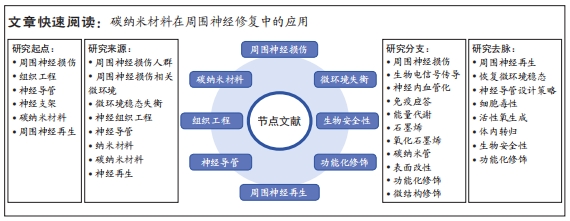
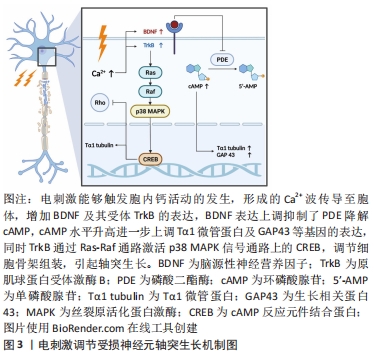
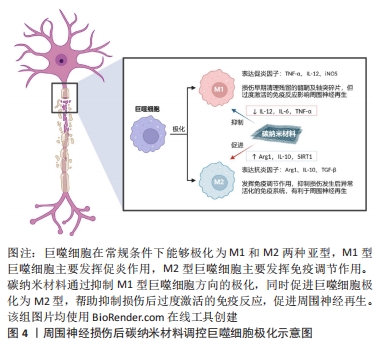
[1] WATTS G. Jiang Baoguo: one, two, three against trauma in China. Lancet. 2017;390(10104):1729.
[2] 孙国平,罗选翔,潘彬.人工神经导管治疗周围神经损伤的材料类型和应用现状[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(3):334-336.
[3] 顾玉东.周围神经损伤治疗的近期进展[C].浙江省医学会手外科学分会成立大会暨2008年学术年会论文汇编,2008,24(2):65-65.
[4] 顾玉东.提高周围神经损伤的诊治水平[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2003,5(1):1-4.
[5] BERIS A, GKIATAS I, GELALIS I, et al. Current concepts in peripheral nerve surgery. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(2):263-269.
[6] GAO Y, WANG YL, KONG D, et al. Nerve autografts and tissue-engineered materials for the repair of peripheral nerve injuries: a 5-year bibliometric analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(6):1003.
[7] 钱运,范存义.石墨烯促进周围神经再生的研究进展[J].中华手外科杂志,2019,35(2):158-160.
[8] BELLAMKONDA RV. Peripheral nerve regeneration: an opinion on channels, scaffolds and anisotropy. Biomaterials. 2006;27(19):3515-3518.
[9] 王乐禹,邱小忠,王璞玥,等.组织工程研究的现状及应关注的重要基础科学问题[J].中国科学基金,2020,34(2):213-220.
[10] 李晓强,莫秀梅,范存义.神经导管研究与进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2007,27(7):112-116.
[11] QIAN Y, LIN H, YAN Z, et al. Functional nanomaterials in peripheral nerve regeneration: Scaffold design, chemical principles and microenvironmental remodeling. Mater Today. 2021;51:165-187.
[12] WANG H, KUNKEL DD, MARTIN TM, et al. Heteromultimeric K+ channels in terminal and juxtaparanodal regions of neurons. Nature. 1993;365(6441):75-79.
[13] KRISHNAN AV, LIN CS, PARK SB, et al. Axonal ion channels from bench to bedside: a translational neuroscience perspective. Prog Neurobiol. 2009;89(3):288-313.
[14] BRADKE F, FAWCETT JW, SPIRA ME. Assembly of a new growth cone after axotomy: the precursor to axon regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(3):183-193.
[15] BAHREMANDI TOLOU N, SALIMIJAZI H, KHARAZIHA M, et al. A three-dimensional nerve guide conduit based on graphene foam/polycaprolactone. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;126:112110.
[16] BAKHTIARY S, CHEGENI A, BABAEIPOUR V, et al. Culture and maintenance of neural progressive cells on cellulose acetate/graphene‑gold nanocomposites. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;210:63-75.
[17] KUMAR MN, MUZZARELLI RA, MUZZARELLI C, et al. Chitosan chemistry and pharmaceutical perspectives. Chem Rev. 2004;104(12):6017-6084.
[18] ARANLDI P, DI LISA D, MADDALENA L, et al. A facile approach for the development of high mechanical strength 3D neuronal network scaffold based on chitosan and graphite nanoplatelets. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;271:118420.
[19] HU X, WANG X, XU Y, et al. Electric conductivity on aligned nanofibers facilitates the transdifferentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into schwann cells and regeneration of injured peripheral nerve. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(11):1901570.
[20] BARREJÓN M, ZUMMO F, MIKHALCHAN A, et al. TEGylated double-walled carbon nanotubes as platforms to engineer neuronal networks. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;15(1):77-90.
[21] MAENG WY, TSENG WL, LI S, et al. Electroceuticals for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biofabrication. 2022. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac8baa.
[22] MCGREGOR CE, ENGLISH AW. The role of BDNF in peripheral nerve regeneration: activity-dependent treatments and Val66Met. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:522.
[23] KILGORE KL, BHADRA N. Reversible nerve conduction block using kilohertz frequency alternating current. Neuromodulation. 2014;17(3):242-254.
[24] LI X, YANG W, XIE H, et al. CNT/sericin conductive nerve guidance conduit promotes functional recovery of transected peripheral nerve injury in a rat model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36860-36872.
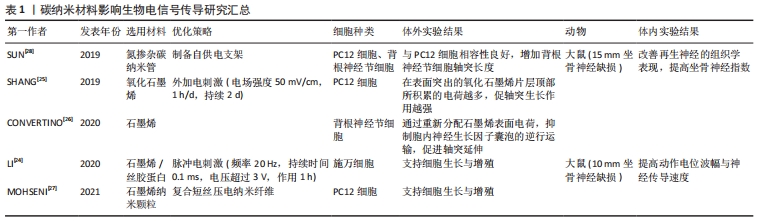
[25] SHANG L, HUANG Z, PU X, et al. Preparation of graphene oxide-doped polypyrrole composite films with stable conductivity and their effect on the elongation and alignment of neurite. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(3):1268-1278.
[26] CONVERTINO D, FABBRI F, MISHRA N, et al. Graphene promotes axon elongation through local stall of nerve growth factor signaling endosomes. Nano Lett. 2020;20(5):3633-3641.
[27] MOHSENI M, S A AR, H SHIRAZI F, et al. Preparation and characterization of self-electrical stimuli conductive gellan based nano scaffold for nerve regeneration containing chopped short spun nanofibers of PVDF/MCM41 and polyaniline/graphene nanoparticles: Physical, mechanical and morphological studies. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;167:881-893.
[28] SUN Y, QUAN Q, MENG H, et al. Enhanced neurite outgrowth on a multiblock conductive nerve scaffold with self-powered electrical stimulation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(10):e1900127.
[29] ZHENG N, FITZPATRICK V, CHENG R, et al. Photoacoustic carbon nanotubes embedded silk scaffolds for neural stimulation and regeneration. ACS Nano. 2022;16(2):2292-2305.
[30] QIAN Y, ZHAO X, HAN Q, et al. An integrated multi-layer 3D-fabrication of PDA/RGD coated graphene loaded PCL nanoscaffold for peripheral nerve restoration. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):323.
[31] HU Y, CHEN Z, WANG H, et al. Conductive nerve guidance conduits based on morpho butterfly wings for peripheral nerve repair. ACS Nano. 2022;16(2):1868-1879.
[32] WANG J, WANG H, MO X, et al. Reduced graphene oxide-encapsulated microfiber patterns enable controllable formation of neuronal-like networks. Adv Mater. 2020;32(40):e2004555.
[33] DOMINICI C, MORENO-BRAVO JA, PUIGGROS SR, et al. Floor plate-derived netrin-1 is dispensable for commissural axon guidance. Nature. 2017;545(7654):350-354.
[34] CATTIN AL, BURDEN JJ, VAN EMMENIS L, et al. Macrophage-induced blood vessels guide schwann cell-mediated regeneration of peripheral nerves. Cell. 2015;162(5):1127-1139.
[35] 张逸,任思聪.支架材料对成血管微环境的影响及作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(21):3391-3397.
[36] LEE TH, YEN CT, HSU SH. Preparation of polyurethane-graphene nanocomposite and evaluation of neurovascular regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(1):597-609.
[37] MUKHERJEE S, SRIRAM P, BARUI AK, et al. Graphene oxides show angiogenic properties. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(11):1722-1732.
[38] QIAN Y, SONG J, ZHAO X, et al. 3D Fabrication with integration molding of a graphene oxide/polycaprolactone nanoscaffold for neurite regeneration and angiogenesis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(4):1700499.
[39] QIAN Y, WANG X, SONG J, et al. Preclinical assessment on neuronal regeneration in the injury-related microenvironment of graphene-based scaffolds. NPJ Regen Med. 2021;6(1):31.
[40] DYBOWSKA-SARAPUK L, SOSNOWICZ W, KRZEMINSKI J, et al. Printed graphene layer as a base for cell electrostimulation—preliminary results. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(21):7865.
[41] JAKUS AE, SECOR EB, RUTZ AL, et al. Three-dimensional printing of high-content graphene scaffolds for electronic and biomedical applications. ACS Nano. 2015;9(4):4636-4648.
[42] LU D, MAHMOOD A, QU C, et al. Erythropoietin Enhances Neurogenesis and Restores Spatial Memory in Rats after Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2005;22(9):1011-1017.
[43] SALEHI M, NASERI-NOSAR M, EBRAHIMI-BAROUGH S, et al. Sciatic nerve regeneration by transplantation of Schwann cells via erythropoietin controlled-releasing polylactic acid/multiwalled carbon nanotubes/gelatin nanofibrils neural guidance conduit. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(4):1463-1476.
[44] GAIHRE B, POTES MA, SERDIUK V, et al. Two-dimensional nanomaterials-added dynamism in 3D printing and bioprinting of biomedical platforms: unique opportunities and challenges. Biomaterials. 2022;284:121507.
[45] ZHANG D, YAO Y, DUAN Y, et al. Surface-anchored graphene oxide nanosheets on cell-scale micropatterned Poly (d, l-lactide-co-caprolactone) conduits promote peripheral nerve regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(7):7915-7930.
[46] QIAN Y, CHENG Y, OUYANG Y, et al. Multilayered spraying and gradient dotting of nanodiamond-polycaprolactone guidance channels for restoration of immune homeostasis. NPG Asia Mater. 2019;11(1):1-24.
[47] ORECCHIONI M, BEDOGNETTI D, SGARRELLA F, et al. Impact of carbon nanotubes and graphene on immune cells. J Transl Med. 2014;12(1):138.
[48] CARTONI R, NORSWORTHY MW, BEI F, et al. The mammalian specific protein armcx1 regulates mitochondrial transport during axon regeneration. Neuron. 2016;92(6):1294-1307.
[49] FÜNFSCHILLING U, SUPPLIE LM, MAHAD D, et al. Glycolytic oligodendrocytes maintain myelin and long-term axonal integrity. Nature. 2012;485(7399):517-521.
[50] HERVERA A, DE VIRGILIIS F, PALMISANO I, et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate axonal regeneration through the release of exosomal NADPH oxidase 2 complexes into injured axons. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(3):307-319.
[51] KIM M, KIM H, KIM D, et al. Heme oxygenase 1 in schwann cells regulates peripheral nerve degeneration against oxidative stress. ASN Neuro. 2019;11:175909141983894.
[52] LV W, DENG B, DUAN W, et al. Schwann cell plasticity is regulated by a weakened intrinsic antioxidant defense system in acute peripheral nerve injury. Neuroscience. 2018;382:1-13.
[53] AKHAVAN O, GHADERI E, AKHAVAN A. Size-dependent genotoxicity of graphene nanoplatelets in human stem cells. Biomaterials. 2012;33(32):8017-8025.
[54] PULSKAMP K, DIABATÉ S, KRUG HF. Carbon nanotubes show no sign of acute toxicity but induce intracellular reactive oxygen species in dependence on contaminants. Toxicol Lett. 2007;168(1):58-74.
[55] YANG K, LI Y, TAN X, et al. Behavior and toxicity of graphene and its functionalized derivatives in biological systems. Small. 2013;9(9-10):1492-1503.
[56] LI Y, LIU Y, FU Y, et al. The triggering of apoptosis in macrophages by pristine graphene through the MAPK and TGF-beta signaling pathways. Biomaterials. 2012;33(2):402-411.
[57] LALWANI G, D’AGATI M, KHAN AM, et al. Toxicology of graphene-based nanomaterials. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;105(Pt B):109-144.
[58] SASIDHARAN A, PANCHAKARLA LS, SADANANDAN AR, et al. Hemocompatibility and macrophage response of pristine and functionalized graphene. Small. 2012;8(8):1251-1263.
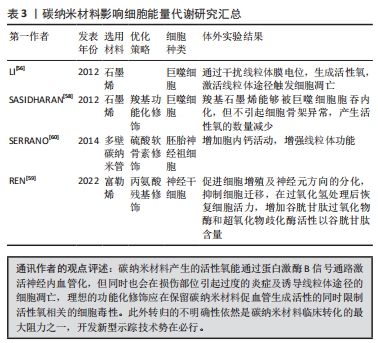
[59] REN H, LI J, PENG A, et al. Water-soluble, alanine-modified fullerene c60 promotes the proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5714.
[60] SERRANO MC, NARDECCHIA S, GARCÍA-RAMA C, et al. Chondroitin sulphate-based 3D scaffolds containing MWCNTs for nervous tissue repair. Biomaterials. 2014;35(5):1543-1551.
[61] LIU Z, CAI W, HE L, et al. In vivo biodistribution and highly efficient tumour targeting of carbon nanotubes in mice. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2(1):47-52.
[62] PANWAR N, SOEHARTONO AM, CHAN KK, et al. Nanocarbons for biology and medicine: sensing, imaging, and drug delivery. Chem Rev. 2019;119(16):9559-9656.
[63] SONG S, SHEN H, YANG T, et al. Indocyanine green loaded magnetic carbon nanoparticles for near infrared fluorescence/magnetic resonance dual-modal imaging and photothermal therapy of tumor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(11):9484-9495.
[64] WANG H, YANG ST, CAO A, et al. Quantification of carbon nanomaterials in vivo. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46(3):750-760.
[65] LIU L, ZHU C, FAN M, et al. Oxidation and degradation of graphitic materials by naphthalene-degrading bacteria. Nanoscale. 2015;7(32):13619-13628.
[66] LI D, HU X, ZHANG S. Biodegradation of graphene-based nanomaterials in blood plasma affects their biocompatibility, drug delivery, targeted organs and antitumor ability. Biomaterials. 2019;202:12-25.
[67] NEWMAN L, JASIM DA, PRESTAT E, et al. Splenic capture and in vivo intracellular biodegradation of biological-grade graphene oxide sheets. ACS Nano. 2020;14(8):10168-10186.
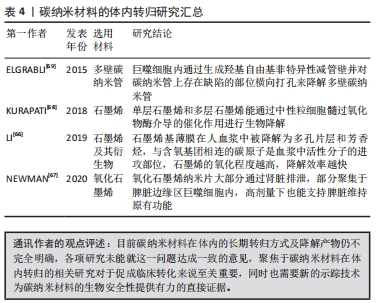
[68] KURAPATI R, MUKHERJEE SP, MARTÍN C, et al. Degradation of single-layer and few-layer graphene by neutrophil myeloperoxidase. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018;57(36):11722-11727.
[69] ELGRABLI D, DACHRAOUI W, MÉNARD-MOYON C, et al. Carbon nanotube degradation in macrophages: live nanoscale monitoring and understanding of biological pathway. ACS Nano. 2015;9(10):10113-10124.
|