中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (15): 2416-2422.doi: 10.12307/2024.387
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
生物医用支架仿生设计及在组织工程中的应用
梁 辰,朱同贺,朱忆尧,李瑞芝
- 上海工程技术大学化学化工学院,上海市 201620
-
收稿日期:2023-04-12接受日期:2023-07-08出版日期:2024-05-28发布日期:2023-09-23 -
通讯作者:朱同贺,副教授,上海工程技术大学化学化工学院,上海市 201620 -
作者简介:梁辰,男,2000年生,河南省安阳市人,汉族,在读硕士,主要从事生物功能材料方面的研究。
Biomimetic design of biomedical scaffolds and their application in tissue engineering
Liang Chen, Zhu Tonghe, Zhu Yiyao, Li Ruizhi
- School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China
-
Received:2023-04-12Accepted:2023-07-08Online:2024-05-28Published:2023-09-23 -
Contact:Zhu Tonghe, Associate professor, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China -
About author:Liang Chen, Master candidate, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China
摘要:
文题释义:
生物医用支架:将工程学、仿生学及再生医学等原理进行结合,通过组织工程技术使用生物活性材料构建而成的一类支架,是临床用于治疗大面积组织损伤、缺损及坏死的方法之一,有望作为自体移植或异体移植的最佳代替治疗手段之一。仿生设计:通过生物材料类型的选择、合理成型加工技术的使用、精准可控的结构的设计,并根据细胞生物学、细胞力学等理论,仿生真实细胞外基质微环境对生物医用支架进行设计。
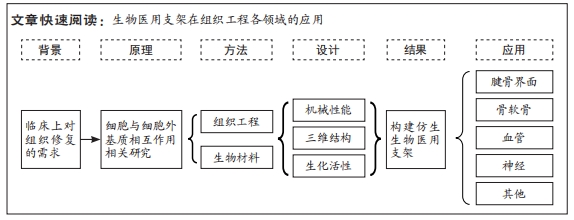
背景:基于解剖学对生物组织功能与结构的认识,对于具有恢复、维持或改善组织功能的生物活性材料仿生设计是目前再生医学领域研究的热点。
目的:从生物医用支架的机械性能、三维空间结构和生化活性对细胞行为的影响进行讨论,并综述生物医用支架在组织工程领域的应用。方法:应用计算机检索中国知网、万方、Web of Science、PubMed数据库2003年1月至2023年4月发表的文献,中文检索词为“细胞外基质,组织工程,支架,生物材料,仿生结构,机械性能,三维结构,腱骨界面,骨软骨,神经导管,人造血管;英文检索词为“extracellular matrix,tissue engineering, scaffolds,biomimetic structures,biomaterials,tendon bone interfaces,osteochondral,neural conduits,artificial blood vessels”。
结果与结论:细胞处在一个复杂且动态变化的三维环境中,因此细胞外基质是生物材料模拟的最终目标,在设计生物医用支架的仿生结构时需要与其所处真实的微环境相似,让细胞可以正常地贴壁、生长和迁移,并保持其多样的生理功能。生物医用支架在机械性能、三维空间结构以及生物化学性质方面对细胞外基质的仿生设计可以对组织修复过程中的细胞起到决定性作用,从而影响组织修复最后的结果。进行仿生设计的生物医用支架在腱骨界面、骨软骨界面、神经、血管再生等领域已有广泛的应用,在临床上提供了一个有前途的新思路。
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-7031-4963(梁辰)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
梁 辰, 朱同贺, 朱忆尧, 李瑞芝. 生物医用支架仿生设计及在组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(15): 2416-2422.
Liang Chen, Zhu Tonghe, Zhu Yiyao, Li Ruizhi. Biomimetic design of biomedical scaffolds and their application in tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2416-2422.
2.1.1 细胞与细胞外基质 细胞是构成生命体的基本单位,当组织受到损伤时细胞会通过一系列的生理活动对受损组织进行修复[7],只有在一个适宜细胞进行一系列生理活动的场所——细胞外基质中,细胞才能以最快速、最精确、最合适的方式对组织进行修复[8]。细胞外基质是由多种蛋白、蛋白聚糖和糖胺聚糖等构成一个具有三维结构复杂的动态结构[9](表1)。基本上所有类型的细胞在多种信号的控制和调节下都会自发合成和分泌基质大分子,从而参与细胞外基质的形成[10];而同时细胞外基质提供的信号如趋化因子等和机械信号等一同被嵌入细胞外基质中的细胞,通过表面受体(例如整合素、盘状结构域受体、细胞表面蛋白聚糖以及透明质酸受体CD44等)整合,进而反过来影响生长、迁移、分化、存活、保持稳态以及形态改变等细胞过程[9]。

对于范围小、深度浅的组织损伤,以往生物材料只需要满足生物相容性的要求就可以对组织修复带来不错的效果。已经有许多研究表明当面对长程、大面积的组织缺损时,在满足生物相容性的同时,生物医用支架对于细胞外基质的仿生设计包括机械性能、三维空间结构及生化活性等在组织修复过程中同样起到决定性作用[17]。
2.1.2 组织工程与生物材料 组织工程在1980年代后期被定义为一个新兴的跨学科领域,是将工程和生命科学原理相结合以开发生物替代品用于恢复、维持或改善组织功能的一项技术[18]。经典组织工程的要素是细胞、生物材料支架及生物活性因子[19]。通过组织工程技术的原理,生物医用支架对所需修复的目标组织细胞所在微环境进行模拟,最终达到恢复、维持或改善组织功能的目的。
目前组织工程中用于构建生物医用支架的材料基本分为两大类:天然材料和人工合成的聚合物材料。天然材料一般由天然的动植物以及微生物中提取而来,或者是经过纯化的单个细胞外基质组分加工而成,具有优异的生物活性,但机械强度相对难以调控[20]。合成材料的性能如机械强度及降解性能均可控易调,但难以促进细胞黏附和增殖以及体内降解时不可避免地产生酸性降解产物。因此,目前在对生物医用支架的构建中常常采用天然与合成材料相结合的方法进行设计[21-22],譬如将天然材料与合成材料进行复合改性,通过嵌段共聚[23]、接枝共聚[24]、点击化学等方法在合成材料上引入仿生天然细胞外基质成分的化学基团及生物活性位点来对合成材料进行仿生改性[25-26]。
2.2 生物医用支架的仿生设计 细胞处在一个复杂且动态变化的三维环境中,因此细胞外基质是生物材料模拟的最终目标[27],在设计生物医用支架的仿生结构时需要与其所处真实的微环境相似,让细胞可以正常的贴壁、生长和迁移并保持其多样的生理功能。从根本上来说,机械性能、三维空间结构和生化特性(包括配体与生长因子的修饰)基本代表了细胞可以接受的来自细胞外基质的3类影响因素,并且起到了决定性作用。
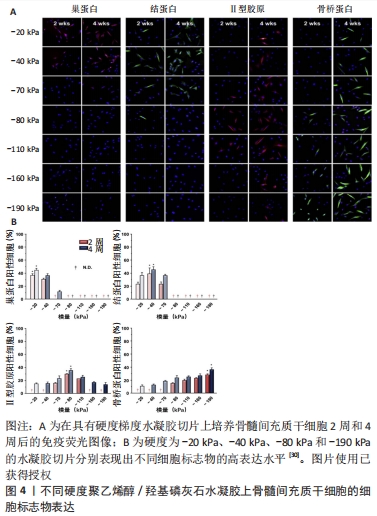
2.2.1 生物医用支架的机械性能 不同生物组织由于功能不同有着不同的弹性与刚度。有研究表明,基底刚度对骨髓间充质干细胞的分化有着决定性影响[28-29],当基底刚度为20 kPa时,观察到骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化;当基底刚度为40 kPa时,利于骨髓间充质干细胞的肌腱分化;当基底刚度为80 kPa时,则适合骨髓间充质干细胞的软骨分化;相比之下,刚度为190 kPa的基底使骨髓间充质干细胞呈现出典型的骨细胞形态(图4)[30]。此外,有些组织的硬度是处在动态变化过程中,比如在伤口愈合及疾病发展的过程中[31]。生物医用支架表面硬度对细胞的黏附和肌动蛋白细胞骨架的重排起重要作用[32]。由此,细胞骨架重排后的一些行为,如形貌的改变、位置的迁移以及生长也都受生物医用支架表面硬度的影响[33]。当植入材料的力学性能与原有组织的力学性能不匹配时,会造成由于力学失衡而引起的瘢痕效应及结缔组织增生。
PREVITERA等[34]在软硬不同的凝胶上培养原代混合海马神经元培养物,发现生长在较硬质基底上的神经元显示出了更明显的分枝。CHEN等[35]研究了基质硬度对内皮细胞和单核细胞迁移及黏附的影响,发现相较20 kPa的基质,在较软(8 kPa)或较硬(40 kPa)基质上培养的内皮细胞对单核细胞有着更大的趋化作用。XIE等[36]调控基底材料聚二甲基硅氧烷的硬度,分别将脂肪基质细胞接种在上面,培养3 d后观察到细胞形态的变化,在硬质基底上的脂肪基质细胞表现出更大的铺展面积、细胞的纤毛也更多更长;通过表征脂肪基质细胞中微丝和微管的分布观察了细胞骨架变化,发现相较于在软质底物上,在硬质底物上微丝与微管的表达都要更强且细胞扩散的面积更大。
光硬度是生物医用支架影响细胞行为的因素,其他的机械特性包括其机械拉伸力、受力方向、压力等也影响着细胞的行为。GRIER等[37]将人间充质干细胞在一种胶原-糖胺聚糖支架上进行培养,培养6 d且每6 h进行一次持续10 min的循环拉伸应变,实验结果表明循环拉伸应变的应用显著上调了肌腱特异性细胞外基质蛋白和表型标记物的表达,同时促进了Samd2/3的磷酸化表达,表明张力刺激与转化生长因子β家族生长因子的产生存在联系。CORBIN等[38]将磁性物质夹杂到软质的聚二甲基硅氧烷弹性体中,制造了一种通过调节磁性梯度在种植细胞的情况下可实现立刻变硬的基材,用来研究动态硬度变化对细胞行为的影响,证明了底物硬度变化对人源心肌细胞和心脏成纤维细胞的影响,具有形态学、成熟性和基因表达变化。RITTER等[39]发现通过机械拉伸后,人牙周韧带成纤维细胞中分配给核因子κB和凋亡途径的基因表达升高,包括白细胞介素1β的相对基因表达高出 5.8 倍,核因子κB的相对基因表达高出1.7 倍,Bad的相对基因表达高出5.2 倍,CRADD 的相对基因表达高出 2.1 倍, Fas的相对基因表达高出 2.0倍。CHAN等[40]通过运用小鼠的囊胚来模拟充液腔,实验表明管腔内的压力大小的变化会对外胚层细胞的分裂行为产生一定的影响,从而改变细胞的命运。MANOKAWINCHOKE等[41]通过分析全局基因表达谱推断了诱导多功能干细胞响应间歇压缩力的机制,RNA测序数据的基因本体分析表明,间歇压缩力差异调控的基因主要与代谢过程、膜和蛋白质结合有关;基于分析表明,间歇压缩力诱导细胞周期类别中的基因并下调与代谢过程相关的基因;流式细胞术检测显示间歇压缩力诱导细胞周期和增殖,同时减少了凋亡细胞数量。
生物医用支架对于细胞外基质机械特性的仿生研究已经从具体实验的统计分析逐渐过渡到通过数学建模及计算机软件模拟分析来评估支架对细胞形态、细胞行为等的影响[42],但随之而来的还有模型构建合理性及精确度问题,如APOLINAR-FERNáNDEZ等[43]从不同角度评估牵引力显微镜在体外机械力对细胞形态研究中的准确性和计算效率,拓展了三维牵引力显微镜的精度和效率表征,强调了未来三维牵引力显微镜体外应用需要考虑的要素。
2.2.2 生物医用支架的三维结构 为了最大程度地模拟细胞在机体内所处的微环境,生物医用支架的空间结构设计十分重要。以往的大部分研究都是基于二维平面结构对细胞的影响,但三维环境更加贴近细胞所处的微环境,在三维体系中梯度浓度是普遍存在的[44]。由于在三维空间中局部更细小微环境的性质不同,也可能会导致同一空间中不同位置的细胞表现出不同的行为[45]。此外,细胞生长在不同空间结构的基底上,细胞与基底材料形成的黏着斑是不同的,细胞黏着斑是细胞与细胞外基质接触并结合而形成的一种动态的、体积较大的蛋白复合体,黏着斑起到了传递生物化学信号并调节多种信号通路的作用,所以空间结构的改变通过影响黏着斑,从而影响细胞黏附及一系列细胞内信号传递行为[46]。
研究表明细胞处于二维和三维环境中的行为与功能是有差异的,不同维度的空间结构培养的细胞表型显著不同[47]。DUNN等[48]发现在单层胶原凝胶上培养的大鼠肝细胞在1周内基本停止分泌白蛋白,而在胶原夹层系统中的肝细胞则可以保持正常形态并持续分泌白蛋白至少42 d。BRENNAN等[49]采用熔体电写技术制备了不同孔径的聚己内酯纤维支架,并研究纤维孔径对人骨髓干细胞形态、黏附、增殖、机械信号及成骨的影响,结果显示接种在最低孔径(100 μm)纤维结构中的人骨髓干细胞表现出最高的接种率以及保持最好的细胞形态,并且显著增强了人骨髓干细胞胶原蛋白和矿物的沉积。此外有研究表明,纳米颗粒的粒径大小也被证明对细胞有显著影响[50]。DUAN等[51]研究多孔生物活性玻璃支架微孔密度对大鼠骨髓基质细胞附着、增殖及成骨化的影响,结果发现微孔支架显著促进了初始细胞的黏附、碱性磷酸酶活性和成骨相关基因/蛋白表达,以及合适的微孔密度会调节纤连蛋白的吸附,进而促进整合素受体结合亲和力、黏附复合物的形成和随后的FAK/MAPK信号通路激活。WERNER等[52]通过立体光刻技术制备了具有明确几何特征的三维表面,研究材料表面曲率对人间充质干细胞迁移和分化产生的影响,通过延时显微镜发现,由于细胞骨架的作用力将细胞体抬升,导致在凹面上的细胞迁移速度比在凸面上快,而同样是因为细胞骨架的作用导致在凸面上的细胞核产生变形、层粘连蛋白水平升高,从而相比凹面更容易向成骨分化。
细胞在三维环境中的基因表达水平与在二维环境中也有很大的差别[53]。LINVILLE等[54]使用荧光标记的多能干细胞衍生的脑微血管内皮细胞样细胞和脑周细胞样细胞的基因家族,比较体外二维和三维微环境下血脑屏障基因的表达和功能,结果表明三维微环境增加了血脑屏障的表型和内皮特性。三维环境同样影响细胞对药物或毒物的反应,例如在肿瘤药物的筛选中,肿瘤细胞的单层生长和成球生长对药物刺激的响应,相比贴壁单层生长的细胞,具有球粒形成能力的细胞显示出更强的耐药性[55]。在细胞毒性药物测试中,接种在三维环境中皮肤细胞的存活率要高于二维环境中的皮肤细胞[56]。
此外,材料表面立体微图案提供的形貌特征也被证实可以控制多种细胞行为[57-60]。MIAO等[61]在体外实验中比较了宏观、微观和纳米级修饰植入物表面的反应,涉及不同的细胞类型,例如成骨细胞[62]、上皮细胞[63]、成纤维细胞[64]、巨噬细胞[65]、细菌[66],结果表明纳米图案对几乎所有细胞类型都是有利的。也有越来越多的研究证实,材料表面的纳米结构通过直接或者间接的途径影响细胞,细胞被描述成一个个机械单元,其中细胞骨架的结构变化会改变细胞核的形状,从而改变染色体排列与基因的表达[67-68]。
近年来,通过先进的成型加工手段如三维生物打印[69]、近场直写熔体静电纺丝等技术对于材料立体纳米结构的精确设计成为了研究人员研究细胞行为的有力手段[70]。ZHANG等[71]采用三维打印技术制造了一种高通量芯片,用于骨生物医用支架材料三维结构特性对骨诱导及骨再生影响的筛选。包括微流控技术等在内[72],这种集成式的、高通量的生物医用支架显著缩短了研究细胞行为的周期,并且减少了实验动物不必要的牺牲,对新型生物医用支架的研发起到积极作用。
2.2.3 生物医用支架的生化活性 生物医用支架还通过生化特性影响细胞。材料的生化特性可以决定细胞在其上的黏附、迁移等行为[73]。设计具有不同生化特性的生物医用支架,对于研究细胞黏附和形貌与细胞功能之间的相互作用非常重要。研究人员为了更好地模拟细胞外基质内存在的生化信号,常常会对材料进行改性,例如胶原蛋白和纤连蛋白作为典型的纤维蛋白,对于调节细胞黏附、迁移和分化有着显著影响,因此它们常被用来修饰生物材料表面来改善细胞附着能力[74]。
吸附在生物材料上的细胞外基质蛋白会介导材料与细胞的相互作用。MPOYI等[75]使用黏附有这种蛋白质吸附层纳米结构的聚碳酸酯表面培养C2C12成肌细胞,通过润湿性和原子力显微镜成像发现在纳米间隙中的蛋白质也会吸附细胞,细胞对这种具有蛋白质吸附层的纳米形貌做出了反应,形成了更少但更大的局灶性粘连,并且与平坦的表面相比,模仿细胞外基质表面凹陷的形貌使得细胞实现了更高水平的肌源分化。SUN等[76]证明了氢氧化铝纳米颗粒表面上的羟基含量会影响人树突状细胞和单核细胞的成熟。MORISHIGE等[77]比较了未修饰以及使用-COOH、-NH2、-SO3H或-CHO基团修饰的无定形二氧化硅颗粒,发现进行表面修饰可减少人单核细胞的内体破裂、白细胞介素1β和活性氧的产生。LI等[78]用聚乙二醇、聚乙二醇-RGD和聚乙二醇-RDG基团修饰了介孔二氧化硅微棒支架,结果表明调节介孔二氧化硅微棒支架上的化学性质显著影响其在体外和体内的固有炎症反应,聚乙二醇修饰的介孔二氧化硅微棒增强了体外促炎细胞因子的产生,使免疫细胞特别是CD11bGr.1髓细胞能够在体内浸润到支架中;相反,与聚乙二醇修饰的介孔二氧化硅微棒相比,聚乙二醇-RGD和聚乙二醇-RDG修饰的介孔二氧化硅微棒显示出降低的炎症效应。URE?A等[79]研究发现与传统的Ti表面对比,具有低弹性模量的Ti-Nb和具有孔隙的Ti-NbNH4Cl表面培养21 d后显示出高的细胞活力和增殖及良好的黏附性,细胞均匀分布在整个表面上,并且碱性磷酸酶活性结果显示Ti-Nb的细胞分化水平更高。
尽管对于生物医用支架生化活性的设计取得了不小的进展,包括接枝、嵌段等方式对生物材料进行改性,以及通过共混活性因子、负载药物分子等方式赋予生物材料特定的功能,都为生物医用支架的仿生设计提供了新的思路,但大部分的材料与技术仍尚未被临床所接受[80],因为细胞的增殖、分化、迁移等行为是受多种因素协同效应所影响,所以正如前文所述,结合机械性能、三维空间结构的仿生设计并使用先进增材制造技术进行的精确化、定制化、智能化生物医用支架制造可能是未来发展方向之一[81]。
2.3 生物医用支架的在组织工程中的应用
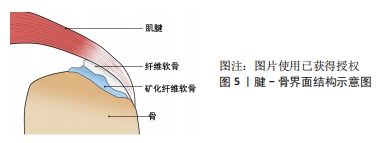
2.3.1 腱骨界面仿生 腱骨界面的损伤包括肩袖损伤、前交叉韧带损伤、距腓前韧带损伤等,是运动医学领域常见的疾病。如图5所示腱骨界面是由梯度渐变的骨、矿化纤维软骨、纤维软骨和肌腱4层组织所构成,在接受到肌肉收缩的力时具有传递和缓冲作用[82]。
目前通过手术及物理治疗对上述腱骨界面损伤的重构及功能再生效果难以令人满意[83],而通过对腱骨界面进行仿生设计的生物医用支架成为了促进腱-骨界面在受损后快速优质再生研究的热点之一。WANG等[84]通过静电纺丝和双重交联的方法,使用聚氨酯和明胶制备了纳米纤维微观结构卷曲并互相连接的静电纺纳米纤维支架,用以仿生腱骨界面的天然微观结构,卷曲静电纺纳米纤维支架与天然肌腱组织具有相似的拉伸应力,并能够诱导干细胞成软骨分化,在使用卷曲静电纺纳米纤维支架修复兔巨大肩袖撕裂3个月后,观察到兔腱骨界面得到了完全恢复,肩袖组织脂肪浸润同时也受到抑制。TANG等[85]通过制备骨、纤维软骨和肌腱组织相应的脱细胞支架薄片,然后与骨髓间充质干细胞片复合形成一种梯度的“书页型”三相脱细胞支架,移植到兔腱骨界面损伤部位,发现其可以有效加速腱骨界面的愈合。
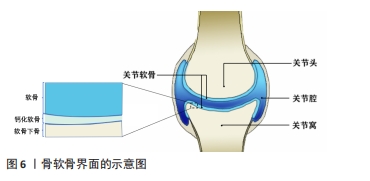
2.3.2 骨-软骨界面仿生 关节软骨及软骨缺损同样也是运动医学领域常见的损伤之一,通常会导致患者的关节处疼痛以及功能障碍,由于软骨组织上没有血管、缺乏内源性修复细胞的特点导致其自愈能力极其有限[86]。图6显示了骨软骨界面的基本结构,主要由软骨、钙化软骨、软骨下骨组成。对于骨-软骨缺损通常采用微骨折手术和同种异体骨软骨移植的治疗方法,但可能造成不可逆的骨变性、排异反应以及纤维软骨等问题。而近年来随着对自体组织仿生的研究,运用组织工程技术制造的生物医用支架为骨软骨组织的修复提供了一种新的策略。CHEN等[87]设计开发了一种具有层状特异性分化的双相骨软骨支架,其中透明质酸作为上下层基质,通过两种化学交联方法分别实现了对软骨再生层和软骨下骨的两层理化性质及生物学性质的差异,并促进了关节软骨和软骨下骨的一体化再生。CHENG等[88]开发了一种基于丝素蛋白和甲壳素的混合纳米纤维增强支架,并且浸渍有转化生长因子β1,以模拟细胞外基质并促进软骨再生,该支架具有优异生物相容性并显示出合适的弹性和硬度;作为一种软骨生长因子,转化生长因子β1被引入到复合支架中,并通过诱导细胞归巢来调节支架的性能,在治疗大鼠软骨缺损时,负载转化生长因子β1的混合纳米纤维功能化复合支架显著加速了软骨再生。
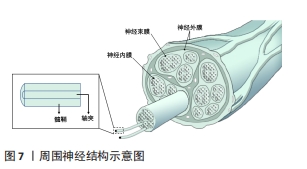
2.3.3 神经仿生 周围神经损伤在临床上是是一种常见且严重的病症,占据外科创伤病例的2%-5%。当受损神经长度较短时,可直接通过手术缝合的方式进行修复,但面对长程的神经缺损时就需采取他法。临床上对于修复长程神经缺损的“金标准”是自体神经移植,但其也因为供体不足、供区功能受损以及神经瘤等问题而具有一定的局限性[89],因此,对神经进行仿生的生物医用支架被视为治疗长程周围神经损伤研究的热点领域。图7展示了周围神经的基本结构。WANG等[90]利用静电纺丝技术制备了一种具有温度响应性的双层纳米纤维膜,在纤维膜上可以实现均匀接种施万细胞,并根据温度变化形成多孔道的神经导管,导管内壁具有的取向纤维结构可以促进神经突触的定向延伸;通过大鼠坐骨神经缺损模型的验证,该多通道导管在促进缺损神经的再生以及功能恢复方面有着积极作用。YANG等[91]将具有良好排列结构的静电纺压电左旋聚乳酸纳米纤维作为神经导管的壳材料,将碳纳米管作为具有高导电性和低细胞毒性的理想电活性物质均匀掺入甲基丙烯酸化水凝胶溶液中,以开发柔软的导电水凝胶;为了给神经细胞提供仿生微环境,将这种导电复合水凝胶嵌入到对齐的静电纺丝左旋聚乳酸压电导管中,得到自发电的导电神经支架,实验表明这种自发电的导电神经支架具有加速轴突生长、促进髓鞘再生和改善神经功能恢复等功能,有望成为增强周围神经再生的实用高效移植物。
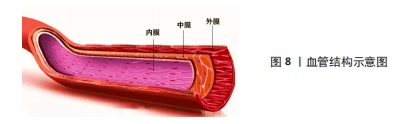
2.3.4 血管仿生 心血管疾病是目前在全球造成死亡的主要原因之一。随着生物医学工程的发展,目前人工血管对于大口径的血管置换已经趋于成熟,但对于内径小于6 mm的人工血管替代人体小动脉或静脉却一直存在技术空白,其主要原因就在于术后血栓的形成、内膜增生等问题[92],因此,如何构建一种可以长期保持通畅的小口径人工血管是当下研究的热点。如图8所示,血管基本结构分为内膜、中膜和外膜,所以利用组织工程原理对其结构进行仿生设计制造的生物医用支架为这一问题带来了新的思路[93]。ZHU等[94]通过原位编织及热致相分离相结合的方法制备了一种采用聚氨酯弹性体与聚乳酸-羟基乙酸聚合物织物增强的具有仿生细胞外基质三维多孔结构的小口径血管移植物(PPTG),制备的PPTG内表面光滑致密,移植物壁蓬松多孔,管状聚乳酸-羟基乙酸聚合物织物均匀分散聚氨酯弹性体基质,为PPTG提供了机械支撑;力学测试和溶血结果表明,PPTG具有与自体血管匹配的力学性能和稳定的血液相容性,兔颈动脉缺损置换术后6周,PPTG组未发生阻塞。DU等[95]对猪冠状动脉进行去细胞化制备了去细胞化猪冠状动脉,通过包覆海藻酸钠以及明胶的混合水凝胶,同时结合小鼠成纤维细胞(L929细胞)制备了一种双层杂化支架,在细胞接种后均表现出良好的生物相容性,能够满足人工血管构建的需要。WANG等[96]设计了一种人工血管,该血管对于天然血管进行仿生,其具有在体内缓释一氧化氮的功能,可以促进血管组织再生并同时抑制血管钙化,从而提高血管长期畅通率,为解决小口径人工血管再狭窄的问题提供了新思路。
| [1] LOUIS F, SOWA Y, IRIE S, et al. Injectable Prevascularized Mature Adipose Tissues (iPAT) to Achieve Long-Term Survival in Soft Tissue Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(23):e2201440. [2] YAN L, ZHENG C, YUAN D, et al. Fast Construction of Biomimetic Organic–Inorganic Interface by Crosslinking of Calcium Phosphate Oligomers: A Strategy for Instant Regeneration of Hard Tissue. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022; 1(23):2201161. [3] YANG R, SHI L, SI H, et al. Gallic Acid Improves Comorbid Chronic Pain and Depression Behaviors by Inhibiting P2X7 Receptor-Mediated Ferroptosis in the Spinal Cord of Rats. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023;14(4):667-676. [4] 唐俊杰,李文杰,李根,等.骨组织工程诱导性支架材料修复骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(3):340-346. [5] LIN X, KONG B, ZHU Y, et al. Bioactive Fish Scale Scaffolds with MSCs-Loading for Skin Flap Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9:2201226. [6] BAI B, HAO J, HOU M, et al. Repair of Large-Scale Rib Defects Based on Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Designed Biomimetic 3D-Printed Scaffolds with Bone-Mineralized Microenvironments. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(37): 42388-42401. [7] STEVENS AJ, HARRIS AR, GERDTS J, et al. Programming multicellular assembly with synthetic cell adhesion molecules. Nature. 2023;614(7946):144-152. [8] 张宁.仿生细胞外基质微环境的构建及对细胞行为的调控和应用[D].南京: 东南大学,2018. [9] MAHADIK P, PATWARDHAN S. ECM stiffness-regulated exosomal thrombospondin-1 promotes tunneling nanotubes-based cellular networking in breast cancer cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023;742:109624. [10] 李晓军.细胞群体极化、排列和迁移行为研究[D].北京:北京理工大学, 2021. [11] MADHUSOODANAN J. Matrix mimics shape cell studies. Nature. 2019;566: 563-565. [12] MA Z, MAO C, JIA Y, et al. Extracellular matrix dynamics in vascular remodeling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020;319(3):C481-C499. [13] VASUDEVAN J, JIANG K, FERNANDEZ JG, et al. Extracellular matrix mechanobiology in cancer cell migration. Acta Biomater. 2023;163:351-364. [14] POMERLEAU V, NICOLAS V R, JURKOVIC CM, et al. FOXL1+ Telocytes in mouse colon orchestrate extracellular matrix biodynamics and wound repair resolution. J Proteomics. 2023;271:104755. [15] YASUDA T, ISHIHARA T, ICHIMURA A, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics define muscle fiber type by modulating cellular metabolic pathways. Cell Rep. 2023;42(5):112434. [16] DAVIS GE, KEMP SS. Extracellular Matrix Regulation of Vascular Morphogenesis, Maturation, and Stabilization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2023;13(4):a041156. [17] GROSBOIS J, BAILIE EC, KELSEY TW, et al. Spatio-temporal remodelling of the composition and architecture of the human ovarian cortical extracellular matrix during in vitro culture. Hum Reprod. 2023;38(3):444-458. [18] CAO Z, YUAN H, LI N, et al. The Preparation of Biomineralized PIC/HA Hybrid Composites with Strain-Stiffening and the Effect on MC3T3-E1 Cells. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2022;43(11):e2200135. [19] MAO X, LI T, CHENG J, et al. Nerve ECM and PLA-PCL based electrospun bilayer nerve conduit for nerve regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1103435. [20] LIN X, KONG B, ZHU Y, et al. Bioactive Fish Scale Scaffolds with MSCs-Loading for Skin Flap Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(21):e2201226. [21] LI S, YANG L, ZHAO Z, et al. Fabrication of mechanical skeleton of small-diameter vascular grafts via rolling on water surface. Biomed Mater. 2023; 18(3).doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/acb89a. [22] ECHAZÚ MIA, PERNA O, OLIVETTI CE. Recent Advances in Synthetic and Natural Biomaterials-Based Therapy for Bone Defect. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22:2100383. [23] URTAZA U, GUARESTI O, GORROÑOGOITIA I, et al. 3D printed bioresorbable scaffolds for articular cartilage tissue engineering: a comparative study between neat polycaprolactone (PCL) and poly(lactide-b-ethylene glycol) (PLA-PEG) block copolymer. Biomed Mater. 2022;17:045028. [24] SHAO W, CUI C, XIONG J, et al. Small-Diameter PLCL/PCL Nanofiber Grafted TSF Vascular Scaffolds with a Double-Layer Structure for Vascular Tissue Engineering. Macromol Mater Eng. 2021;306:2100462. [25] SOUSA GF, AFEWERKI S, DITTZ D, et al. Catalyst-Free Click Chemistry for Engineering Chondroitin Sulfate-Multiarmed PEG Hydrogels for Skin Tissue Engineering. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(2):45. [26] RAUT MP, ASARE E, MOHAMED SMDS, et al. Bacterial Cellulose-Based Blends and Composites: Versatile Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):986. [27] WU J, PAN Z, ZHAO ZY, et al. Anti-Swelling, Robust, and Adhesive Extracellular Matrix-Mimicking Hydrogel Used as Intraoral Dressing. Adv Mater. 2022;34(20):e2200115. [28] AI C, LIU L, WONG K, et al. The effect of chondroitin sulfate concentration and matrix stiffness on chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomater Sci. 2023;10.1039/d2bm01980a. [29] SHENG R, LIU J, ZHANG W, et al. Material Stiffness in Cooperation with Macrophage Paracrine Signals Determines the Tenogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(17):e2206814. [30] OH SH, AN DB, KIM TH, et al. Wide-range stiffness gradient PVA/HA hydrogel to investigate stem cell differentiation behavior. Acta Biomater. 2016;35: 23-31. [31] PROUVÉ E, RÉMY M, FEUILLIE C, et al. Interplay of matrix stiffness and stress relaxation in directing osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(17):4978-4996. [32] ENGLER AJ, SEN S, SWEENEY HL, et al. Matrix Elasticity Directs Stem Cell Lineage Specification. Cell. 2006;126(4):677-689. [33] WULLKOPF L, WEST AKV, LEIJNSE N, et al. Cancer cells’ ability to mechanically adjust to extracellular matrix stiffness correlates with their invasive potential. Mol Biol Cell. 2018;29(20):2359-2507. [34] PREVITERA ML, LANGHAMMER CG, FIRESTEIN BL. Effects of substrate stiffness and cell density on primary hippocampal cultures. J Biosci Bioeng. 2010;110(4):459-470. [35] CHEN WC, TIAN BX, LIANG JQ, et al. Matrix stiffness regulates the interactions between endothelial cells and monocytes. Biomaterials. 2019; 221:119362. [36] XIE J, ZHANG DM, ZHOU CC, et al. Substrate elasticity regulates adipose-derived stromal cell differentiation towards osteogenesis and adipogenesis through β-catenin transduction. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:83-95. [37] GRIER WK, MOY AS, HARLEY BAC. Cyclic tensile strain enhances human mesenchymal stem cell smad 2/3 activation and tenogenic differentiation in anisotropic collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds. Eur Cell Mater. 2017; 33:227-239. [38] CORBIN EA, VITE A, PEYSTER EG, et al. Tunable and Reversible Substrate Stiffness Reveals a Dynamic Mechanosensitivity of Cardiomyocytes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(23):20603-20614. [39] RITTER N, MUSSIG E, STEINBERG T, et al. Elevated expression of genes assigned to NF-κB and apoptotic pathways in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts following mechanical stretch. Cell Tissue Res. 2007;328:537-548. [40] CHAN CJ, COSTANZO M, RUIZ-HERRERO T, et al. Hydraulic control of mammalian embryo size and cell fate. Nature. 2019;571:112-116. [41] MANOKAWINCHOKE J, LIMRAKSASIN P, OKAWA H, et al. Intermittent compressive force induces cell cycling and reduces apoptosis in embryoid bodies of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Int J Oral Sci. 2022;14:1. [42] PERIER-METZ C, DUDA GN, CHECA S. A mechanobiological computer optimization framework to design scaffolds to enhance bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:980727. [43] APOLINAR-FERNÁNDEZ A, BARRASA-FANO J, CÓNDOR M, et al. Traction force reconstruction assessment on real three-dimensional matrices and cellular morphologies. Int J Eng Sci. 2023;186:103828. [44] WU J, PAN Z, ZHAO Z, et al, Anti-Swelling, Robust, and Adhesive Extracellular Matrix-Mimicking Hydrogel Used as Intraoral Dressing. Adv Mater. 2022;34: 2200115. [45] FRIEDL P, SAHAI E, WEISS S, et al. New dimensions in cell migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:743-747. [46] SOUZA C, JAYME CC, REZENDE N, et al. Synergistic effect of photobiomodulation and phthalocyanine photosensitizer on fibroblast signaling responses in an in vitro three-dimensional microenvironment. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2021;222:112256. [47] SUN Q, PEI F, ZHANG M, et al. Curved Nanofiber Network Induces Cellular Bridge Formation to Promote Stem Cell Mechanotransduction. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(3):e2204479. [48] DUNN JCY, YARMUSH ML, KOEBE HG, et al. Hepatocyte function and extracellular matrix geometry: long-term culture in a sandwich configuration. FASEB J. 1989;3(2):174-177. [49] BRENNAN CM, EICHHOLZ KF, HOEY DA. The effect of pore size within fibrous scaffolds fabricated using melt electrowriting on human bone marrow stem cell osteogenesis. Biomed Mater. 2019;14:065016. [50] ZHANG W, WANG XC, LI XY, et al. A 3D porous microsphere with multistage structure and component based on bacterial cellulose and collagen for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;236:116043. [51] DUAN B, NIU H, ZHANG W, et al. Microporous density-mediated response of MSCs on 3D trimodal macro/micro/nano-porous scaffolds via fibronectin/integrin and FAK/MAPK signaling pathways. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5:3586-3599. [52] WERNER M, BLANQUER SBG, HAIMI SP, et al. Surface Curvature Differentially Regulates Stem Cell Migration and Differentiation via Altered Attachment Morphology and Nuclear Deformation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2017;4:1600347. [53] BOUZOS E, ASURI P. Sandwich Culture Platforms to Investigate the Roles of Stiffness Gradients and Cell-Matrix Adhesions in Cancer Cell Migration. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(6):1729. [54] LINVILLE RM, SKLAR MB, GRIFNO GN, et al. Three-dimensional microenvironment regulates gene expression, function, and tight junction dynamics of iPSC-derived blood–brain barrier microvessels. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022;19:87. [55] HONOKI K, FUJII H, KUBO A, et al. Possible involvement of stem-like populations with elevated ALDH1 in sarcomas for chemotherapeutic drug resistance. Oncol Rep. 2010;24(2):501-505. [56] SUN T, JACKSON S, HAYCOCK JW, et al. Culture of skin cells in 3D rather than 2D improves their ability to survive exposure to cytotoxic agents. J Biotechnol. 2006;122(3):372-381. [57] ZHANG X, ZHANG T, LIU B, et al. Effects of Biomimetic Micropatterned Surfaces on the Adhesion and Morphology of Cervical Cancer Cells. ACS Omega. 2022;7:19913-19919. [58] KUNRATH MF, DIZ FM, MAGINI R, et al. Nanointeraction: The profound influence of nanostructured and nano-drug delivery biomedical implant surfaces on cell behavior. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;284:102265. [59] ZHANG Y, JIANG N, GAN Z. Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Substrates with Micro/Nanohierarchical Patterned Structures for Cell Culture. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22:2200300. [60] LI J, LIU X, TAO W. Micropatterned composite membrane guides oriented cell growth and vascularization for accelerating wound healing. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbac108. [61] MIAO X, WANG D, XU L, et al. The response of human osteoblasts, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, macrophages and oral bacteria to nanostructured titanium surfaces: a systematic study. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:1415-1430. [62] MAALOUF M, KHALIL AA, MAIO YD, et al. Polarization of Femtosecond Laser for Titanium Alloy Nanopatterning Influences Osteoblastic Differentiation. Nanomaterials. 2022;12:1619. [63] COSTA P, BLOWES LM, LALY AC, et al. Regulation of collective cell polarity and migration using dynamically adhesive micropatterned substrates. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:291-300. [64] ECKERT J, JACK JWAL, ENG LM, et al. Hypergravity affects cell traction forces of fibroblasts. Biophys J. 2021;120:773-780. [65] LUO Y, YUAN P, HU S, et al. Inflammatory environment-adaptive patterned surface for spatiotemporal immunomodulation of macrophages. Acta Biomater. 2022;153:139-148. [66] FILIPOV E, ANGELOVA L, VIG S, et al. Investigating Potential Effects of Ultra-Short Laser-Textured Porous Poly-ε-Caprolactone Scaffolds on Bacterial Adhesion and Bone Cell Metabolism. Polymers. 2022;14:2382. [67] ANARKOLI AO, EPHRAIM JW, RIMAL R, et al. Hierarchical fibrous guiding cues at different scales influence linear neurite extension. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:350-359. [68] LI MJ, FU XL, GAO HC, et al. Regulation of an osteon-like concentric microgrooved surface on osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. Biomaterials. 2019;216:119269. [69] SUN X, YANG J, MA J, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinted BMSCs-laden highly adhesive artificial periosteum containing gelatin-dopamine and graphene oxide nanosheets promoting bone defect repair. Biofabrication. 2023;15(2). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/acb73e. [70] CHEN Z, LIU Y, HUANG J, et al. Influences of Process Parameters of Near-Field Direct-Writing Melt Electrospinning on Performances of Polycaprolactone/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(16):3404. [71] ZHANG B, WANG W, GUI X, et al. 3D printing of customized key biomaterials genomics for bone regeneration. Appl Mater Today. 2022;26:101346. [72] LIU HW, SU WT, LIU CY, et al. Highly Organized Porous Gelatin-Based Scaffold by Microfluidic 3D-Foaming Technology and Dynamic Culture for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8449. [73] DENNIS SC, WHITLOW J, DETAMORE MICHAEL S, et al. Hyaluronic-Acid–Hydroxyapatite Colloidal Gels Combined with Micronized Native ECM as Potential Bone Defect Fillers. Langmuir. 2017;33(1):206-218. [74] REN K, HU M, ZHANG H. Layer-by-layer assembly as a robust method to construct extracellular matrix mimic surfaces to modulate cell behavior. Prog Polym Sci. 2019;92:1-34. [75] MPOYI EN, CANTINI M, REYNOLDS PM, et al. Protein Adsorption as a Key Mediator in the Nanotopographical Control of Cell Behavior. ACS Nano. 2016;10(7):6638-6647. [76] SUN B, JI Z, LIAO YP, et al. Engineering an Effective Immune Adjuvant by Designed Control of Shape and Crystallinity of Aluminum Oxyhydroxide Nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2013;7(2):10834-10849. [77] MORISHIGE T, YOSHIOKA Y, INAKURA H, et al. The effect of surface modification of amorphous silica particles on NLRP3 inflammasome mediated IL-1β production, ROS production and endosomal rupture. Biomaterials. 2010;31(26):6833-6842. [78] LI W, LU Y, LUO G, et al. The effect of surface modification of mesoporous silica micro-rod scaffold on immune cell activation and infiltration. Biomaterials. 2016;83:249-256. [79] UREÑA J, TSIPAS S, JIMÉNEZ-MORALES A, et al. Cellular behaviour of bone marrow stromal cells on modified Ti-Nb surfaces. Mater Design. 2018;140: 452-459. [80] LIU S, YU JM, GAN YC, et al. Biomimetic natural biomaterials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: new biosynthesis methods, recent advances, and emerging applications. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):16. [81] AKBARI M, KHADEMHOSSEINI A. Tissue bioprinting for biology and medicine. Cell. 2022;85(15):2644-2648. [82] YANG R, LI G, ZHUANG C, et al. Gradient bimetallic ion–based hydrogels for tissue microstructure reconstruction of tendon-to-bone insertion. Sci Adv. 2021;7:eabg3816. [83] DANG GP, WEN Q, WAN QQ, et al. Regulation and Reconstruction of Cell Phenotype Gradients Along the Tendon-Bone Interface. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;33:2210275. [84] WANG L, ZHU T, KANG Y, et al. Crimped nanofiber scaffold mimicking tendon-to-bone interface for fatty-infiltrated massive rotator cuff repair. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:149-161. [85] TANG Y, CHEN C, LIU F, et al. Structure and ingredient-based biomimetic scaffolds combining with autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheets for bone-tendon healing. Biomaterials. 2020;241:119837. [86] YANG M, ZHANG ZC, YUAN FZ, et al. An immunomodulatory polypeptide hydrogel for osteochondral defect repair. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:678-689. [87] CHEN X, JIANG C, WANG T, et al. Hyaluronic acid-based biphasic scaffold with layer-specific induction capacity for osteochondral defect regeneration. Mater Design. 2022;216:110550. [88] CHENG G, DAI JH, DAI JW, et al. Extracellular matrix imitation utilizing nanofibers-embedded biomimetic scaffolds for facilitating cartilage regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2021;410:128379. [89] 李金瑞.聚己内酯/壳聚糖多通道神经导管的构建及其修复大鼠坐骨神经缺损的研究[D].上海:东华大学,2022. [90] WANG J, XIONG H, ZHU T, et al. Bioinspired Multichannel Nerve Guidance Conduit Based on Shape Memory Nanofibers for Potential Application in Peripheral Nerve Repair. ACS Nano. 2020;14:12579-12595. [91] YANG YF, YIN X, WANG HD, et al. Engineering a wirelessly self-powered and electroconductive scaffold to promote peripheral nerve regeneration. Nano Energy. 2023;107:108145. [92] LIBERALE L, BADIMON L, MONTECUCCO F, et al. Inflammation, Aging, and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(8):837-847. [93] 顾其胜,陈西广,赵成如.壳聚糖基海洋生物医用材料[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2020. [94] ZHU TH, GU HB, MA WX, et al. A fabric reinforced small diameter tubular graft for rabbits’ carotid artery defect. Compos Part B-Eng. 2021;225: 109274. [95] DU J, HU X Y, SU Y, et al. Gelatin/sodium alginate hydrogel-coated decellularized porcine coronary artery to construct bilayer tissue engineered blood vessels. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;209:2070-2083. [96] WANG F, QIN K, WANG K, et al. Nitric oxide improves regeneration and prevents calcification in bio-hybrid vascular grafts via regulation of vascular stem/progenitor cells. Cell Rep. 2022;39:110981. |
| [1] | 余伟杰, 刘爱峰, 陈继鑫, 郭天赐, 贾易臻, 冯汇川, 杨家麟. 机器学习在腰椎间盘突出症诊治中的优势和应用策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [2] | 杨玉芳, 杨芷姗, 段棉棉, 刘毅恒, 唐正龙, 王 宇. 促红细胞生成素在骨组织工程中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [3] | 陈凯佳, 刘景云, 曹 宁, 孙建波, 周 燕, 梅建国, 任 强. 组织工程技术在股骨头坏死治疗中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [4] | 林泽玉, 徐 林. 痛风致骨破坏机制的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [5] | 梅静怡, 刘 江, 肖 聪, 刘 鹏, 周浩浩, 林展翼. 组织工程血管构建过程中平滑肌细胞增殖变化及代谢模式[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| [6] | 王姗姗, 舒 晴, 田 峻. 物理因子促进干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [7] | 张克凡, 石 辉. 细胞因子治疗骨关节炎的研究现状及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [8] | 徐 溶, 王豪杰, 耿梦想, 孟 凯, 王 卉, 张克勤, 赵荟菁. 多孔聚四氟乙烯人工血管制备及功能化改性研究的进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [9] | 陈小芳, 郑国爽, 李茂源, 于炜婷. 可注射海藻酸钠水凝胶的制备及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [10] | 刘 闯, 单 烁, 于腾波, 周 欢, 杨 磊. 骨科止血材料临床应用的优势、不适与面临的挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 795-803. |
| [11] | 王嘉旎, 陈俊宇. 金属离子促血管生成机制及在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [12] | 沈子青, 夏 天, 单一波, 朱睿君, 万昊鑫, 丁 浩, 潘 枢, 赵 军. 负载外泌体水凝胶修饰3D打印支架构建血管化的气道替代物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [13] | 李佳琪, 黄元礼, 李 妍, 王春仁, 韩倩倩. 非交联透明质酸分子质量降解的机制及影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 747-752. |
| [14] | 朱礼威, 王江玥, 白 丁. 纳米复合甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶在不同骨缺损环境中应用的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [15] | 张 明, 王 斌, 贾 凡, 陈 杰, 唐 玮. 基于脑电图的脑机接口技术在脑卒中患者上肢运动功能康复中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 581-586. |
现今在临床上运用工程学、仿生学及再生医学等原理,通过组织工程技术使用生物材料构建的生物医用支架成为了严重组织损伤最有前途的治疗方法之一[5]。由于细胞在天然的细胞外基质微环境中能够快速的迁移、分化、增殖来达到组织再生的目的,因此生物医用支架在结构及理化性质上对细胞外基质微环境的仿生设计,对于组织修复的效果起到了决定性作用[6]。而事实上细胞时刻处于一个复杂且动态变化的微环境中,如何通过生物医用支架的设计来构建一个尽可能贴近细胞所处真实的微环境,实现对细胞行为的调控,进而达到组织修复的目的,是现在迫切需要解决的新问题。材料给予的机械信号包括硬度、拉伸力等会直接影响细胞的形貌、黏附等行为,生物医用支架的三维结构包括孔径大小、取向结构、表面粗糙程度等也会影响细胞的形貌、迁移等行为,而生物医用支架的生化活性会对细胞的生长、凋亡等活动产生一定影响。文章将主要从生物医用支架的机械性能、三维空间结构和生化活性对细胞行为的影响进行讨论,并综述生物医用支架目前几个重要的应用领域。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者于2022年12月至2023年4月进行文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2003年1月至2023年4月。
1.1.3 检索的数据库 中国知网、万方、Web of Science、PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“细胞外基质,组织工程,支架,生物材料,仿生结构,机械性能,三维结构,腱骨界面,骨软骨,神经导管,人造血管;英文检索词为“extracellular matrix,tissue engineering,scaffolds,biomimetic structures,biomaterials,tendon bone interfaces,osteochondral,neural conduits,artificial blood vessels”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、实验性论文、原著。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 书籍《壳聚糖基海洋生物医用材料》。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索到文献832篇,包括中文文献161篇、英文文献671篇。
1.1.8 检索策略 中文数据库检索策略以中国知网为例,见图1;英文数据库检索策略以PubMed为例,见图2。
纳入标准:综述及原著文字简洁易懂、概括性强、论据全面;实验性文献方法明确、创新点突出。
排除标准:剔除重复性文献;文章内容与题目关联性低的文献;正文内容无法获得的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估与数据提取 检索到文献832篇,首先对通过检索词检索到的文献进行标题与摘要的阅读,剔除内容重复的文章,而后通过入选标准中的纳入标准进行文献质量评估,最终纳入96篇文献进行综述,包括中文文献5篇、英文文献91篇,见图3。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该文较为系统地阐述了在生物医用支架的仿生设计时需要考虑的几个因素,即细胞在组织修复过程中影响细胞行为的主要因素包括机械性能、三维结构和生物化学性质,介绍了几种在仿生结构设计上较为典型的生物医用支架应用领域。
3.3 综述的局限性 由于综述中生物医用支架目前应用领域愈发广泛,可能对于文献的概括及整理不够全面。
3.4 综述的重要意义 生物医用支架在临床上的应用研究必将朝着范围更广泛、结构更复杂、加工更精细、功能更全面、使用更智能的方向发展,而对于生物医用支架的仿生设计也将朝着更加复合、可控的方向进行研究。在此阶段对前人研究成果进行梳理及概括,对未来生物医用支架的发展有着积极的帮助。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
生物医用支架:将工程学、仿生学及再生医学等原理进行结合,通过组织工程技术使用生物活性材料构建而成的一类支架,是临床用于治疗大面积组织损伤、缺损及坏死的方法之一,有望作为自体移植或异体移植的最佳代替治疗手段之一。仿生设计:通过生物材料类型的选择、合理成型加工技术的使用、精准可控的结构的设计,并根据细胞生物学、细胞力学等理论,仿生真实细胞外基质微环境对生物医用支架进行设计。
通过大量的文献检索、查阅与总结,对如何进行生物医用支架的仿生设计进行了讨论。基于临床上对组织修复生物医用支架的大量需求,结合前人对细胞与细胞外基质之间相互作用的相关研究,总结得出了细胞外基质对细胞行为进行调控、影响的3个主要因素,分别为支架的机械性能、支架的三维空间结构以及支架所具有的生化活性。基于上述对细胞行为影响的3个因素对生物医用支架进行仿生设计,并通过前人的研究证实了其对细胞行为产生具体影响,列举了几个典型的通过仿生设计构建而成的生物医用支架及其在组织工程中的应用,最后对文章的特点及意义进行了阐述。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||