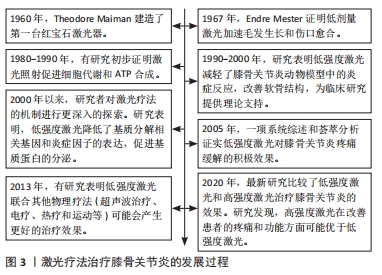
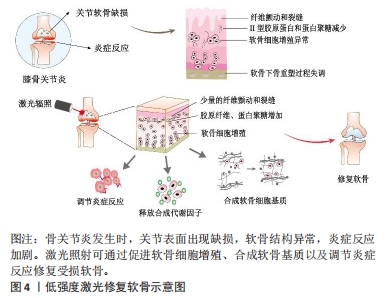
[1] HAWKER GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019; 37(Suppl 120):3-6.
[2] CUI A, LI H, WANG D, et al. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. E Clin Med. 2020; 29-30:100587.
[3] REN Y, HU J, TAN J, et al. Incidence and risk factors of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis among the Chinese population: analysis from a nationwide longitudinal study. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1491.
[4] LV Z, YANG YX, LI J, et al. Molecular Classification of Knee Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:725568.
[5] KAN HS, CHAN PK, CHIU KY, et al. Non-surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Hong Kong Med J. 2019;25(2):127-133.
[6] MAGNI A, AGOSTONI P, BONEZZI C, et al. Management of Osteoarthritis: Expert Opinion on NSAIDs. Pain Ther. 2021;10(2):783-808.
[7] FLYNN DM. Chronic musculoskeletal pain: nonpharmacologic, noninvasive treatments. Am Fam Physician. 2020;102(8):465-477.
[8] GANJEH S, REZAEIAN ZS, MOSTAMAND J. Low Level Laser Therapy in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Narrative Review. Adv Ther. 2020;37(8):3433-3449.
[9] HUANG YY, CHEN ACH, HAMBLIN MR. Low level laser and light therapy. Handbook of Biomedical Optics. 2016:771-814.
[10] CHOW R, LIEBERT A, TILLEY S, et al. Guidelines versus evidence: what we can learn from the Australian guideline for low-level laser therapy in knee osteoarthritis? A narrative review. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;36(2):249-258.
[11] WYSZYŃSKA J, BAL-BOCHEŃSKA M. Efficacy of High-Intensity Laser Therapy in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis: A First Systematic Review. Photomed Laser Surg. 2018;36(7):343-353.
[12] COLLINS NJ, HART HF, MILLS KAG. Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: rehabilitation and outcomes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(3):378-391.
[13] GEENEN R, OVERMAN CL, CHRISTENSEN R, et al. EULAR recommendations for the health professional’s approach to pain management in inflammatory arthritis and osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(6):797-807.
[14] ROMANOS GE. Laser Fundamental Principles. Adv Laser Sur in Dent. 2021: 3-11.
[15] MUSSTTAF RA, JENKINS DFL, JHA AN. Assessing the impact of low level laser therapy (LLLT) on biological systems: a review. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019; 95(2):120-143.
[16] MESTER A. Laser Biostimulation. Photomed Laser Surg. 2013;31(6):237-239.
[17] WHITE PF, ZAFEREO J, ELVIR-LAZO OL, et al. Treatment of drug-resistant fibromyalgia symptoms using high-intensity laser therapy: a case-based review. Rheumatol Int. 2017;38(3):517-523.
[18] HAWKINS D, ABRAHAMSE H. How Long After Laser Irradiation Should Cellular Responses be Measured to Determine the Laser Effect? J Laser Appl. 2007;19(2):74-83.
[19] AVCI P, GUPTA A, SADASIVAM M, et al. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: stimulating, healing, restoring. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013;32(1): 41-52.
[20] OHSHIRO T. A new effect-based classification of laser applications in surgery and medicine. Laser Therapy. 1996;8(4):233-239.
[21] SONG HJ, SEO HJ, KIM D. Effectiveness of high-intensity laser therapy in the management of patients with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2020;33(6):875-884.
[22] DA SILVA SERGIO LP, DE SOUZA DA FONSECA A, MENCALHA AL, et al. Photobiomodulation on extracellular matrix. Laser Physics. 2023;33(3): 033001.
[23] OLIVEIRA S, ANDRADE R, HINCKEL BB, et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Effects of Light Therapy on Cartilage Regeneration for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):1700S-1719S.
[24] CHEN JL, HSU CC, CHEN WCC, et al. Intra-Articular Laser Therapy May Be a Feasible Option in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis in Elderly Patients. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:1-8.
[25] PAOLILLO FR, PAOLILLO AR, JOÃO JP, et al. Ultrasound plus low-level laser therapy for knee osteoarthritis rehabilitation: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38(5):785-793.
[26] DE MATOS BRUNELLI BRAGHIN R, LIBARDI EC, JUNQUEIRA C, et al. The effect of low-level laser therapy and physical exercise on pain, stiffness, function, and spatiotemporal gait variables in subjects with bilateral knee osteoarthritis: a blind randomized clinical trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2018;41(26): 3165-3172.
[27] AHMAD MA, HAMID MS, YUSOF A. Effects of low-level and high-intensity laser therapy as adjunctive to rehabilitation exercise on pain, stiffness and function in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiotherapy. 2022;114:85-95.
[28] MOSTAFA MSEM, HAMADA HA, KADRY AM, et al. Effect of High-Power Laser Therapy Versus Shock Wave Therapy on Pain and Function in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2022;40(3):198-204.
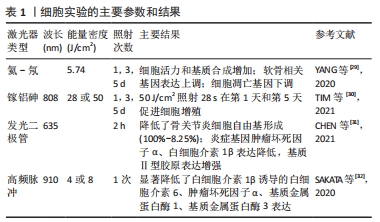
[29] YANG X, LIU TC, LIU S, et al. Promoted Viability and Differentiated Phenotype of Cultured Chondrocytes With Low Level Laser Irradiation Potentiate Efficacious Cells for Therapeutics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:468.
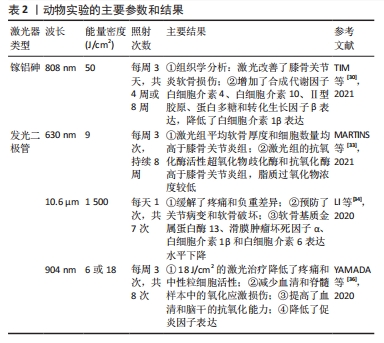
[30] TIM CR, MARTIGNAGO CCS, ASSIS L, et al. Effects of photobiomodulation therapy in chondrocyte response by in vitro experiments and experimental model of osteoarthritis in the knee of rats. Lasers Med Sci. 2021;37(3): 1677-1686.
[31] CHEN IC, SU CY, FANG CH, et al. Preventative treatment of red light-emitting diode protected osteoarthritis-like chondrocytes from oxidative stress-induced inflammation and promoted matrix gene expression. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2021;127:23-31.
[32] SAKATA S, KUNIMATSU R, TSUKA Y, et al. High-Frequency Near-Infrared Diode Laser Irradiation Attenuates IL-1β-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines and Matrix Metalloproteinases in Human Primary Chondrocytes. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):881.
[33] MARTINS LPO, SANTOS FFD, COSTA TED, et al. Photobiomodulation Therapy (Light-Emitting Diode 630 nm) Favored the Oxidative Stress and the Preservation of Articular Cartilage in an Induced Knee Osteoarthritis Model. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2021;39(4):272-279.
[34] LI Y, WU F, WEI J, et al. The Effects of Laser Moxibustion on Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Rats. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2020; 38(1):43-50.
[35] NAMBI G. Does low level laser therapy has effects on inflammatory biomarkers IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-13 in osteoarthritis of rat models—a systemic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;36(3):475-484.
[36] YAMADA EF, BOBINSKI F, MARTINS DF, et al. Photobiomodulation therapy in knee osteoarthritis reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in rats. J Biophotonics. 2020;13(1):e201900204.
[37] LI Y, WU F, LAO L, et al. Laser irradiation activates spinal adenosine A1 receptor to alleviate osteoarthritis pain in monosodium iodoacetate injected rats. J Integr Neurosci. 2020;19(2):295-302.
[38] ASSIS L, TIM C, MAGRI A, et al. Interleukin-10 and collagen type II immunoexpression are modulated by photobiomodulation associated to aerobic and aquatic exercises in an experimental model of osteoarthritis. Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(9):1875-1882.
[39] SANCHES M, ASSIS L, CRINITI C, et al. Chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate associated to photobiomodulation prevents degenerative morphological changes in an experimental model of osteoarthritis in rats. Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(3):549-557.
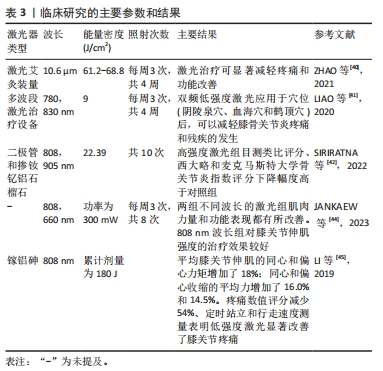
[40] ZHAO L, CHENG K, WU F, et al. Effect of laser moxibustion for knee osteoarthritis: a multisite, double-blind randomized controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 2021;48(6):924-932.
[41] LIAO FY, LIN CL, LO SF, et al. Efficacy of Acupoints Dual-Frequency Low-Level Laser Therapy on Knee Osteoarthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:6979105.
[42] SIRIRATNA P, RATANASUTIRANONT C, MANISSORN T, et al. Short-Term Efficacy of High-Intensity Laser Therapy in Alleviating Pain in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Single-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial. Pain Res Manag. 2022;2022:1319165.
[43] EKICI B, ORDAHAN B. Evaluation of the effect of high-intensity laser therapy (HILT) on function, muscle strength, range of motion, pain level, and femoral cartilage thickness in knee osteoarthritis: randomized controlled study. Lasers Med Sci. 2023;38(1):218.
[44] JANKAEW A, YOU YL, YANG TH, et al. The effects of low-level laser therapy on muscle strength and functional outcomes in individuals with knee osteoarthritis: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1):165.
[45] LI CF, CHEN YJ, LIN TY, et al. Immediate responses of multi‐focal low level laser therapy on quadriceps in knee osteoarthritis patients. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019;35(11):702-707.
[46] STAUSHOLM MB, NATERSTAD IF, COUPPÉ C, et al. Effectiveness of Low-Level Laser Therapy Associated with Strength Training in Knee Osteoarthritis: Protocol for a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Methods Protoc. 2021;4(1):19.
[47] ROBBINS SR, ALFREDO PP, JUNIOR WS, et al. Low-level laser therapy and static stretching exercises for patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomised controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2022;36(2):204-213.
[48] KHOLVADIA A, CONSTANTINOU D, GRADIDGE PJ. Exploring the efficacy of low-level laser therapy and exercise for knee osteoarthritis. S Afr J Sports Med. 2019;31(1):v31i1a6058.
[49] STAUSHOLM MB, NATERSTAD IF, JOENSEN J, et al. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2019;9(10):e031142.
[50] AHMAD MA, MOGANAN M, HAMID MSA, et al. Comparison Between Low-Level and High-Intensity Laser Therapy as An Adjunctive Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial. Life (Basel). 2023;13(7):1519.
[51] WU M, LUAN L, PRANATA A, et al. Is high intensity laser therapy more effective than other physical therapy modalities for treating knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:956188.
[52] MIGLIARIO M, SABBATINI M, MORTELLARO C, et al. Near infrared low‐level laser therapy and cell proliferation: The emerging role of redox sensitive signal transduction pathways. J Biophotonics. 2018;11(11):e201800025.
[53] MONICI M, CIALDAI F, FUSI F, et al. Effects of pulsed Nd: YAG laser at molecular and cellular level. A study on the basis of Hilterapia. Energy Health. 2008;3:27-33.
[54] DOMPE C, MONCRIEFF L, MATYS J, et al. Photobiomodulation—Underlying Mechanism and Clinical Applications. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1724.
[55] HAMBLIN MR, CARROLL JD, ARANY P, et al. Photo-excitation of electrons in cytochrome c oxidase as a theory of the mechanism of the increase of ATP production in mitochondria by laser therapy. Mech Low Light Ther. 2014;8932:26-31.
[56] AMAROLI A, PASQUALE C, ZEKIY A, et al. Photobiomodulation and Oxidative Stress: 980 nm Diode Laser Light Regulates Mitochondrial Activity and Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:6626286.
[57] WANG Y, HUANG YY, WANG Y, et al. Red (660 nm) or near-infrared (810 nm) photobiomodulation stimulates, while blue (415 nm), green (540 nm) light inhibits proliferation in human adipose-derived stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7781.
[58] LAZAROWSKI ER, BOUCHER RC, HARDEN TK. Mechanisms of release of nucleotides and integration of their action as P2X-and P2Y-receptor activating molecules. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64(4):785-795.
[59] ROKIC M, CASTRO P, LEIVA-SALCEDO E, et al. Opposing Roles of Calcium and Intracellular ATP on Gating of the Purinergic P2X2 Receptor Channel. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1161.
[60] DE LA ROSA G, GóMEZ AI, BAÑOS MC, et al. Signaling Through Purinergic Receptor P2Y2 Enhances Macrophage IL-1β Production. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(13):4686.
[61] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89: 1252-1261.
[62] CHEN H, TAN XN, HU S, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Chondrocyte Proliferation and Differentiation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:664168.
[63] LU C, LI Y, HU S, et al. Scoparone prevents IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes through the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;106:1169-1174.
[64] JERE SW, HOURELD NN. Regulatory Processes of the Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway and Photobiomodulation in Diabetic Wound Repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(8):4210.
[65] KIM JE, WOO YJ, SOHN KM, et al. Wnt/β‐catenin and ERK pathway activation: A possible mechanism of photobiomodulation therapy with light‐emitting diodes that regulate the proliferation of human outer root sheath cells. Lasers Surg Med. 2017;49(10):940-947.
[66] LI K, LIANG Z, ZHANG J, et al. Attenuation of the inflammatory response and polarization of macrophages by photobiomodulation. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;35(7):1509-1518.
[67] ESCHWEILER J, HORN N, RATH B, et al. The Biomechanics of Cartilage—An Overview. Life (Basel). 2021;11(4):302.
[68] THOMSEN S. Pathologic Analysis of Photothermal and Photomechanical Effects of Laser–Tissue Interactions. Photochem Photobiol. 1991;53(6): 825-835.
[69] ALEXANDROVSKAYA YM, BAUM OI, SHEKHTER AB, et al. Mechanisms of laser activation of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis healing. Laser Physics Letters. 2018;15(8):085601.
[70] SOBOL E, BAUM O, SHEKHTER A, et al. Laser-induced micropore formation and modification of cartilage structure in osteoarthritis healing. J Biomed Opt. 2017;22(9):91515. |