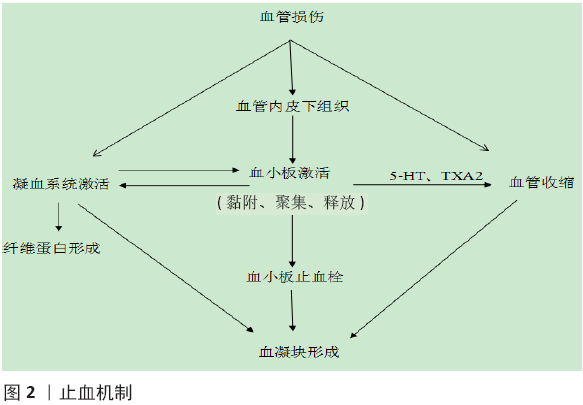
2.1 止血主要机制 止血是控制损伤部位出血的过程,通过血凝块的形成封闭破裂的血管,从而止血。止血机制涉及血小板和可溶性凝血因子,它们总是以非活性形式存在于血液中,随时准备好在受伤后几秒内被激活。当血管受损时血液暴露于周围组织的成分中,其中一些成分与血小板结合并活化血小板,活化的血小板参与止血的所有阶段:首先,活化的血小板分泌诱导血管收缩的化学物质,从而减少失血,这被称为血管痉挛,是对组织损伤最直接的反应,血管痉挛也可以由局部疼痛感受器或内皮细胞释放的物质引发;其次,活化血小板彼此之间形成黏附,聚集在一起形成血小板止血栓,同时分泌能吸引附近其他血小板的物质,形成正反馈回路,加速止血栓的形成和传播;第三,活化血小板的表面充当了凝固的场所,形成血凝块(图2)。
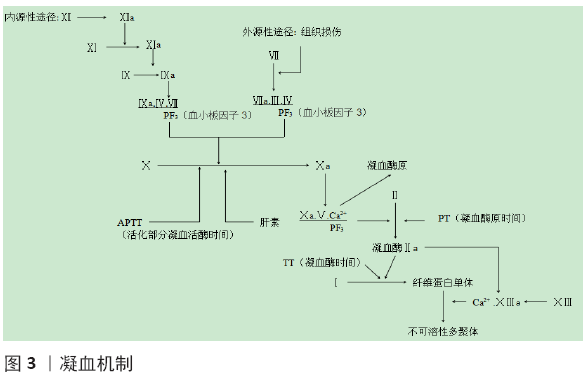
凝血是一种复杂的连锁反应,其中一个凝血因子激活多步骤途径的下一个凝血因子。凝血2种激活途径:外源性途径由组织损伤引起,内源性途径涉及血管内多个因子,是一种正反馈回路,可放大凝血功能。这两种途径融合成共同途径,产生凝血酶并最终产生纤维蛋白。凝血酶在凝血级联反应中起重要作用,它通过切割可溶性纤维蛋白原以产生不溶性纤维蛋白;凝血酶还可以进一步激活血小板,并启动正反馈途径(图3)。
如果血小板止血栓的形成不能提供足够的止血效果,则采用机械和热力的方式帮助凝血,传统的方法有施加压力、结扎和透热电凝法,当这些方法对出血处理无效时应使用止血材料。所有止血剂的目的都是通过模仿、促进或绕过凝血级联的特定步骤来起作用[4]。
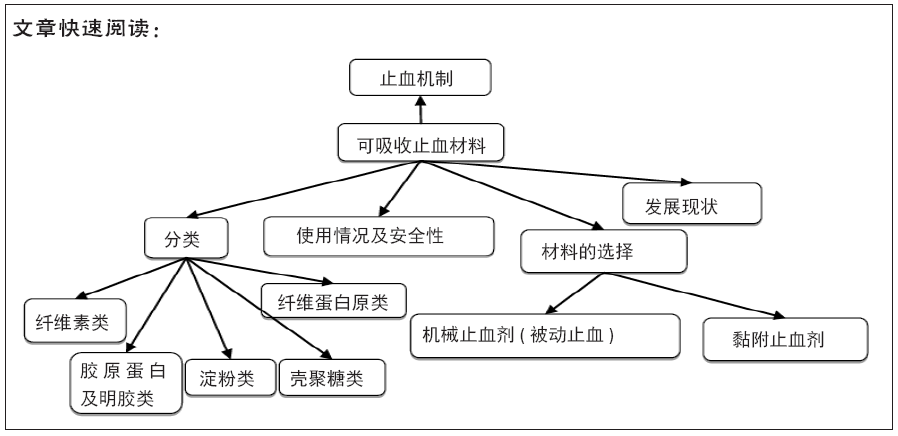
2.2 常见可吸收止血材料的分类
2.2.1 纤维素类 1945年氧化纤维素类止血材料被引入外科手术,其易于使用,具有良好的生物相容性和杀菌性。再生氧化纤维素是纤维素经过氧化处理制成的纤维素酸纱布状或棉状可吸收止血材料。再生氧化纤维素作为一种纤维素衍生物,无毒性,具有良好的生物相容性和生物降解性。再生氧化纤维素的降解产物含有葡萄糖和纤维二糖,可在体内2-7 d内被吸收,4-8周内完全降解。再生氧化纤维素的止血机制可能是由于材料表面粗糙导致血小板破裂,产生大量血小板凝血因子,将纤维蛋白原转化为纤维蛋白,形成血栓,从而发挥止血效果;或是纤维素中羟基与血浆中Ca2+形成交联键形成凝胶状血块,堵塞受损血管抑制出血。再生氧化纤维素类止血材料对抑制小血管出血有明显作用,被广泛应用于外科手术中,且对革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌有广谱杀菌作用[5]。
纤维素类止血材料具有棉纱的外观纹理及柔软、薄的特性,可以方便修剪成任意形状,以符合出血部位的位置要求,易与出血部位充分接触,方便包裹和填充伤口,从而提高止血效果,达到快速止血的目的[6]。目前纤维素类止血材料是市场中份额比重最大的,主要是各种可吸收纱布类产品,临床上常用材料为美国Johnson & Johnson公司的Surgicel?、北京泰科斯曼科技发展有限公司泰绫?及云南德华生物药业有限公司的医用即溶止血纱布德纳泰?。Surgicel?对周围组织几乎无特异性反应,可作为止血基质促血块凝结,加速止血全过程;使用方便,极易附着在不规则出血面,且在器械、手套等医用器械表面无黏附,但是纤维素类产品有很强的吸水性,所以使用时应保持器械干燥,再加以取用[7]。
2.2.2 淀粉类 淀粉是葡萄糖的高聚合物,可在体内通过α-淀粉酶降解为葡萄糖。淀粉含有大量羟基,具有良好的亲水性。随着淀粉改性技术的发展,可以在不影响其降解性的情况下提高强度,例如加入增塑剂可以提高淀粉的塑性。改性后的淀粉(如微孔淀粉、交联淀粉等)与天然淀粉相比具有许多新的性能[8]。
淀粉类止血材料的原理是微孔多聚糖颗粒的表面微孔起到分子筛作用,可在瞬间吸取血液中的水分,将血液中的有形成分(如:凝血因子、血小板、纤维蛋白、红细胞等)聚集在颗粒表面,产生“即时凝胶”,起到机械封堵血管破口作用;与此同时,血小板、凝血因子和纤维蛋白的局部浓度显著升高,同时启动激活并加快加强了内源性凝血机制[9]。淀粉类止血产品适用于心胸外科手术、泌尿外科和耳鼻喉科外科手术。
淀粉类代表产品有美国Medafor公司的Arista? 阿里斯泰止血粉、杭州协合医疗器械有限公司的欣速聆?。Arista?AH可以储存在室温下,保质期长,便于取用,而且装有不同剂量的装配涂抹器,可以将干燥产品涂抹在表面上。且具有生物相容性,可在24-48 h内被吸收[10]。
2.2.3 胶原蛋白及明胶类 胶原蛋白是软组织的主要成分,包含3种相互缠绕的蛋白质,呈三螺旋结构。胶原蛋白占细胞外基质的很大一部分,在组织中起结构支架作用,具有良好的细胞相容性,并影响细胞功能,如分化、迁移和蛋白质的合成。胶原蛋白具有大面积吸水表面,将材料贴敷于创伤表面,可以吸入比自身质量大数倍的血流量血液,吸水量可达自身体积30倍以上。胶原蛋白敷料可以提供抗炎、抗纤维化和止痛的特性,并促进血管生成,使机体恢复正常状态和功能。
胶原蛋白敷料中最常使用是Ⅰ型或变性的Ⅰ型胶原蛋白,且大多数胶原蛋白敷料中都含有牛、羊或经过处理的猪胶原蛋白[11]。胶原止血剂领域的主要改进和变化在于产品形式的改变,第一个胶原蛋白类止血产品,美国Avicone公司的AviteneTM最初是粉状物,该产品系列已扩展到非织造纤维网材料及海绵形式[12]。许多胶原蛋白或变性胶原蛋白敷料将胶原蛋白与银结合在一起,以减少敷料中的生物负荷[13]。
明胶是一种水解胶体,由胶原蛋白经酶(酸或碱)水解制成,明胶类止血材料在血液凝结级联反应的最后阶段起作用,以促进纤维蛋白的形成,有海绵、粉末和颗粒等形式。明胶材料能够适应不规则伤口和手术腔。明胶吸收的血液最多可达其质量的40倍,并膨胀至其初始尺寸的200%。干燥的明胶海绵可以切成任何大小和形状,可以干涂也可以直接施加于出血表面,一旦施加压力就可以止血。明胶的代表产品有美国ETHICON公司的Surgifoam?和Baxter公司的Floseal?。明胶的优点:成本相对较低,可以在室温下保存,具有良好的吸收性和耐受性,使用明胶类止血材料很少有脓肿或肉芽肿形成的报道。但是存在一些安全问题,包括在狭小空间内使用时可能会“膨胀”,从而可能造成组织损坏, 因此不能在血管内使用[14]。
与氧化纤维素不同,胶原蛋白及明胶类止血材料的pH值为中性,因此可以单独使用,或者与局部生物制剂如凝血酶一起使用,有助于止血,通常4-6周被体内吸收,因此可以留置体腔内或创腔内[15]。
2.2.4 壳聚糖 壳聚糖是一种天然的生物聚合物,由几丁质脱乙酰化生成,是一种碱性多糖,由葡萄糖胺聚合而成,储量丰富,来源广泛,自身和分解产物无毒。葡萄糖胺是一种存在于人体中的物质,具有良好的生物相容性,这些特性都使之成为一种理想的生物医学材料。壳聚糖由于其聚阳离子性质具有黏膜黏附特性,可与黏液中的唾液酸-糖蛋白产生相互作用。氨基葡萄糖聚体带正电荷的游离氨基具有止痛作用,该止痛作用是由于离子在炎症区域释放而产生的[16]。壳聚糖及其衍生物能够增强血小板的黏附和聚集作用,通过与带负电荷的血小板和红细胞的相互作用导致血液凝块形成;此外,血小板被激活并释放有效物质,从而加速凝血。壳聚糖还具有抗菌活性,可与其他材料制成止血敷料一起使用。壳聚糖是具有生物活性理想止血剂的候选者。
壳聚糖代表产品有美国Medtrade公司的CeloxTM、青岛博益特生物材料有限公司的术益纱?。CeloxTM是由几丁质的天然来源(虾和其他甲壳类动物壳)提纯而成的壳聚糖共聚物,可用于多种生物医学应用,包括促进伤口愈合、骨组织工程和止血,是一种适用于急性创伤性出血的快速止血产品。仅含有壳聚糖的止血材料止血能力有限,为了改善止血性能,将壳聚糖与其他功能成分混合制备基于壳聚糖的复合材料,可以实现快速有效的止血。壳聚糖的复合材料已被制成多种形式如:薄膜、海绵、水凝胶、颗粒和纤维[17]。
2.2.5 纤维蛋白原类 纤维蛋白原类止血材料主要由人类血浆制备的纤维蛋白原(含有凝血因子ⅩⅢ、纤维结合蛋以及抑肽酶)和凝血酶浓缩物组成,当这两种成分混合时模拟凝血酶链反应的最后一步,通过凝血酶激活纤维蛋白原,纤维蛋白原逐渐聚集最后形成纤维蛋白固化物,起到术前和术后止血和组织黏合作用。纤维蛋白密封剂于1998年批准上市,是目前被美国食品药品管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)批准用作止血剂、密封剂和黏合剂的唯一制剂。液体胶水类产品主要有美国Baxter公司的Tisseel?、Tissucol?、美国ETHICON公司的Evicel?;干燥贴片类产品有美国Baxter公司的Tachosil?和美国CSL Behring公司的Tachocomb?。纤维蛋白类的密封剂在神经外科中被广泛应用,可以通过提供水密封闭,防止脑脊液泄漏。Tisseel?、Tissucol?是纤维蛋白密封剂最早期的产品,上市已超过30年[18]。
2.3 可吸收止血材料使用情况及安全性 选择合适的止血材料需要临床安全性数据,大多数止血材料的研究都是在创伤和围术期进行的,所以有必要评估止血材料在更复杂重症监护环境中的功效和安全性。
2.3.1 纤维素类 通常,纤维素从体腔部位吸收时并不发生细胞反应或纤维变性。国内外内文献报道氧化再生纤维素在心脏外科手术及妇科腹腔镜止血等方面作用明显,安全可靠[19]。Surgicel?是最经典的局部止血剂之一,被广泛用于外科领域,易于操作,价格便宜,并且不会有凝血蛋白类产品所具有的传播病毒感染的风险。除了上述优点,ACUNER 等[20]的研究显示,再生氧化纤维素单独或与秋水仙碱联合使用可以有效预防囊膜挛缩。
但是Surgicel?在使用过程中也存在感染、不完全吸收、压迫神经等不良事件。李劲松[21]对手术中41例使用Surgicel?止血纱布贴敷大脑半球肿瘤残腔的患者进行临床分析,发现其中13例术后出现较严重颅高压症状。LIN等[22]的报道显示,在颅内出血清创手术中使用Surgicel?可能与手术中形成肿瘤状占位性病变引起的肉芽肿有关,建议在外科手术的时候需要谨慎。ARORA 等[23]报道2例在法洛氏四联症心脏手术中使用Surgicel?止血出现不良反应的患者。ROYDS等[24]报道了1例接受甲状腺全切除术治疗多结节性甲状腺肿的患者使用Surgicel?对双侧喉返神经周围进行止血,出现伤口明显红斑和肿胀的现象。
尽管再生氧化纤维素可以在体内被吸收,但取决于材料用量、血液饱和度和组织部位,使用过量材料可能在术后后期无法生物降解,导致肉芽形成,使得残留/复发性肿瘤的放射学和临床鉴别诊断变得复杂。相关临床手术应尽可能控制材料用量或者采用其他止血方式,以减少不良反应的发生。在矫形过程或视神经周围手术中,应该在出血停止时立刻取走止血材料。在心脏及颅骨、脊髓和胸膜腔(靠近脊柱)等神经外科手术中应该注意使用,以避免存在因压迫或局部炎症反应引起局部缺血的风险[23]。尚没有结论表明使用再生氧化纤维素可控制胆汁、尿液、胰腺和气腔的渗漏。外科医生应该注意到使用Surgicel?的风险,在使用时应使用最小有效量的再生氧化纤维素,并去除无助止血的多余物质。另外,在尝试手术之前应准确评估患者手术史。
2.3.2 淀粉类 淀粉类止血材料可以适用于各种涂抹器。Arista?AH遇到血液时会形成分子晶格,从而产生止血活性。已被应用在心胸外科、泌尿外科、普外科、耳鼻喉科及整形外科[10]。
一项顾性研究显示,在心胸外科手术期间应用Arista?AH可以减少术中止血时间,减少术后失血量,并减少术后48 h的输血需求。此外没有与Arista?AH广泛应用相关的不良事件发生。在复杂的心胸外科手术中,Arista?AH作为辅助的局部止血剂可以安全有效地减少失血[25]。刘鹏等[26]报道Arista? AH对脊柱后路手术中的出血止血效果与常规外科操作技术相同,优点是手术中操作简单,而在对于前路手术中椎体切除过程中的止血效果略优于常规操作技术。
刘天盛等[27]的研究显示,在全髋关节置换术中使用微孔多聚糖颗粒可减少术后伤口引流及输血需求。但这和BRUCKNER等[25]的研究结论不同。BRUCKNER等认为Arista?AH表现出较差的出血控制,对原发性全膝关节置换术中血肿形成或伤口感染发生率无临床显著影响,在这种外科手术环境中可能无需使用,或者更适合于低出血量的不同应用。
需要注意的是与流体接触后,微孔多聚糖颗粒可立即膨胀至其原始体积的5倍,由于其膨胀作用,禁止在狭窄区域使用Arista?AH。虽然微孔多聚糖颗粒可以减少出血已被明确,但是其可吸收止血性在其他文献中也受到质疑[25]。
2.3.3 胶原蛋白及明胶类 胶原蛋白在许多手术中和术后都起着关键作用,天然胶原蛋白由于其低抗原性及与大多数内源性组织的生物相容性,被用于外科手术修复。基于胶原蛋白的伤口敷料可用于覆盖烧伤创面和治疗溃疡,与生长因子和基于细胞的全层创面治疗相比具有经济优势[28]。临床数据也显示胶原蛋白在临床方面止血效果良好。
研究表明,伤口敷料也可以为愈合伤口提供临时的屏障功能,并建立潮湿的愈合环境,从而加快伤口愈合。胶原蛋白类敷料可以体外促进成纤维细胞的迁移和增殖,从而加速伤口修复的能力。WU 等[11]通过对2000至2016年同行发表的58篇文献研究显示,在擦伤、烧伤、糖尿病足溃疡和压迫伤的伤口中,使用再生氧化纤维素 /胶原蛋白敷料可以帮助控制和预防严重的组织炎症恶化并促进健康组织形成。鲁瑶[29]报道可吸收胶原蛋白止血海绵在腔镜甲状腺手术中具有安全、有效的止血效果。
ECHAVE 等[30]通过对2003至2013年期间所有类型外科手术中使用Floseal?有关的文献回顾认为,FloSeal?在外科手术中是一种有效的材料,可减少止血时间、术中和术后出血的频率及住院时间,从而减少卫生资源的消耗。XU等[31]的临床研究显示,在后路脊柱融合手术中止血胶原蛋白海绵比明胶海绵具有更好的止血效果,具有较低的术后引流量和失血量。
在涉及血液保存装置的外科手术中应小心使用牛胶原蛋白制品,因为这些制剂可以通过过滤器。明胶海绵的生产中会采用甲醛作为交联剂,甲醛残留物对人体极为有害,可产生刺激、过敏和诱变反应,因此必须严格控制甲醛残留含量;使用时可能会由于其膨胀而引起附近其他组织结构的压缩和坏死,因此应使用实现止血效果的最少量[32]。
2.3.4 壳聚糖 壳聚糖是有效的止血材料,但多数情况下用于战争和重大出血的动物模型。临床数据显示,壳聚糖在临床止血方面也有不错的效果。陈宏伟等[33]报道壳聚糖止血海绵对冠状动脉支架植入后股动脉拔管具有止血作用,并且并发症减少。EFEO?LU 等[34]通过对临床肝硬化患者小型口腔外科手术后出血进行随机单盲研究,结果显示CeloxTM和 Surgicel?两种止血材料均可有效控制出血。SEETHAMSETTY 等[35]也在口腔手术中得到结论:壳聚糖敷料是一种有效的止血剂,可显著减少拔牙后出血并能更好地控制疼痛。
壳聚糖类的止血材料存在以下问题:降解后呈酸性,在动物体内植入后会导致急性炎症反应和慢性炎症,影响创伤的愈合;降解速度慢,因此会产生组织粘连、纤维囊肿等问题,并形成严重的瘢痕组织。应谨慎使用植物来源的多糖类止血材料,因为大于50 g的多糖含量可能会影响葡萄糖负荷[32]。
2.3.5 纤维蛋白原类 TachoSil?适用于手术中的支持性治疗,可以用于改善止血,促进组织密封,以及在血管手术中进行缝合支持[36]。ESPOSITO 等[18]通过对硬脑(脊)膜封闭手术的文献回顾,结果显示纤维蛋白密封剂可以有效防止脑脊液泄漏,并具有可接受的安全性。KAWASAKI 等[37]通过对接受肝切除术或活体捐献的患者中进行疗效和安全性的随机试验后发现,TachoSil?和传统止血材料TachoComb的止血功效及安全性都相似。COLOMBO等[36]的文献回顾分析显示,当标准技术不足时TachoSil?可作为手术中的支持性治疗,从而改善止血并促进组织密封,减少术后并发症和住院费用。FILOSSO 等[38]的随机试验显示,TachoSil?治疗肺部恶性肿瘤重做术患者术后漏气方面效果显著,TachoSil?优于标准缝合,可减少接受重做胸腔手术患者的术后漏气。
目前尚未获得TachoSil?在神经外科或胃肠手术中应用的具体数据,如果TachoSil?在使用中进入到血管中可能造成血栓栓塞并发症的发生[36]。事实上任何含凝血酶的止血产品都不应在血管内注射,因为可能造成低血压及血栓形成。
纤维蛋白胶类产品不适合临床手术上动脉和较大静脉出血情况的使用,使用纤维蛋白胶类产品时必须注意产品不能进入血管,避免血栓形成[39]。含有氨甲环酸的液体纤维蛋白黏合剂具有神经毒性,因此不能用于脑脊液渗漏或硬脑膜撕裂的手术中。液体纤维蛋白黏合剂在预防胰腺、胆道、泌尿系统、肠道和空气泄漏方面无效[36],因此不建议常规使用。
2.4 可吸收生物止血材料的选择 可吸收止血材料的使用依赖于医生经验或偏好,临床医生需要根据患者实际情况,合理选择一个或多个止血材料组合,考虑的因素包括:伤口的大小和形状、出血严重程度、功效、不良反应、便利性及储存规格(表1)。
再生氧化纤维素、淀粉、明胶/胶原蛋白及壳聚糖类止血材料主要通过提供血小板活化和聚集作用形成血小板,被称为机械止血剂。它们不具有生物活性,在没有血浆成分(尤其是凝血因子Ⅷ和Ⅻ)的情况下,机械止血剂无法诱导血小板活化,主要依靠患者自身的纤维蛋白产生止血作用,因此被认为是被动止血剂,仅适用于凝血系统完整的患者。而对于具有功能完整的凝血系统的患者,由于材料的即时可用性和极高的成本效益可以用作一线药物,在出血部位上施加直接压力可以控制残留的出血[32]。
纤维蛋白原类止血材料可以在凝血级联反应中参与形成纤维蛋白凝块,可用于自发性或药物诱发性凝血障碍的患者,因具有止血作用和组织封闭作用而被称为黏附止血剂[32]。
KHOSHMOHABAT 等[40]的研究认为止血材料的等级可为:再生氧化纤维素>壳聚糖>标准伤口垫。CHIARA 等[32]通过对2000至2016年的66篇的文献回顾,认为局部止血材料是针对于不同适应证的产品,在不同的临床条件下应选择合适的产品:例如纤维蛋白胶或纤维蛋白贴剂在自发性或药物引起的凝血障碍时有效,而具有完整凝血系统的患者应首选机械止血剂。MARTYN等[41]通过回顾性队列研究对院内2011至2012接受过心血管手术(瓣膜手术和/或冠状动脉搭桥术)、颈动脉内膜切除术、胆囊切除术或子宫切除术患者止血材料的经济学研究显示,与其他种类止血材料相比,再生氧化纤维素止血剂的成本降低了28%-56%,再生氧化纤维素的平均每次止血剂单位降低了16%-41%。接受再生氧化纤维素治疗患者的住院时间和总手术费用较低,说明适当选择合适的止血剂有可能影响临床结果和治疗费用。
2.5 可吸收生物止血材料的发展现状 随着技术的进步及对产品质量需求的提高,越来越多的可吸收止血材料正在研发中,新型复合材料的开发成为研发趋势。 RADWAN-PRAG?OWSKA等[42]研发了使用L-天冬氨酸和L-谷氨酸作为交联剂的新型壳聚糖止血材料,RAHIMI 等[43]研发了壳聚糖银纳米颗粒复合膜,实验数据证明材料均有较强的抗菌活性,且生物相容性好。
随着国内水产品加工行业的迅速发展,以海洋材料为主的胶原蛋白明胶类止血材料的开发成为研究热点。SUN 等[44]通过脱水及戊二醛交联技术制备罗非鱼胶原蛋白海绵,该材料的结构有助于吸收伤口渗出液,补充氧气和细胞增殖,并具有良好的血液相容性。CHENG 等[45]通过共价偶联和冷冻干燥技术制备了海洋生物材料来源的胶原肽羧甲基壳聚糖海绵,在促进细胞活力和成纤维细胞迁移方面具有出色的生物学活性。XIE 等[46]研发的壳聚糖-胶原-海藻酸壳聚糖-胶原-海藻酸盐垫是通过涂料涂装和冷冻干燥制得的,并将其附着在聚氨酯上以组成复合敷料,该复合材料可以促进伤口愈合且具有良好的生物安全性。动物实验显示,鱼皮、水母等海洋生物改性材料对创面起到一定止血作用,可以有效缩短出血时间,减少出血量,达到快速止血的效果,这些物料可以作为止血交联物的原料,为今后医用止血海绵的制备提供理论依据[46]。
其他方面,王文涛[47]研发的可吸收骨蜡涂抹在松质骨创面后,可在一定时间内可以起到止血的效果,并且可以被机体吸收,对于骨折愈合无不良反应。需要注意的是,由于止血功效研究中使用了多种损伤模型,因此很难全面评估新技术。许多研究都只评估了小型动物损伤模型,评估绵羊或猪等大型动物的伤害模型可更准确地预测材料性能。
目前,国内可吸收止血材料行业相对来说基础薄弱,技术研发能力偏低,产品质量较低,与国外行业差距大。止血材料研究领域落后于其他医学进展,很少有重大进展,临床所用多为经典材料。随着全球人口的增加和年龄的增长,会进一步给医疗保健系统和医疗服务提供者带来压力,也同时给医疗护理市场带来发展。