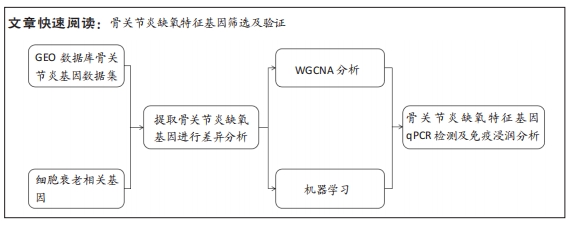
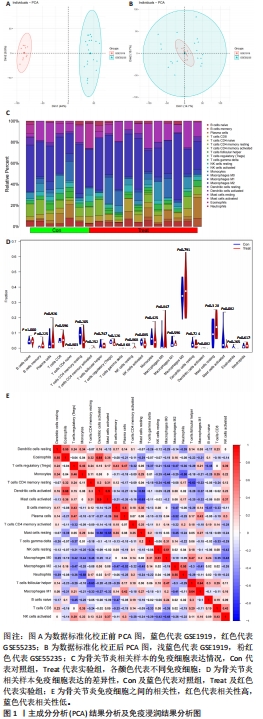
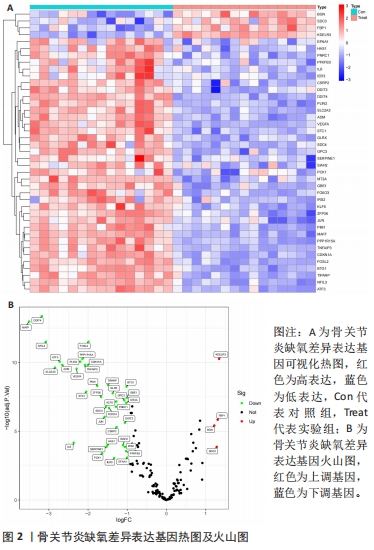
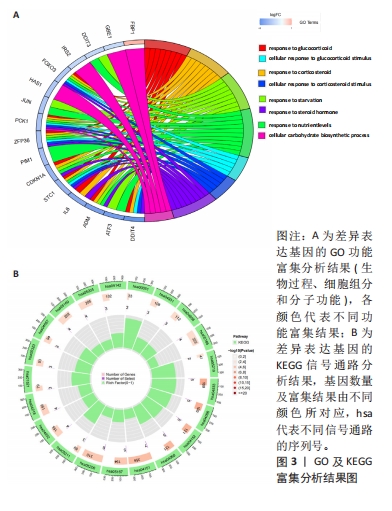
[1] TANG X, WANG S, ZHAN S, et al. The prevalence of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in china: results from the china health and retirement longitu dinal study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(3):648-653.
[2] CHARLIER E, DEROYER C, CIREGIA F, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Bioc hem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49-65.
[3] LEE JW, KO J, JU C, et al. Hypoxia signaling in human diseases and therapeutic targets. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(6):1-13.
[4] HENROTIN Y, KURZ B, AIGNER T. Oxygen and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: friends or foes? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(8): 643-654.
[5] CAMACHO DM, COLLINS KM, POWERS RK, et al. Next-Generation Machine Learning for Biological Networks. Cell. 2018;173(7):1581-1592.
[6] JAMSHIDI A, PELLETIER JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J. Machine-learning-based patient-specific prediction models for knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(1):49-60.
[7] LU K, WEI S, WANG Z, et al. Identification of novel biomarkers in Hunner’s interstitial cystitis using the CIBERSORT, an algorithm based on machine learning. BMC Urol. 2021;21(1):109.
[8] CHEN L, ZHANG YH, WANG S, et al. Prediction and analysis of essential genes using the enrichments of gene ontology and KEGG pathways. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0184129.
[9] KANEHISA M, FURUMICHI M, TANABE M, et al. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(1): 353-361.
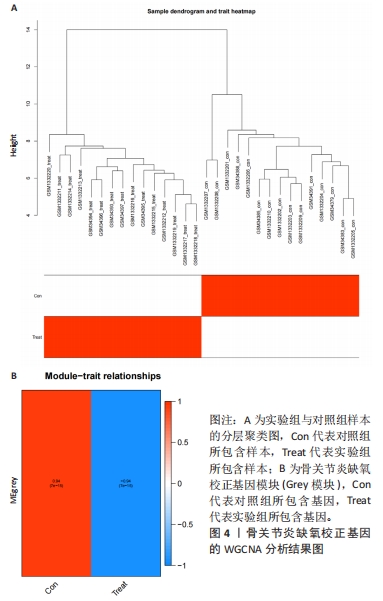
[10] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559.
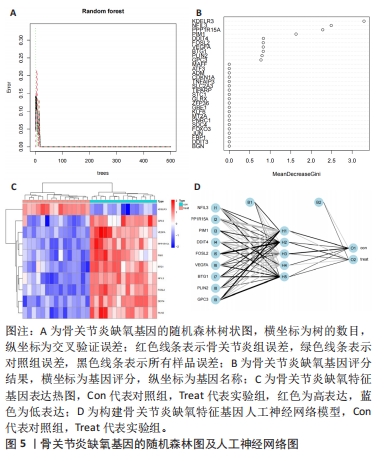
[11] CHEN X, ISHWARAN H. Random forests for genomic data analysis. Genomics. 2012;99(6):323-329.
[12] ZOU J, HAN Y, SO SS. Overview of artificial neural networks. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;458:15-23.
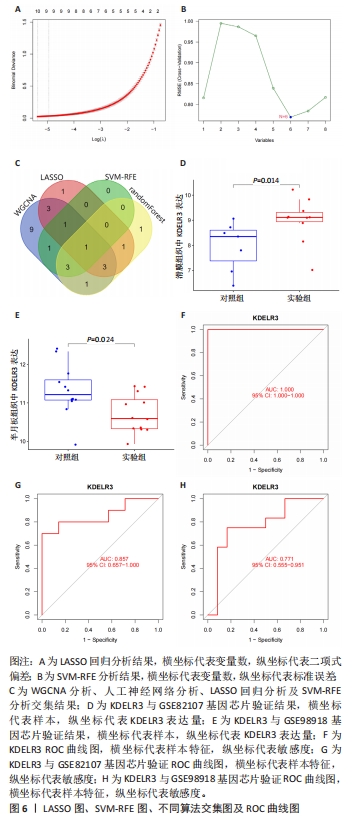
[13] LI Z, SILLANPAA MJ. Overview of LASSO-related penalized regression methods for quantitative trait mapping and genomic selection. Theor Appl Genet. 2012;125(3):419-435.
[14] GAO J, KWAN PW, SHI D. Sparse kernel learning with LASSO and Bayesian inference algorithm. Neural Netw. 2010;23(2):257-264.
[15] CHEN D, SHEN J, ZHAO W, et al. Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res. 2017;5:16044.
[16] OO WM. Prospects of disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs. Clin Geriatr Med. 2022;38(2):397-432.
[17] WONG BW, MARSCH E, TREPS L, et al. Endothelial cell metabolism in health and disease: impact of hypoxia. EMBO J. 2017;36(15):2187-2203.
[18] PFANDER D, CRAMER T, SWOBODA B. Hypoxia and HIF-1alpha in osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2005;29(1):6-9.
[19] YUDOH K, NAKAMURA H, MASUKO-HONGO K, et al. Catabolic stress induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha in articular chondrocytes: involvement of HIF-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):904-914.
[20] MARKWAY BD, CHO H, JOHNSTONE B. Hypoxia promotes redifferentiation and suppresses markers of hypertrophy and degeneration in both healthy and osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(4):92.
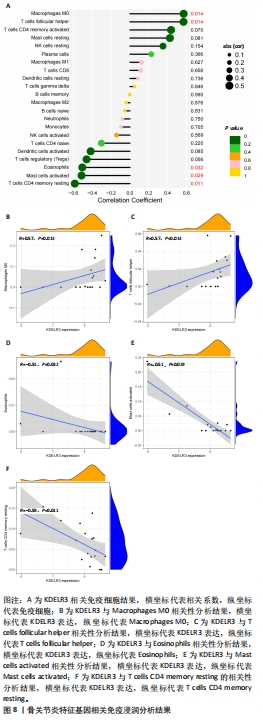
[21] WU CL, HARASYMOWICZ NS, KLIMAK MA, et al. The role of macrophages in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5): 544-554.
[22] ZHANG H, CAI D, BAI X. Macrophages regulate the progression of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):555-561.
[23] CARDAMONE C, PARENTE R, FEO GD, et al. Mast cells as effector cells of innate immunity and regulators of adaptive immunity. Immunol Lett. 2016;178:10-14.
[24] SAVVIDOU O, MILONAKI M, GOUMENOS S, et al. Glucocorticoid signaling and osteoarthritis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019;480:153-166.
[25] MATSUZAKI T, ALVAREZ-GARCIA O, MOKUDA S, et al. FoxO transcription factors modulate autophagy and proteoglycan 4 in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(428):eaan0746.
[26] LIN C, SHAO Y, ZENG C, et al. Blocking PI3K/AKT signaling inhibits bone sclerosis in subchondral bone and attenuates post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(8):6135-6147.
[27] TRYCHTA KA, BACK S, HENDERSON MJ, et al. KDEL receptors are differentially regulated to maintain the er proteome under calcium deficiency. Cell Rep. 2018;25(7):1829-1840.
[28] SCHWARZ DS, BLOWER MD. The endoplasmic reticulum: structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(1):79-94.
[29] OAKES SA, PAPA FR. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol. 2015;10:173-194.
[30] TAKADA K, HIROSE J, SENBA K, et al. Enhanced apoptotic and reduced protective response in chondrocytes following endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritic cartilage. Int J Exp Pathol. 2011;92(4):232-242.
[31] RELLMANN Y, EIDHOF E, DREIER R. Review: ER stress-induced cell death in osteoarthritic cartilage. Cell Signal. 2021;78:109880.
[32] KANG M, HUANG CC, LU Y, et al. Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone. 2020;141:115627.
[33] SHAN Y, QI C, LIU Y, et al. Increased frequency of peripheral blood follicular helper T cells and elevated serum IL21 levels in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(3):1095-1102.
[34] RAGIPOGLU D, DUDECK A, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M, et al. The role of mast cells in bone metabolism and bone disorders. Front Immunol. 2020;11:163.
|