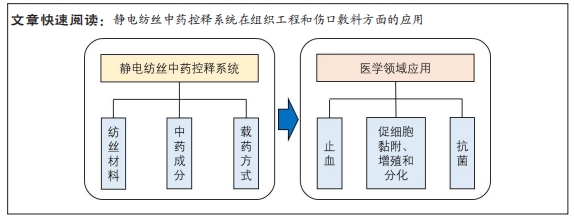
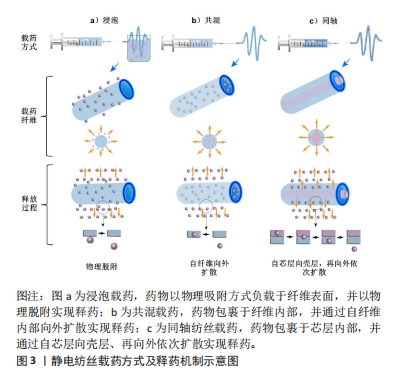
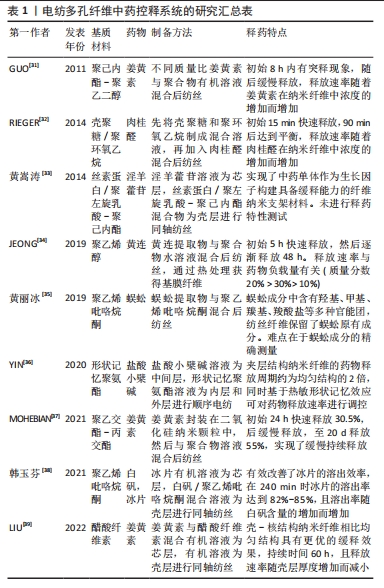
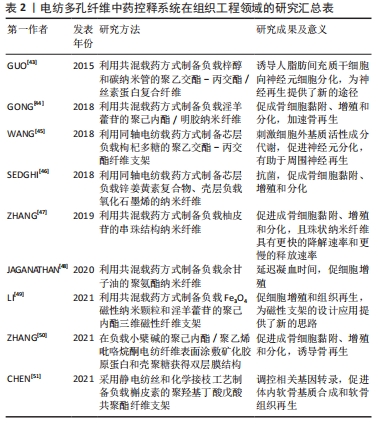
[1] WANG WY, ZHOU H, WANG YF, et al. Current policies and measures on the development of traditional Chinese medicine in China. Pharmacol Res. 2021;163:105187.
[2] WANG RN, ZHAO HC, HUANG JY, et al. Challenges and strategies in progress of drug delivery system for traditional Chinese medicine Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma (Danshen). Chin Herb Med. 2021;13(1): 78-89.
[3] GAO F, HU Y, FANG G, et al. Recent developments in the field of the determination of constituents of TCMs in body fluids of animals and human. J Pharmaceut Biomed. 2014;87:241-260.
[4] PARK H, OTTE A, PARK K. Evolution of drug delivery systems: from 1950 to 2020 and beyond. J Control Release. 2022;342:53-65.
[5] ADEPU S, RAMAKRISHNA S. Controlled drug delivery systems: current status and future directions. Molecules. 2021;26(19):5905.
[6] GORAIN B, PANDEY M, LENG NH, et al. Advanced drug delivery systems containing herbal components for wound healing. Int J Pharm. 2022;617: 121617.
[7] KAPAHI H, KHAN NM, BHARDWAJ A, et al. Implication of nanofibers in oral drug delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(15):2021-2036.
[8] 高仓健,杨振,刘舒云,等.静电纺丝技术在肩袖损伤修复中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):637-642.
[9] LI WJ, LAURENCIN CT, CATERSON EJ, et al. Electrospun nanofibrous structure: a novel scaffold for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;60(4):613-621.
[10] LIU X, YANG Y, YU D, et al. Tunable zero-order drug delivery systems created by modified triaxial electrospinning. Chem Eng J. 2019;356:886-894.
[11] HAN D, YU X, CHAI Q, et al. Stimuli-responsive self-immolative polymer nanofiber membranes formed by coaxial electrospinning. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(13):11858-11865.
[12] 李伟铭,于强,徐保利,等.中药缓控释制剂研究进展[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2023,21(1):200-203.
[13] 邹翔,宫甜,朱室儒,等.五味子总木脂素胃漂浮片的制备及质量评价[J].中国药房,2020,31(11):1336-1341.
[14] 耿燕娜,娄婷婷,武毅君,等.杜仲漂浮型脉冲释药片的研制[J].中国药业,2020,29(7):82-86.
[15] WONG PT, CHOI SK. Mechanisms of drug release in nanotherapeutic delivery systems. Chem Rev. 2015;115(9):3388-3432.
[16] 毕玉杰,马笃军,彭力平,等.中医药联合医用水凝胶治疗疾病的策略及意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(3):419-425.
[17] HE Q, ZHANG J, LIAO Y, et al. Current advances in microsphere based cell culture and tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;39:107459.
[18] GANESH KR, RAJAN TP. A review on electrospinning of natural bio herbs blended with polyvinyl alcohol nanofibres for biomedical applications. J Nat Fibers. 2022;19(15):11984-12003.
[19] 谢晓峰,周寒璞,赵聪,等.中药白芨/聚乙烯醇纳米静电纺丝膜的制备和生物相容性评价[J].肝胆胰外科杂志,2020,32(10):619-623.
[20] TAN G, WANG L, PAN W, et al. Polysaccharide electrospun nanofibers for wound healing applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:3913-43931.
[21] CHEN K, LI Y, LI Y, et al. Silk fibroin combined with electrospinning as a promising strategy for tissue regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(2): 2200380.
[22] CAO P, WU G, YAO Z, et al. Effects of amylose and amylopectin molecular structures on starch electrospinning. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;296(15): 119959.
[23] YANG Q, GUO J, ZHANG S, et al. PVA/PEO/PVA-g-APEG nanofiber membranes with cytocompatibility and anti-cell adhesion for biomedical applications. Colloids Surf A. 2023;657:130638.
[24] HUANG J, ZHOU X, SHEN Y, et al. Asiaticoside loading into polylactic-co-glycolic acid electrospun nanofibers attenuates host inflammatory response and promotes M2 macrophage polarization. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020; 108(1):69-80.
[25] ZHAO XH, NIU YN, MI CH, et al. Electrospinning nanofibers of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates for applications in medical tissue engineering. J Polym Sci. 2021;59(18):1994-2013.
[26] JI X, GUO J, GUAN F, et al. Preparation of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/nanocellulose composite film and evaluation of its biomedical performance. Gels. 2021;7(4):223.
[27] ALIMOHAMMADI M, FAKHRAEI O, MORADI A, et al. Controlled release of azithromycin from polycaprolactone/chitosan nanofibrous membranes. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 2023;71:103246.
[28] 崔志香,司军辉,宋来瑞,等.聚乙烯醇/壳聚糖复合纳米纤维载药体系制备及释药性能[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2015,31(8):185-190.
[29] CHENG H, YANG X, CHE X, et al. Biomedical application and controlled drug release of electrospun fibrous materials. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018;90:750-763.
[30] 马玥珑,李佳,王虹.静电纺丝制备载药纳米纤维的研究进展[J].哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2021,26(5):130-140.
[31] GUO G, FU S, ZHOU L, et al. Preparation of curcumin loaded poly (ε-caprolactone)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers and their in vitro antitumor activity against glioma 9L cells. Nanoscale. 2011;3(9):3825-3832.
[32] RIEGER K, SCHIFFMAN J. Electrospinning an essential oil: cinnamaldehyde enhances the antimicrobial efficacy of chitosan/poly (ethylene oxide) nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;113:561-568.
[33] 黄嵩涛,王红,张忠芮,等.静电纺丝素/胶原/聚合物复合纤维的制备及其力学性能的研究[J].高分子通报,2014;27(6):101-106.
[34] JEONG J, LEE S. Electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membranes containing coptidis rhizoma extracts for potential biomedical applications. Text Res J. 2019;89(17):3506-3518.
[35] 黄丽冰,徐玉龙,曹宽,等.含中药蜈蚣成分超细纤维的制备[J].纺织导报,2019(1):63-66.
[36] YIN X, TAN P, LUO H, et al. Study on the release behaviors of berberine hydrochloride based on sandwich nanostructure and shape memory effect. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;109:110541.
[37] MOHEBIAN Z, BABAZADEH M, ZARGHAMI N, et al. Anticancer efficiency of curcumin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles/nanofiber composites for potential postsurgical breast cancer treatment. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 2021;61:102170.
[38] 韩玉芬.负载中药“核壳”结构纳米纤维的制备及性能研究[D].北京:北京化工大学,2021.
[39] LIU Y, CHEN X, GAO Y, et al. Electrospun core-sheath nanofibers with variable shell thickness for modifying curcumin release to achieve a better antibacterial performance. Biomolecules. 2022;12(8):1057.
[40] SABRA S, RAGAB DM, AGWA MM, et al. Recent advances in electrospun nanofibers for some biomedical applications. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020;144: 105224.
[41] LI D, YUAN T, ZHANG X, et al. Icariin: a potential promoting compound for cartilage tissue engineering. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1647-1656.
[42] 陈微.中药有效成分功能化改性软骨组织工程支架的制备及性能研究[D].长沙:湖南大学,2021.
[43] GUO JH, LIU Y, LV ZJ, et al. Potential neurogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells on electrospun catalpol-loaded composite nanofibrous scaffolds. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(10):2597-2608.
[44] GONG M, CHI C, YE J, et al. Icariin-loaded electrospun PCL/gelatin nanofiber membrane as potential artificial periosteum. Colloids Surf B. 2018;170: 201-209.
[45] WANG J, TIAN L, HE L, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide encapsulated Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid Nanofibers: cost effective herbal medicine for potential application in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8669.
[46] SEDGHI R, SAYYARI N, SHAABANI A, et al. Novel biocompatible zinc-curcumin loaded coaxial nanofibers for bone tissue engineering application. Polymer. 2018;142:244-255.
[47] ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, WATTS D, et al. Electrospun naringin-loaded beaded nanofiber with controlled release property for bone tissue engineering applications. Sci Adv Mater. 2019;11(10):1433-1442.
[48] JAGANATHAN SK, MANI MP. Electrospun novel nanocomposite comprising polyurethane integrated with ayurveda amla oil for bone tissue engineering. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2020;92(1):e20180369.
[49] LI K, ZHANG Y, XU J, et al. Three-dimensional magnetic fibrous scaffold with icariin expanded by supercritical CO2 for bone tissue engineering under static magnetic field. Compos B Eng. 2021;226:109304.
[50] ZHANG Y, WANG T, LI J, et al. Bilayer membrane composed of mineralized collagen and chitosan cast film coated with berberine-loaded PCL/PVP electrospun nanofiber promotes bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:684335.
[51] CHEN W, LI Y, HUANG Y, et al. Quercetin modified electrospun PHBV fibrous scaffold enhances cartilage regeneration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(8):92.
[52] 陈晨,李永圆,王海霞,等.制剂技术在提高中药抗菌活性方面的应用及前景分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(7):247-253.
[53] PEDRAM RZ, MOKHTARI J, ABBASI M. Calendula officinalis extract/PCL/Zein/Gum arabic nanofibrous bio-composite scaffolds via suspension, two-nozzle and multilayer electrospinning for skin tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;135:530-543.
[54] YUE Y, LIU X, PANG L, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides/PVA nanofiber membranes containing astragaloside IV-loaded liposomes and their potential use for wound healing. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2022;2022:9716271.
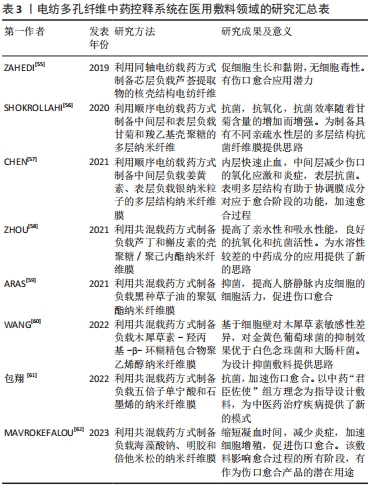
[55] ZAHEDI E, ESMAEILI A, ESLAHI N, et al. Fabrication and characterization of core-Shell electrospun fibrous mats containing medicinal herbs for wound healing and skin tissue engineering. Mar Drugs. 2019;17(1):27.
[56] SHOKROLLAHI M, BAHRAMI SH, NAZARPAK MH, et al. Multilayer nanofibrous patch comprising chamomile loaded carboxyethyl chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) and polycaprolactone as a potential wound dressing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;147:547-559.
[57] CHEN K, PAN H, JI D, et al. Curcumin-loaded sandwich-like nanofibrous membrane prepared by electrospinning technology as wound dressing for accelerate wound healing. Mater Sci Eng C. 2021;127:112245.
[58] ZHOU L, CAI L, RUAN H, et al. Electrospun chitosan oligosaccharide/polycaprolactone nanofibers loaded with wound-healing compounds of Rutin and Quercetin as antibacterial dressings. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;183:1145-1154.
[59] ARAS C, TÜMAY ÖZER E, GÖKTALAY G, et al. Evaluation of nigella sativa oil loaded electrospun polyurethane nanofibrous mat as wound dressing. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021;32(13):1718-1735.
[60] WANG X, HU X, LI S, et al. Preparation of antibacterial nanofibers by electrospinning polyvinyl alcohol containing a luteolin hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. New J Chem. 2022;46(5):2360-2367.
[61] 包翔.具有抗氧化活性的新型中药复合纳米材料促进创伤修复的应用研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2022.
[62] MAVROKEFALOU E, MONOU PK, TZETZIS D, et al. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of electrospun sodium alginate fiber films for wound healing applications. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 2023;81:104298. |