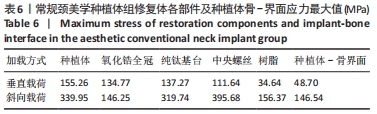
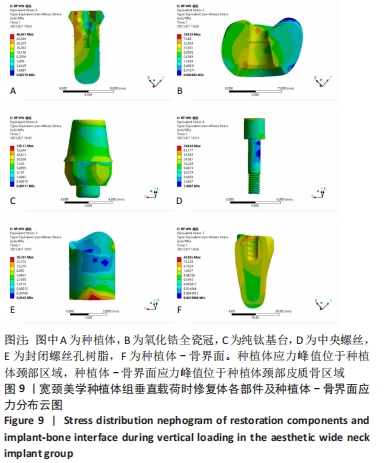
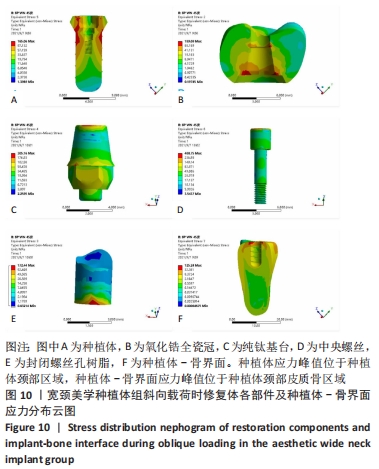
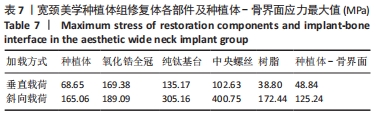
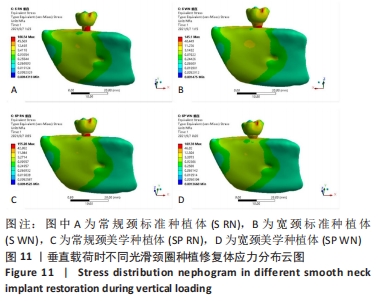
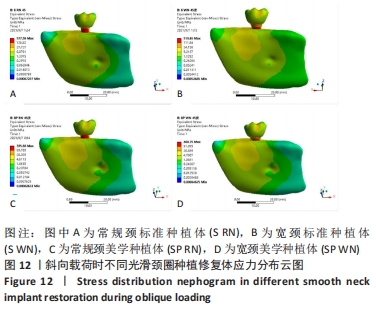
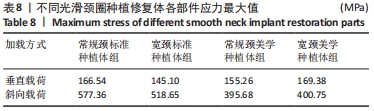
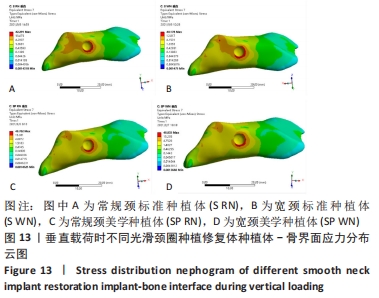
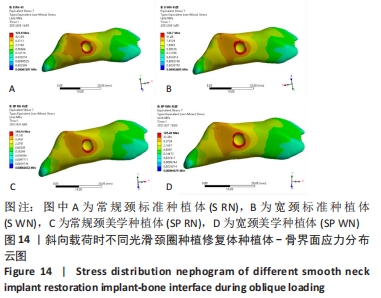
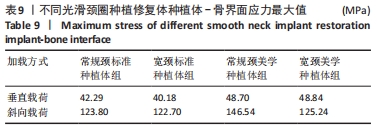
[1] 安尼卡尔·安尼瓦尔,帕丽黛姆·图尔迪,阿迪力·麦木提敏,等.上颌前牙区不同种植修复体在不同咬合受力下的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(16):2531-2536.
[2] 杜巧琳,顾新华.牙种植体形态结构设计的研究进展[J].口腔医学, 2021,41(5):475-480.
[3] 赖漪娆,史俊宇,赖红昌.种植体光滑颈圈的临床应用[J].口腔医学,2021,41(8):746-750.
[4] 李哲,秦博文,常晓峰,等.面开孔直径对种植修复系统及周围皮质骨影响的有限元分析[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2018,34(2):182-187.
[5] 白布加甫·叶力思,热娜古丽·买合木提,艾孜买提江·赛依提,等.上颌中切牙联冠种植修复体在不同咬合方式中的应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):567-572.
[6] FAVERANI LP, BARÃO VA, RAMALHO-FERREIRA G, et al. The influence of bone quality on the biomechanical behavior of full-arch implant-supported fixed prostheses. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;37: 164-170.
[7] 哈雅楠.动态载荷下不同修复方式对后牙种植单冠应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[D].济南:山东大学,2019.
[8] 施梦汝,谢伟丽,施武阁,等.柱形锥形种植体在不同种植深度的三维有限元研究[J].口腔医学,2019,39(7):577-580.
[9] 黄耀文.不同材料修复下颌第一前磨牙楔状缺损的三维有限元分析[D].南昌:南昌大学,2020.
[10] 陈俊良,李明霞,吕冬梅,等.迷你种植体支持的下颌覆盖义齿三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(10):1491-1495.
[11] HELAL MA, WANG Z. Biomechanical assessment of restored mandibular molar by endocrown in comparison to a glass fiber postretained conventional crown:3D finite element analysis. J Prosthodont. 2019; 28(9):988-996.
[12] 赵楚翘,徐一驰,刘定坤,等.髓腔固位冠及桩核冠修复下颌第一磨牙大面积缺损的生物力学分析[J].口腔医学研究2018,34(5):513-517.
[13] 王悦,郭振兴,谭乃文,等.种植失败病例风险因素的分析与探讨[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2017,52(8):510-512.
[14] OGLE OE. Implant surface material,design and osseointegration. Dent Clin N Am. 2015;59(2):505-520.
[15] YASUTAKE M, KUROSHIMA S, ISHIMOTO T, et al. The influence of bone quality on the biomechanical behavior of full-arch implant-supported fixed prostheses. MaterSci Eng C. 2014;37:164-170.
[16] FROST HM. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(1):3-15.
[17] 王姝,李琼,金武龙.有限元法在口腔种植领域的研究进展[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2018,16(2):125-128.
[18] MESSIAS A, NICOLAU P, GUERRA F. Titanium dental implants with different collar design and surface modifications: A systematic review on survival rates and marginal bone levels. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(1):20-48.
[19] ROODABEH K, ALI H. Evaluation of Implant Collar Surfaces for Marginal Bone Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1-10.
[20] SÁNCHEZ-SILES M, MUOZ-CÁMARA D, SALAZAR-SÁNCHEZ N, et al. Incidence of peri-implantitis and oral quality of life in patients rehabilitated with implants with different neck designs: A 10-year retrospective study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43(10):2168-2174.
[21] 范毅杰,李媛,胡晓文.不同颈部设计种植体在骨愈合期边缘骨变化的临床分析[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志,2018,12(3):169-175.
[22] VALLES C, RODRÍGUEZ-CIURANA X, NART J, et al. Influence of Implant Neck Surface and Placement Depth on Crestal Bone Changes Around Platform-Switched Implants: A Clinical and Radiographic Study in Dogs. J Periodontol. 2017;88(11):1200-1210.
[23] VALLES C, RODRIGUEZ-CIURANA X, MUNOZ F, et al. Influence of implant neck surface and placement depth on crestal bone changes and soft tissue dimensions around platform-switched implants: A histologic study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(7):869-883.
[24] 栗兴超,董福生,李向军,等.不同颈部结构钛人工牙种植体的骨结合性能研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2017,31(3):129-132.
[25] WENG D, NAGATA M, LEITE CM, et al. Influence of microgap location and configuration on the periimplant bone morphology in submerged implants. An experimental study in dogs. Clin Oral Implan Res. 2010; 19(5):1141-1147.
[26] ROMANOS GE, AYDIN E, GAERTNER K, et al. Long-Term Results after Subcrestal or Crestal Placement of Delayed Loaded Implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17(1):133-141.
[27] ALOMRANI AN, HERMANN JS, JONES AA, et al. Influence of a machined collar on crestal bone changes around titanium implants: a histometric study in the canine mandible. Int J Oral Max Impl. 2005;20(5):677.
[28] HARTMAN GA, COCHRAN DL. Initial implant position determines the magnitude of crestal bone remodeling. J Periodontol. 2004;75(4):572-577.
[29] SCHWARZ F, HEGEWALD A, BECKER J. Impact of implant–abutment connection and positioning of the machined collar/microgap on crestal bone level changes: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implan Res. 2014;25(4):417-425.
[30] 高健,赵守亮,周成杰.种植体直径-长度比的三维有限元应力分析[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2014,24(5):364-369.
[31] 聂秀吉,李淑娴,马宗民,等.种植体不同设计参数对下颌骨牙齿种植的影响[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(6):890-895.
[32] 牛金磊,陈建宇,陈贤帅,等.种植体颈部微螺纹结构对种植稳定性影响的三维有限元分析[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2013,14(6):344-348.
[33] HAN A, TSOI J, RODRIGUES FP, et al. Bacterial adhesion mechanisms on dental implant surfaces and the influencing factors. Int J Adhes Adhe. 2016;69:58-71.
[34] 李彦.牙列缺损种植修复的咬合评估与设计[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2016,51(4):219-223.
[35] 陈江.咬合重建的点线面设计与种植风险防范[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2018,53(12):805-809.
|