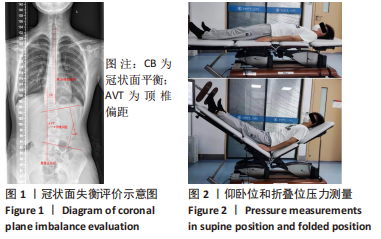
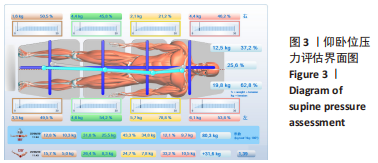
[1] CHENG JC, CASTELEIN RM, CHU WC, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15030.
[2] 儿童青少年脊柱弯曲异常防控技术指南编写组,马军. 《儿童青少年脊柱弯曲异常防控技术指南》解读[J]. 中国学校卫生,2022,43(2):165-170.
[3] LAW M, MA WK, LAU D, et al. Cumulative effective dose and cancer risk for pediatric population in repetitive full spine follow-up imaging: How micro dose is the EOS microdose protocol? Eur J Radiol. 2018;101:87-91.
[4] 中国青少年脊柱侧凸筛查临床实践指南及路径指引[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(23):1574-1582.
[5] FORTIN C, GRUNSTEIN E, LABELLE H, et al. Trunk imbalance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J. 2016;16(6):687-693.
[6] GRUNSTEIN E, FORTIN C, PARENT S, et al. Reliability and Validity of the Clinical Measurement of Trunk List in Children and Adolescents With Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2013;1(6): 419-424.
[7] 游国鹏,杜青,陈楠,等. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者步态运动学及足底压力特征分析[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2013,35(7):537-541.
[8] 陈梦婕,罗义,马琪超,等. 青少年特发性脊柱侧弯的冠状位平衡与足底压力的相关性[J]. 中华全科医学,2020,18(4):542-546.
[9] MA Q, LIN H, WANG L, et al. Correlation between spinal coronal balance and static baropodometry in children with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Gait Posture. 2020;75:93-97.
[10] HORNG J, LIU XC, THOMETZ J, et al. Evaluation of plantar pressures and center of pressure trajectories in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2021;280:131-135.
[11] LEE W, WON BH, CHO SW. Finite element modeling for predicting the contact pressure between a foam mattress and the human body in a supine position. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2017; 20(1):104-117.
[12] ZHAO Q, HUANG Y, WU M, et al. Study of Trunk Morphological Imbalance and Rehabilitation Outcome of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis with Intelligent Medicine. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022; 2022:6775674.
[13] 申韬. “筋骨调衡”手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床疗效及对后肌链张力效应影响[D]. 长沙:湖南中医药大学,2021.
[14] 邓剑平. 基于“柔筋、正骨、通经”理论探讨针推正脊法对LDH后表链肌张力的影响[D]. 长沙:湖南中医药大学,2019.
[15] 叶勇.“筋骨调衡”手法治疗CSA临床疗效及对后肌链生物力学效应研究[D]. 长沙:湖南中医药大学,2016.
[16] 叶勇,邵湘宁,汤伟,等. “筋骨调衡”结合经筋疗法对椎动脉型颈椎病患者角度肌张力与症状功能评分的影响[J]. 中医药导报,2016,22(11):52-54.
[17] PEREZ-MACHADO G, BERENGUER-PASCUAL E, BOVEA-MARCO M, et al. From genetics to epigenetics to unravel the etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Bone. 2020;140:115563.
[18] NEGRINI S, DONZELLI S, AULISA AG, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018; 13:3.
[19] FIDLER MW, JOWETT RL. Muscle imbalance in the aetiology of scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1976;58(2):200-201.
[20] VELDHUIZEN AG, WEVER DJ, WEBB PJ. The aetiology of idiopathic scoliosis: biomechanical and neuromuscular factors. Eur Spine J. 2000;9(3):178-184.
[21] 王帅,王连成,张书豪,等. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者凸凹侧椎旁肌肌电比值与Cobb角、顶椎偏距、冠状面平衡距离的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(9):1402-1406.
[22] Liu Y, Pan A, Hai Y, et al. Asymmetric biomechanical characteristics of the paravertebral muscle in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2019;65:81-86.
[23] Kotwicki T, Tomaszewski M, Andrusiewicz M, et al. Estrogen Receptor Type 1 and Type 2 Presence in Paravertebral Skeletal Muscles: Expression Level and Relation to Phenotype in Children with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(5):739.
[24] Shao X, Chen J, Yang J, et al. Fiber Type-Specific Morphological and Cellular Changes of Paraspinal Muscles in Patients with Severe Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e924415.
[25] Zapata KA, Wang-Price SS, Sucato DJ, et al. Ultrasonographic measurements of paraspinal muscle thickness in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a comparison and reliability study. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2015; 27(2):119-125.
[26] 潘爱星,海涌,刘玉增,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸椎旁肌肉生物力学属性评估[J].中华医学杂志,2018,98(43):3485-3489.
|