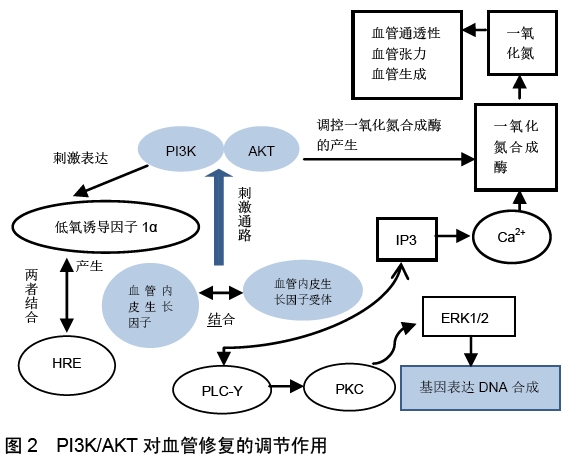
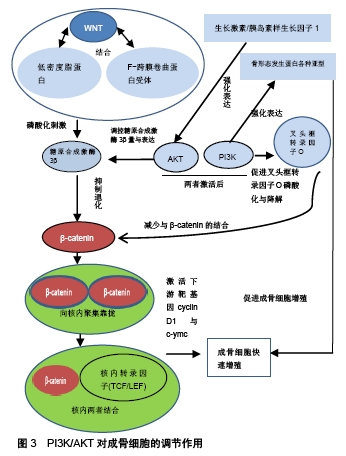
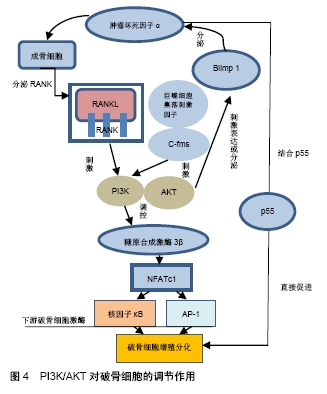
[1] AO W, MING R, JINCHENG W. The pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic review of the literature. Gene. 2018;671:103-109.
[2] 马剑雄,何伟伟,赵杰,等.股骨头坏死发病机制研究的最新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(27):4397-4402.
[3] Microsurgery Department of the Orthopedics Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association; Group from the Osteonecrosis and Bone Defect Branch of the Chinese Association of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery; Microsurgery and Reconstructive Surgery Group of the Orthopedics Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults. Orthop Surg. 2017; 9(1):3-12.
[4] WANG XS, ZHUANG QY, WENG XS, et al. Etiological and clinical analysis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Chinese patients. Chin Med J. 2013;126(2):290-295.
[5] ARBAB D, KÖNIG DP. Atraumatic femoral head necrosis in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2016;113(3):31-38.
[6] IKEUCHI K , HASEGAWA Y , SEKI T , et al. Epidemiology of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(2):278-281.
[7] XIE M, SHI R, PAN Y, et al. Proteasome inhibition-induced downregulation of akt/gsk-3β pathway contributes to abnormality of tau in hippocampal slice. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;50(3):888-895.
[8] ZHAO X, XIONG W, XIAO S, et al. Membrane targeting of TIRAP is negatively regulated by phosphorylation in its phosphoinositide- binding motif. Sci Rep.2017;7(3):43043.
[9] ANDJELKOVIC M , ALESSI DR , MEIER R , et al. Role of Translocation in the Activation and Function of Protein Kinase B. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(50):31515-31524.
[10] KILIC U, CAGLAYAN AB, BEKER MC, et al. Particular phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt on Thr308 via PDK-1 and PTEN mediates melatonin's neuroprotective activity after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Redox Biol. 2017;12(C):657.
[11] RISSO G, BLAUSTEIN M, POZZI B, et al. Akt/PKB: one kinase, many modifications. Biochem J. 2015;468(2):203-214.
[12] TOLEDO-LEYVA A, VILLEGAS-PINEDA JC, ENCARNACIÓN- GUEVARA S, et al. Effect of ovarian cancer ascites on SKOV-3 cells proteome: new proteins associated with aggressive phenotype in epithelial ovarian cancer. Proteome Sci. 2018;16:3.
[13] 耿军辉,张丽军,王亚丽,等.PI3K/Akt信号通路与肿瘤血管新生的研究进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2018,26(9):1462-1466.
[14] VETRI F, CHAVEZ R, XU HL, et al. Complex modulation of the expression of PKC isoforms in the rat brain during chronic type 1 diabetes mellitus. Brain Res. 2013;1490:202-209.
[15] DEL BARCO BARRANTES I, STEPHAN-OTTO ATTOLINI C, SLOBODNYUK K, et al. Regulation of Mammary Luminal Cell Fate and Tumorigenesis by p38α. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(1):257-271.
[16] KAR S, SAMII A, BERTALANFFY H. PTEN/PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling and the cross talk to KRIT1, CCM2, and PDCD10 proteins in cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Rev. 2015;38(2):229-237.
[17] ZHANG C , LI Y , CORNELIA R , et al. Regulation of VEGF expression by HIF-1α in the femoral head cartilage following ischemia osteonecrosis. Sci Reports.2012;2:650.
[18] ZHANG K, HAN ES, DELLINGER TH, et al. Cinnamon extract reduces VEGF expression via suppressing HIF-1α gene expression and inhibits tumor growth in mice. Mol Carcinog.2017;56(2):436-446.
[19] ZENG D, WANG J, KONG P, et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits HIF-1α and VEGF expression in patient with acute leukemia via inhibiting the activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(5):2172-2178.
[20] WANG P, TIAN XF, RONG JB, et al. Protein Kinase B (Akt) Promotes Pathological Angiogenesis in Murine Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy. Acta Hstochemica Et Cytochemica. 2011;44(2): 103-111.
[21] SHARMA VR, GUPTA GK, SHARMA AK, et al. PI3K/Akt/mTOR intracellular pathway and breast cancer: factors, mechanism and regulation. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(11):1633-1638.
[22] JIAO D, WANG J, LU W, et al. Curcumin inhibited HGF-induced EMT and angiogenesis through regulating c-Met dependent PI3K/Akt/ mTOR signaling pathways in lung cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2016; 3:16018.
[23] YANG Y, GAO M, LIN Z, et al. DEK promoted EMT and angiogenesis through regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):98708-98722.
[24] YIN T, WANG G, HE S, et al. Malignant pleural effusion and ascites induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem-like cell properties via the vascular endothelial growth factor (vegf)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (pi3k)/akt/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mtor) pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;291(52):26750.
[25] TSAI JL, LEE YM, PAN CY, et al. The Novel VEGF121-VEGF165 Fusion Attenuates Angiogenesis and Drug Resistance via Targeting VEGFR2-HIF-1α-VEGF165 /Lon Signaling Through PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(3):275-286.
[26] WANG Y, YAN W, LU X, et al. Overexpression of osteopontin induces angiogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells via the avβ3/PI3K/AKT/ eNOS/NO signaling pathway in glioma cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011; 90(8):642-648.
[27] 尹香琳,张婧瑶,刘卫东,等.1-磷酸鞘氨醇受体2介导PI3K/AKT/eNOS通路抑制甲型流感病毒诱导的病毒性肺炎[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(11): 2062-2067.
[28] AHMAD KA, ZE H, CHEN JC,et al. The protective effects of a novel synthetic β-elemene derivative on human umbilical vein endothelial cells against oxidative stress-induced injury: Involvement of antioxidation and PI3k/Akt/eNOS/NO signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother.2018;106:1734-1741.
[29] 王雅婧,张学志,刁力,等.PI3K/AKt/eNOS信号通路在硫化氢抑制ET-1诱导的心肌肥大中的作用[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2014,6(5): 551-554+557.
[30] AGATA M, MAGDALENA W, PIOTR S. Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: current knowledge and, clinical significance. Molecules. 2014;19(9): 14304-14315.
[31] YANG H, ZHANG X, DU K, et al. Inhibition of β-catenin signaling in chondrocytes induces delayed fracture healing in mice. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(4):304-310.
[32] GUNTUR AR, ROSEN CJ, NASKI MC. N-cadherin adherens junctions mediate osteogenesis through PI3K signaling. Bone. 2012; 50(1):54-62.
[33] RISSO G, BLAUSTEIN M, POZZI B, et al. Akt/PKB: one kinase, many modifications. Biochem J. 2015; 468(2):203-214.
[34] MENG YB, LI X, LI ZY, et al. microRNA-21 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by the PI3K/β-catenin pathway. J Orthop Res. 2015; 33(7):957-964.
[35] HU J, MAO Z, HE S, et al. Icariin protects against glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis, increases the expression of the bone enhancer DEC1 and modulates the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin integrated signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017:S0006295217301995.
[36] HUANG L, WANG Y, JIANG Y, et al. High levels of GSK-3β signalling reduce osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Biochem. 2018;163(3):243-251.
[37] DENG S, NIE Z, PENG P, et al. Decrease of GSK3β Ser-9 phosphorylation induced osteoblast apoptosis in rat osteoarthritis model. Curr Med Sci. 2019;39(1):75-80.
[38] LAUZON MA , DAVIAU A , DREVELLE O , et al. Identification of a growth factor mimicking the synergistic effect of fetal bovine serum on BMP-9 cell response. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(17-18):2524-2535.
[39] FONG D, BISSON M, LABERGE G, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-9 activates Smad and ERK pathways and supports human osteoclast function and survival in vitro. Cell Signal. 2013; 25(4): 717-728.
[40] WU X, CHIM SM, KUEK V, et al. HtrA1 is upregulated during RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis, and negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation and BMP2-induced Smad1/5/8, ERK and p38 phosphorylation. FEBS Lett.2014;588(1):143-150.
[41] LAUZON MA, DREVELLE O, DAVIAU A, et al. Effects of BMP-9 and BMP-2 on the PI3K/Akt pathway in MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(17-18):1075-1085.
[42] MIN YL, LIM HW, SANG HL, et al. Smad, PI3K/Akt, and Wnt-dependent signaling pathways are involved in BMP-4-induced ESC self-renewal. Stem Cells, 2010;27(8):1858-1868.
[43] WANG Z, GUO J. Mechanical induction of BMP-7 in osteocyte blocks glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis through PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67(2):567-574.
[44] FURUE K, SENA K, SAKODA K, et al. Involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway in bone morphogenetic protein 9-stimulated osteogenic differentiation and stromal cell-derived factor 1 production in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Eur J Oral Sci. 2017;125(2):119-126.
[45] MUKHERJEE A, ROTWEIN P. Akt promotes BMP2-mediated osteoblast differentiation and bone development. J Cell Sci. 2009; 122(5):716.
[46] REN W, LIU Y, WAN S, et al. BMP9 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of HER2-positive SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells through ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT pathways. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96816.
[47] AGAS D, SABBIETI MG, MARCHETTI L, et al. FGF-2 enhances Runx-2/Smads nuclear localization in BMP-2 canonical signaling in osteoblasts.J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(11):2149-2158.
[48] LU J, BHARGAV D, WEI AQ, et al. Posterolateral intertransverse spinal fusion possible in osteoporotic rats with BMP-7 in a higher dose delivered on a composite carrier. Spine. 2008;33(3):242.
[49] BAHIA PK , PUGH V , HOYLAND K , et al. Neuroprotective effects of phenolic antioxidant tBHQ associate with inhibition of FoxO3a nuclear translocation and activity. J Neurochem. 2012;123(1):182-191.
[50] MA Y, WANG H. PI3K/Akt/FoxO: a novel participant in signal transduction in bone cells under mechanical stimulation. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(10):923-926.
[51] HAMANN I, PETROLL K, GRIMM L, et al. Insulin-like modulation of Akt/FoxO signaling by copper ions is independent of insulin receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014; 558:42-50.
[52] 陈小香,邓伟民,魏秋实,等.从GH/IGF-1轴与PI3K/Akt通路探讨老年骨质疏松症的发病机制[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(11):1412-1415.
[53] YUAN FL, XU RS, JIANG DL, et al. Leonurine hydrochloride inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by inhibiting the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Bone.2015;75:128-137.
[54] DUAN L, REN Y. Role of notch signaling in osteoimmunology-from the standpoint of osteoclast differentiation. Eur J Orthod. 2013;35(2): 175-182.
[55] MEDINA MA, ANDRADE VM, CARACCI MO, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling stimulates the expression and synaptic clustering of the autism-associated Neuroligin 3 gene. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):45.
[56] MOORE SF, VAN DEN BOSCH MT, HUNTER RW, et al. Dual regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3)α/β by protein kinase C (PKC)α and Akt promotes thrombin-mediated integrin αIIbβ3 activation and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288(6):3918-3928.
[57] TAYLOR A, ROTHSTEIN D, RUDD CE. Small-Molecule Inhibition of PD-1 Transcription Is an Effective Alternative to Antibody Blockade in Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res. 2018;78(3):706-717.
[58] MOON JB , KIM JH , KIM K , et al. Akt induces osteoclast differentiation through regulating the GSK3β/NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Immunol. 2012;188(1):163-169.
[59] ZHA L, HE L, LIANG Y, et al. TNF-α contributes to postmenopausal osteoporosis by synergistically promoting RANKL-induced osteoclast formation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:369-374.
[60] WU LC, GUO QF, YANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes osteoclast formation via PI3K/Akt Pathway‐Mediated Blimp1 expression upregulation. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(6): 1308-1315.
[61] VAN WIJNEN AJ, VAN DE PEPPEL J, VAN LEEUWEN JP, et al. MicroRNA Functions in Osteogenesis and Dysfunctions in Osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2013;11(2):72-82.
[62] ZHAO C, SUN W, ZHANG P, et al. miR-214 promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting Pten/PI3k/Akt pathway. RNA Biol. 2015;12(3):343-353.
|