[1] 杨连甲,唐农轩.骨科临床病理学[M].西安:世界图书出版西安有限公司, 2020:150.
[2] 汪国翔,章晓云.骨关节炎病变过程中炎症细胞因子及相关信号通路的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2266-2273.
[3] 易南星,梁倩倩,张伟强,等.骨性关节炎相关滑膜炎症研究进展[J].昆明医科大学学报,2019,40(3):136-139.
[4] 李元城,张卫国.关节软骨损伤治疗进展[J].解放军医学杂志,2013,38(5): 423-427.
[5] CONAGHAN PG, ARDEN N, AVOUAC B, et al. Safety of Paracetamol in Osteoarthritis: What Does the Literature Say? Drugs Aging. 2019;36(Suppl 1):7-14.
[6] MACHADO GC, MAHER CG, FERREIRA PH, et al. Efficacy and safety of paracetamol for spinal pain and osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled trials. BMJ. 2015;350:h1225.
[7] MELLATI A, HASANZADEH E, GHOLIPOURMALEKABADI M, et al. Injectable nanocomposite hydrogels as an emerging platform for biomedical applications: A review. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;131:112489.
[8] ZHAO H, LIU M, ZHANG Y, et al. Nanocomposite hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Nanoscale. 2020;12(28):14976-14995.
[9] 韩明睿,刘倩倩,孙洋.骨关节炎发病机制及药物调控新进展[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):807-812.
[10] LI M, YIN H, YAN Z, et al. The immune microenvironment in cartilage injury and repair. Acta Biomater. 2021;140:23-42.
[11] KOEN R. Advanced nanogel engineering for drug delivery. Soft Matter. 2008;5(4): 707-715.
[12] 杨洁.基于基因工程多肽杂化纳米水凝胶的制备及在生物医学中的应用[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2016.
[13] WANG Y, YUAN K, SHANG Z, et al. Construction of nanohydrogels for enhanced delivery of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs and improving chemotherapy efficacy. Eur Polym J. 2023;186:111838-111846.
[14] GHIMIRE A, ZORE OZ, THILAKARATHNE VK, et al. “Stable-on-the-Table” Biosensors: Hemoglobin-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Nanogel BioElectrodes with High Thermal Stability and Enhanced Electroactivity. Sensors (Basel). 2015;15(9):23868-23885.
[15] 苏日辉,夏凌,李攻科,等.智能水凝胶在分离分析中的应用研究进展[J].分析科学学报,2019,35(3):377-384.
[16] ZHANG Y, ZHANG P, GAO X, et al. Preparation of exosomes encapsulated nanohydrogel for accelerating wound healing of diabetic rats by promoting angiogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;120:111271.
[17] QUAZI MZ, PARK N. DNA Hydrogel-Based Nanocomplexes with Cancer-Targeted Delivery and Light-Triggered Peptide Drug Release for Cancer-Specific Therapeutics. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(5):2127-2137.
[18] THOMAS J, GUPTA N, JOSEPH JP, et al. Mechanical Integrity in a Dynamic Interpenetrating Hydrogel Network of Supramolecular Peptide-Polysaccharide Supports Enhanced Chondrogenesis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(12):5798-5809.
[19] HSU MN, LUO R, KWEK KZ, et al. Sustained release of hydrophobic drugs by the microfluidic assembly of multistage microgel/poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticle composites. Biomicrofluidics. 2015;9(5):052601.
[20] SUN P, JIAO J, WANG X, et al. Nanomedicine hybrid and catechol functionalized chitosan as pH-responsive multi-function hydrogel to efficiently promote infection wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;238:124106.
[21] CORREA S, GROSSKOPF AK, KLICH JH, et al. Injectable liposome-based supramolecular hydrogels for the programmable release of multiple protein drugs. Matter. 2022;5(6):1816-1838.
[22] MA L, YE H, LIU L, et al. Polypropylene membranes with high adsorption capacity and anti-adhesion properties achieved by hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonded self-assembly for uranium extraction from seawater. Chem Eng J. 2023; 451(P2). doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138696
[23] OREFFO RO, DRIESSENS FC, PLANELL JA, et al. Growth and differentiation of human bone marrow osteoprogenitors on novel calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials. 1998;19(20):1845-1854.
[24] BOSE S, TARAFDER S. Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering: A review. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(4): 1401-1421.
[25] LIANG H, JIN C, MA L, et al. Accelerated Bone Regeneration by Gold-Nanoparticle-Loaded Mesoporous Silica through Stimulating Immunomodulation. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2019;11(44):41758-41769.
[26] YANG Q, YIN H, XU T, et al. Engineering 2D Mesoporous Silica@MXene-Integrated 3D-Printing Scaffolds for Combinatory Osteosarcoma Therapy and NO-Augmented Bone Regeneration. Small. 2020;16(14):e1906814.
[27] ZHOU P, XIA Y, CHENG X, et al. Enhanced bone tissue regeneration by antibacterial and osteoinductive silica-HACC-zein composite scaffolds loaded with rhBMP-2. Biomaterials. 2014;35(38):10033-10045.
[28] KIM KJ, JOE YA, KIM MK, et al. Silica nanoparticles increase human adipose tissue-derived stem cell proliferation through ERK1/2 activatio. Int J Nanomed. 2015;10:2261-2272.
[29] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020; 129:110452.
[30] ARRA M, SWARNKAR G, KE K, et al. LDHA-mediated ROS generation in chondrocytes is a potential therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3427.
[31] BOLDUC JA, COLLINS JA, LOESER RF. Reactive Oxygen Species, Aging and Articular Cartilage Homeostasis. Free Radical Bio Med. 2018;132:73-82.
[32] MOTTA F, BARONE E, SICA A, et al. Inflammaging and Osteoarthritis. Clin Rev Allerg Immu. 2022;64(2):222-238.
[33] YAO H, KANG J, LI W, et al. Novel β-TCP/PVA bilayered hydrogels with considerable physical and bio-functional properties for osteochondral repair. Biomed Mater. 2017;13(1):015012.
[34] NEDUNCHEZIAN S, WU C, WU S, et al. Characteristic and Chondrogenic Differentiation Analysis of Hybrid Hydrogels Comprised of Hyaluronic Acid Methacryloyl (HAMA), Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA), and the Acrylate-Functionalized Nano-Silica Crosslinker. Polymers-Basel. 2022;14(10):2003.
[35] YANG G, GAN M, ZHU J, et al. A multifunctional anti-inflammatory drug that can specifically target activated macrophages, massively deplete intracellular H2O2, and produce large amounts CO for a highly efficient treatment of osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 2020;255:120155.
[36] 凌沛学,梁虹,贺艳丽,等.透明质酸钠在关节疾病中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(1):1-4.
[37] 许鹏,王效东,郭雄.透明质酸与骨关节炎[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2002,6(5): 360-363.
[38] WANG M, DENG Z, GUO Y, et al. Designing functional hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Mater Today Bio. 2022;17:100495.
[39] 李棋,唐新,裴福兴,等.透明质酸在骨关节疾病中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(47):8835-8839.
[40] 张越,师宪宪,于奕峰.壳聚糖微球的制备方法研究进展[J].河北科技大学学报,2013,34(5):434-439.
[41] 祝珊珊,谭博文,秦飞,等.槲皮素通过PTEN/PI3K/JNK信号通路减轻小鼠RAW264.7巨噬细胞炎症[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2023,39(3):510-519.
[42] HU Y, GUI Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Quercetin alleviates rat osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes, modulating synovial macrophages polarization to M2 macrophages. Free Radical Bio Med. 2019;145(C):146-160.
[43] FERNANDES TL, GOMOLL AH, LATTERMANN C, et al. Macrophage: A Potential Target on Cartilage Regeneration. Front Immunol. 2020;11:111.
[44] WU CL, HARASYMOWICZ NS, KLIMAK MA, et al. The role of macrophages in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2020;28(5):544-554.
[45] ZHANG L, XING R, HUANG Z, et al. Inhibition of Synovial Macrophage Pyroptosis Alleviates Synovitis and Fibrosis in Knee Osteoarthritis. Mediat Inflamm. 2019; 2019:2165918.
[46] YING J, WANG P, ZHANG S, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 promotes articular cartilage repair through canonical Smad and Hippo pathways in bone mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2018;192:84-90.
[47] EL-REFAIE WM, ELNAGGAR YSR, EL-MASSIK MA, et al. Novel Self-assembled, Gel-core Hyaluosomes for Non-invasive Management of Osteoarthritis: In-vitro Optimization, Ex-vivo and In-vivo Permeation. Pharm Res. 2015;32(9):2901-2911.
[48] YAO Y, WEI G, DENG L, et al. Visualizable and Lubricating Hydrogel Microspheres Via NanoPOSS for Cartilage Regeneration. Adv Sci. 2023;10(15):e2207438.
[49] LI T, YANG J, WENG C, et al. Intra-articular injection of anti-inflammatory peptide-loaded glycol chitosan/fucoidan nanogels to inhibit inflammation and attenuate osteoarthritis progression. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;170:469-478.
[50] CHEN P, MEI S, XIA C, et al. The amelioration of cartilage degeneration by photo-crosslinked GelHA hydrogel and crizotinib encapsulated chitosan microspheres. Oncotarget. 2017;8(18):30235-30251.
[51] CHEN R, XIA C, MEI S, et al. Intra-articular delivery of sinomenium encapsulated by chitosan microspheres and photo-crosslinked GelMA hydrogel ameliorates osteoarthritis by effectively regulating autophagy. Biomaterials. 2016;81:1-13.
[52] ZHOU Y, LIANG K, ZHAO S, et al. Photopolymerized maleilated chitosan/methacrylated silk fibroin micro/nanocomposite hydrogels as potential scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;108:383-390.
[53] Permatasari DA, Karliana D, Iskandarsyah I, et al. Quercetin prevent proteoglycan destruction by inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9, matrix metalloproteinase-13, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-5 expressions on osteoarthritis model rats. J Adv Pharm Technol. 2019; 10(1):2-8.
[54] MA Y, YANG H, ZONG X, et al. Artificial M2 Macrophages for Disease-Modifying Osteoarthritis Therapeutics. Biomaterials. 2021;274:120865.
[55] ZHU W, CUI H, OUALAMB B, et al. 3D bioprinting mesenchymal stem cell-laden construct with core–shell nanospheres for cartilage tissue engineering. Nanotechnology. 2018; 29(18):185101.
[56] 李诚,郑国爽,蒯贤东,等.海藻酸盐支架修复关节软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(7):1080-1088.
[57] 王迎军,刘康时.生物医学材料的研究与发展[J].中国陶瓷,1998(5):26-29,37.
[58] FORMICA FA, ÖZTÜRK E, HESS SC, et al. A Bioinspired Ultraporous Nanofiber-Hydrogel Mimic of the Cartilage Extracellular Matrix. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016; 5(24):3129-3138.
[59] GUNES OC, ALBAYRAK AZ, TASDEMIR S, et al. Wet-electrospun PHBV nanofiber reinforced carboxymethyl chitosan-silk hydrogel composite scaffolds for articular cartilage repair. J Biomater Appl. 2020;35(4-5):515-531.
[60] MOEINZADEH S, PAJOUM SHARIATI SR, JABBARI E. Comparative effect of physicomechanical and biomolecular cues on zone-specific chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2016;92:57-70.
[61] NAJAFI R, CHAHSETAREH H, PEZESHKI-MODARESS M, et al. Alginate sulfate/ECM composite hydrogel containing electrospun nanofiber with encapsulated human adipose-derived stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;238:124098.
[62] KLEIN J. Chemistry. Repair or replacement--a joint perspective. Science. 2009; 323(5910):47-48.
[63] MOSTAKHDEMIN M, NAND A, RAMEZANI M. A novel assessment of microstructural and mechanical behaviour of bilayer silica-reinforced nanocomposite hydrogels as a candidate for artificial cartilage. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2021;116:104333.
[64] GRIMAUDO MA, CONCHEIRO A, ALVAREZ-LORENZO C. Nanogels for regenerative medicine. J Control Release. 2019;313:148-160.
[65] CAUSA F, NETTI PA, AMBROSIO L. A multi-functional scaffold for tissue regeneration: The need to engineer a tissue analogue. Biomaterials. 2007;28(34):5093-5099.
[66] GOLDBERG M, LANGER R, JIA X. Nanostructured materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2007;18(3):241-268.
[67] VAN RIJT S, HABIBOVIC P. Enhancing regenerative approaches with nanoparticles. J R Soc Interface. 2017;14(129):20170093.
[68] FARR J, GRACITELLI GC, SHAH N, et al. High Failure Rate of a Decellularized Osteochondral Allograft for the Treatment of Cartilage Lesions. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(8):2015-2022.
[69] GUO T, TIAN X, LI B, et al. Repair of articular cartilage and subchondral defects in rabbit knee joints with a polyvinyl alcohol/nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 biological composite material. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):176.
[70] YANG J, ZHANG YS, YUE K, et al. Cell-laden hydrogels for osteochondral and cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017;57:1-25.
[71] YANG Z, YI P, LIU Z, et al. Stem Cell-Laden Hydrogel-Based 3D Bioprinting for Bone and Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Front Bioeng Biotech. 2022;10:865770. |
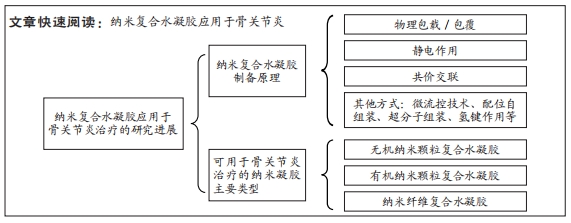
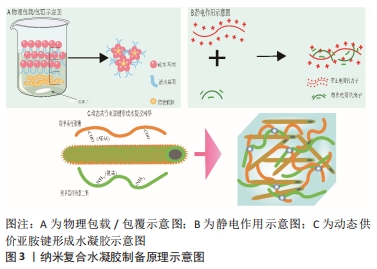
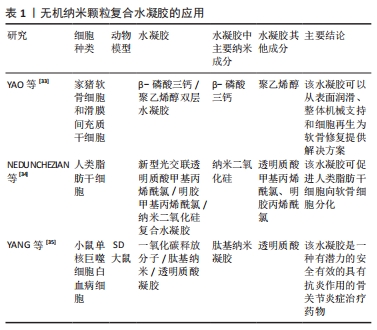
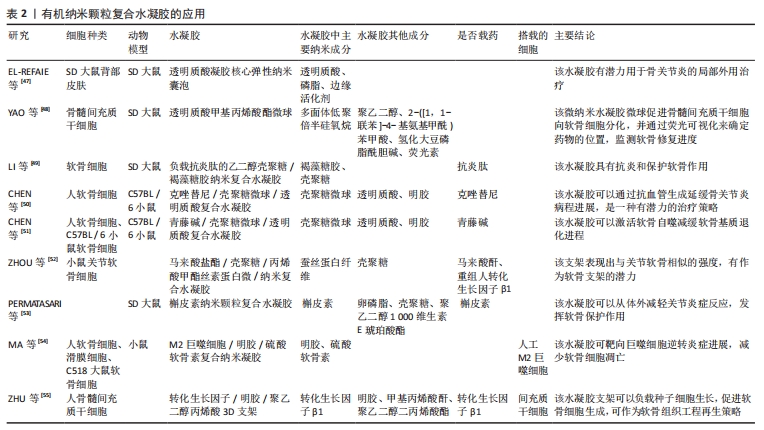

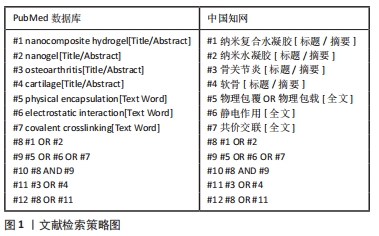
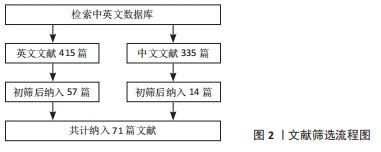
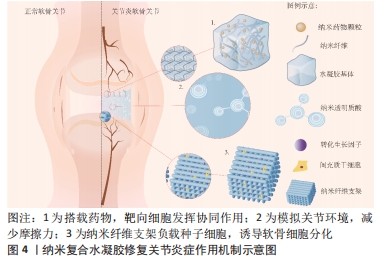 3.2 存在的不足与展望 有研究表明,去细胞化的骨软骨同种异体移植物在植入32例实验者关节内后2年失败率高达72%[68],由此可见,软骨移植目前还远不能达到人们所期望的效果。纳米复合水凝胶的制备方法丰富,可满足生物力学的要求,且具有通过纳米粒子的协同作用来增强刺激响应性等诸多优势,已被广泛应用于软骨组织修复领域[69-71]。该综述按照纳米复合水凝胶的纳米成分加以分类,介绍了多种纳米复合水凝胶修复关节软骨组织的最新研究进展,作者发现在缓解关节炎症和修复软骨组织时,使用纳米复合水凝胶的目的在于创造理想的支架,模仿天然细胞外基质的结构、组成、形态和生物活性,直到形成新的组织。然而毋庸置疑的是,纳米复合水凝胶在实际应用中仍存在缺陷,例如:纳米复合水凝胶中的纳米粒子能够有效提高水凝胶的力学性能,弥补破损软骨组织引起的关节失稳和软骨组织,但与此同时也需将其对细胞代谢、生物活性因子的释放和激活、营养物质的传输等纳入设计理念中。此外,水凝胶支架在体内的生物降解也应有严格的要求,在为机体自身组织愈合期间提供结构支撑、改善周围微环境的同时,也需尽可能减小生物材料自身降解对组织愈合的不良反应。目前大多数相关研究报道的实验设计都有局限性,多采用细胞或小型动物模型,且无论体内或体外实验的周期都较短,缺乏长期效果的观察。
3.2 存在的不足与展望 有研究表明,去细胞化的骨软骨同种异体移植物在植入32例实验者关节内后2年失败率高达72%[68],由此可见,软骨移植目前还远不能达到人们所期望的效果。纳米复合水凝胶的制备方法丰富,可满足生物力学的要求,且具有通过纳米粒子的协同作用来增强刺激响应性等诸多优势,已被广泛应用于软骨组织修复领域[69-71]。该综述按照纳米复合水凝胶的纳米成分加以分类,介绍了多种纳米复合水凝胶修复关节软骨组织的最新研究进展,作者发现在缓解关节炎症和修复软骨组织时,使用纳米复合水凝胶的目的在于创造理想的支架,模仿天然细胞外基质的结构、组成、形态和生物活性,直到形成新的组织。然而毋庸置疑的是,纳米复合水凝胶在实际应用中仍存在缺陷,例如:纳米复合水凝胶中的纳米粒子能够有效提高水凝胶的力学性能,弥补破损软骨组织引起的关节失稳和软骨组织,但与此同时也需将其对细胞代谢、生物活性因子的释放和激活、营养物质的传输等纳入设计理念中。此外,水凝胶支架在体内的生物降解也应有严格的要求,在为机体自身组织愈合期间提供结构支撑、改善周围微环境的同时,也需尽可能减小生物材料自身降解对组织愈合的不良反应。目前大多数相关研究报道的实验设计都有局限性,多采用细胞或小型动物模型,且无论体内或体外实验的周期都较短,缺乏长期效果的观察。