2.1 miR-214的生物学功能 人类miR-214基因来源于动力蛋白3基因(DNM3)互补链的14号内含子,位于人染色体1q24.3区域[11-12]。它的初级转录本可以产生4种成熟的miRNAs:其中miR-199-5p 和 miR-214-3p来自主链, miR-199-3p 和miR-214-5p来自副链[13]。miR-214主要通过与靶基因mRNA的3’端非编码区结合在转录后的水平抑制或沉默靶基因的表达,从而影响靶基因参与的通路及生物进程。2005年,CHENG等[14]发现miR-214与细胞生长和凋亡有关。后来,学者们发现miR-214可能是控制癌细胞信号网络的多效性枢纽之一,有助于协调重要的信号通路以及调控一些关键的基因表达[15-16]。随后,人们相继发现miR-214参与了许多生理和病理信号的调节,在癌症、心血管疾病、骨骼疾病等,可靶向不同的基因,调控mRNA的表达,影响蛋白质翻译,进而导致疾病的发生。
2.2 miR-214促进骨吸收和骨形成的机制 近年来,研究发现miR-214与许多骨组织代谢疾病相关。一些研究发现骨折、骨质疏松患者血清和骨标本的miRNAs表达中,miR-214的表达水平显著性升高[17-18]。而许多骨代谢疾病是骨吸收与骨形成的不平衡导致的,进一步研究可以猜测miR-214可能通过影响骨吸收与骨形成导致疾病的发生[19],但miR-214对骨吸收和骨形成进行调控的机制仍然不清楚。越来越多的研究发现,miR-214在不同的生理病理状态下可靶向不同的基因,增强破骨前体细胞向破骨细胞分化,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化。因此,接下来将回顾近几年发现的miR-214促进骨吸收和抑制骨形成靶向的基因及参与的通路,为将来的应用研究提供理论基础。
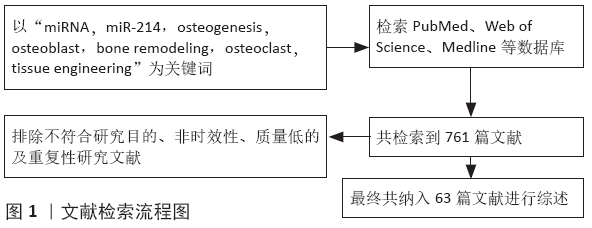
2.2.1 miR-214增强骨吸收的机制 目前研究发现,miR-214可通过靶向PTEN、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3,增强破骨细胞分化,促进骨吸收。PTEN为人第10号染色体缺失的磷酸酶及张力蛋白同源基因,可通过去磷酸化参与细胞调控,而磷酸化和去磷酸化是调节细胞活动的重要方式。生物信息学分析表明,Pten的 3’-UTR含有miR-214的结合位点。在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导破骨细胞分化过程中,miR-214水平与破骨细胞标志因子的表达上调一致;同时,过表达miR-214可使破骨细胞分化的标志因子Acp5、基质金属蛋白酶9、Ctsk等显著上调,破骨细胞数增多;而使用miR-214拮抗剂则使破骨细胞分化水平明显下调[20]。miR-214通过靶向PTEN[21],使PTEN水平降低,Akt磷酸化上调,激活PI3K /Akt/ NFATC1通路,破骨细胞特异性标志基因转录的主要调控因子NFATC1的表达增加,促进骨髓单核细胞向破骨细胞分化[20]。因此,磷脂酰肌醇三激酶/蛋白激酶B (PI3K/Akt) 信号通路可能是miR-214调控破骨细胞功能的信号通路网中心之一。此外,另一项研究在乳腺癌骨转移的破骨细胞中发现miR-214-3p显著升高,靶向肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3使其蛋白水平降低促进破骨细胞分化,使用miR-214-3p拮抗剂可使肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3蛋白的表达升高并减弱骨溶解转移的发展[22-23]。肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3是细胞因子产生和Ⅰ型干扰素的重要调节因子,它通过抑制核因子κ B信号通路抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的破骨细胞形成。在另一项前列腺癌的骨转移研究中,观察到其癌细胞来源的外泌体miR-214表达下调,抑制了核因子kB信号通路的表达[24]。miR-214 对破骨向分化调控的机制见图2。
这些研究证据表明,miR-214不是直接促进破骨相关的因子增强骨吸收,而是通过抑制PTEN、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3等蛋白的翻译,调控相关的通路增强破骨细胞分化,促进骨吸收。
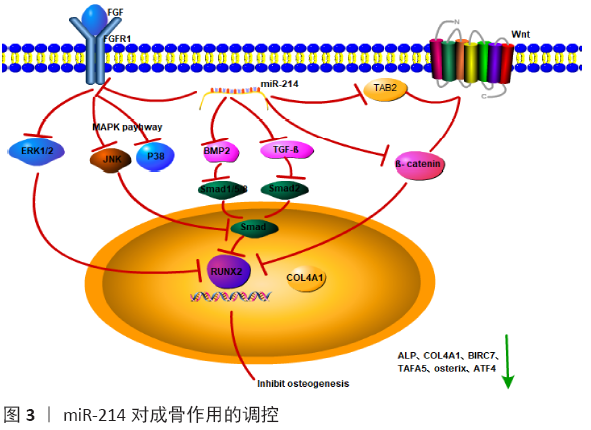
2.2.2 miR-214抑制骨形成的机制 随着年龄的增加,特别是在老年骨质疏松患者中,骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化水平降低,向脂肪细胞分化增强,导致脂肪进行性堆积和骨流失[25-26],而这种骨髓间充质干细胞分化倾向有可能是由于Wnt信号减弱引起的[27]。TAB2和β-catenin是Wnt通路中的关键介质:TAB2基因编码TAB2传递非典型的Wnt信号[28];CTNNB1编码β-catenin,它是典型的Wnt信号中的关键介质,刺激Runx2的表达。通过生物信息学预测发现,miR-214与TAB2和CTNNB1基因的3’端非翻译区具有很强的互补性[19],并且通过构建含有野生型和突变型TAB2和CTNNB1基因3’端非翻译区序列的质粒,结果证明了TAB2和CTNNB1是miR-214的靶基因[19]。在研究牙周韧带干细胞成骨分化中,miR-214通过抑制β-catenin抑制Wnt通路影响成骨分化[29]。另一研究骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中同样证明了上调miR–214抑制了β-catenin的表达进而使Wnt/β-catenin通路衰减,RUNX2水平下降,骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能力减弱[30]。此外,通过建立小鼠动物模型,证明了过表达miR-214-3p抑制了β-catenin信号通路,最终导致骨折延迟愈合[31]。综上,这些研究结果证明了Wnt/β- catenin通路是miR-214调控骨形成的重要信号通路之一。
成纤维细胞生长因子受体1是miR-214的另一靶基因,抑制miR-214可上调成纤维细胞生长因子受体1表达水平增强其下游ERK1/2的磷酸化和Runx2的表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[32]。同时,另一项研究证明了miR-214的上调抑制了JNK和p38蛋白的表达[33],使骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化受到抑制。而ERK1/2、JNK和p38都属于MAPK信号通路的主要途径,可见MAPK信号通路可能是miR-214调控骨形成的另一重要信号通路。miR-214还可通过TGF-β/Smad2[34]、BMP2/Smad信号通路调节骨形成[35]。抑制miR-214可上调成骨基因骨形态发生蛋白2的表达[36],而过表达miR-214则会延缓骨质疏松性骨折大鼠骨折愈合[37]。
COL4A1、BIRC7、TAFA5、osterix和ATF4也是miR-214的靶标基因。COL4A1可促进成骨细胞和细胞外基质的形成[38];BIRC7属于凋亡蛋白家族抑制因子,过表达BIRC7显著逆转了miR-214的抑制作用促进成骨分化[39];TAFA5可以增强核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的破骨细胞分化[40],在最新的成骨细胞研究中,miR-214表达降低的同时TAFA5的表达明显增加,使成骨分化受到抑制[41]。在骨质疏松患者中检测到miR‐214表达水平升高,同时osterix mRNA相应地减少[18]。SHI等[42]同样报道miR-214通过靶向Osterix,对C2C12成肌细胞的成骨分化具有抑制作用,然而也有专家质疑小鼠模型中缺乏Osterix相关的结合位点使结果不成立[43]。ATF4通过促进成骨细胞特异性基因的表达、细胞对氨基酸的摄取和Ⅰ型胶原的合成来促进骨形成[44],ATF4水平的降低抑制了人类牙周韧带干细胞的成骨分化[45-47]。
通过以上的研究发现,miR-214抑制骨形成的方式是多样化的,可直接抑制成骨分化相关的因子或通过调控FGFs/FGFRs、BMPs/Smad、Wnt、MAPKs信号通路等调节骨形成。因此,抑制成骨细胞中的miR-214可能是一种潜在的改善骨质疏松症的合成代谢策略[48]。miR-214对成骨作用的调控的机制见图3。
2.3 miR-214的应用研究进展 近年来,miRNAs因其体积小、在物种间具有完全保守的序列等优点在未来的治疗手段上被寄予厚望。直接在miRNA上进行功能修饰使其沉默或过表达,以及通过病毒、细胞外囊泡、生物支架材料等载体将miRNA递送到目标位点是目前的研究热点。然而载体系统的稳定性高效性和输入体内的miRNA的生物安全性的远期疗效仍需进一步探索[49]。使用反义miRNA寡核苷酸[50]、肽核酸、miRNA海绵体等可以沉默或过表达miRNA的表达[51],在miRNA的3’端和5’端进行修饰可以增加miRNA的稳定性和结合力[52],使它的模拟物或拮抗剂更好地发挥作用。使用病毒、生物支架材料包括细胞外囊泡等载体将miR-214模拟物或拮抗剂传递至体内可能是未来骨代谢疾病的一种治疗手段。但重要的是,由于基于miRNA的体内治疗尝试已经成功,使基于miRNA的疗法在未来成为可能。miR-214作为治疗靶点的潜在用途值得研究[11]。
2.3.1 miR-214模拟物或拮抗剂的载体系统
(1)病毒载体:通过病毒载体将基因转染到细胞在体外和体内实验中有很大的进展。LI等[53]将miR-214海绵体植入杆状病毒转染至骨髓间充质干细胞,可显著增强骨缺损修复的能力,为治疗骨质疏松性骨缺损开辟了新的途径。但是使用病毒载体可能会造成重大的风险,生物安全性得不到保障。因此,需要对病毒载体做进一步的表面修饰才有可能避免这些并发症。然而,由于成本高产生的低效益和生产规模的挑战性,更多的研究者已经在寻找更有效安全的方法(非病毒媒介)进行基因传递。
(2)生物支架材料:基于脂质、生物支架和纳米胶囊的缓释系统也通常用于miRNA递送[11]。生物支架材料方面,JAMES等[54]将miR-214拮抗剂负载于丝素材料上,在种植体表面制备涂层,在促进种植体界面成骨的同时避免全身不良反应,可能成为局部骨组织工程的新手段。另一研究则用聚乙烯亚胺功能化氧化石墨烯复合物负载miR-214抑制剂并与丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石(SF/HAP)组成SF/HAP/GPM支架[55]。同样,SUN等[56]将miR-214拮抗剂负载到多肽SDSSD上修饰聚氨酯PU纳米胶束合成SDSSD?PU/anti-miR-214输送系统,可以选择性地靶向成骨细胞表面,使骨形成增加,而且在体内没有明显的毒性或引发免疫反应。另一个支架材料磷酸钙具有生物相容性、可生物降解、无毒、无免疫原性等特点,且对包括RNA在内的各种分子具有很高的亲和力,易于获取经济效益相对较低。GRAHAM和VAN DER EB[57]首次证明了磷酸钙可用于基因传递。随后,有许多研究证明了磷酸钙纳米颗粒负载miRNAs和siRNAs可以形成稳定的复合物,被靶向细胞内吞,使磷酸钙颗粒成为一种有潜力的转染媒介。并且,生物支架材料可有效地控制miR-214抑制剂地释放,在不负载干细胞的情况下,在骨缺损处获得良好的骨再生。然而,要成为成功的载体,miRNAs缓释系统需要克服许多挑战,包括高效传递、生物稳定性、较短的体内半衰期和明确的靶向性等。
(3)外泌体介导的miRNAs靶向传递:外泌体作为细胞自身分泌的携带miRNA的一种胞外囊泡,是安全有效的体内传递miRNAs的另一途径[10] 。由于骨源性外泌体miRNAs在基因表达调控中的关键作用,骨源性外泌体miRNAs参与调节骨骼重构功能已成为研究热点。据报道,破骨细胞来源的外泌体中携带大量的miR-214[17,58],并可以转移至成骨细胞发挥作用。由此可看出,外泌体可能是miR-214发挥重要作用的媒介。此外,工程外泌体代表了一种很有前途的系统[59],它可以用于RNAi分子的靶向传递,同时避免免疫系统的检测[60-61],在靶向载体方向具有很大的有优势。
2.3.2 疾病检测及诊断预后的标志物 miRNAs是进化上保守、稳定的非编码小RNA分子,由于其在血浆中的稳定性、易于分离以及与特定疾病状态相关的独特表达,是循环生物标志物开发的理想候选,越来越多的miRNAs已被确定为骨骼疾病的诊断和预后生物标志物以及治疗工具。一项新研究认为对miR-214进行血清学检测有可能给强直性脊柱炎的诊断提供新的思路[59]。同样,根据骨质疏松患者中miR‐214表达的差异,可能也可作为原发性骨质疏松症临床应用的潜在生物标志物[18]。因此,疾病中miR-214的表达差异可用于前瞻性地预测疾病的发展及预后,监测治疗效果[61-63]。