中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 416-421.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1931
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
Meta分析评价长柄与短柄人工髋关节假体在置换治疗中的有效和安全性
刘长路,马丽波,刘晓民,黄 健
- 内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010030
Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of short-stem versus long-stem hip arthroplasty
Liu Changlu, Ma Libo, Liu Xiaomin, Huang Jian
- Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
人工髋关节置换:对于药物及其他治疗方式效果欠佳的髋关节疾病患者,人工髋关节置换是极为有效的术式之一。目前,改进人工髋关节假体的生物和机械结构设计仍是研发重点。研究主要比较人工髋关节置换术应用长柄与短柄两种不同假体的治疗效果,选择最优治疗方案。
Meta分析:应用统计学概念及方法收集整理与分析针对于某个概念的众多研究,应用统计学方法设计及计算,找出相关变量的关系进行比较计算,弥补一般文献综述的研究不足。文章基于Meta分析方法,收集相关资料,分析比较了长柄和短柄人工髋关节假体治疗的有效性和安全性。
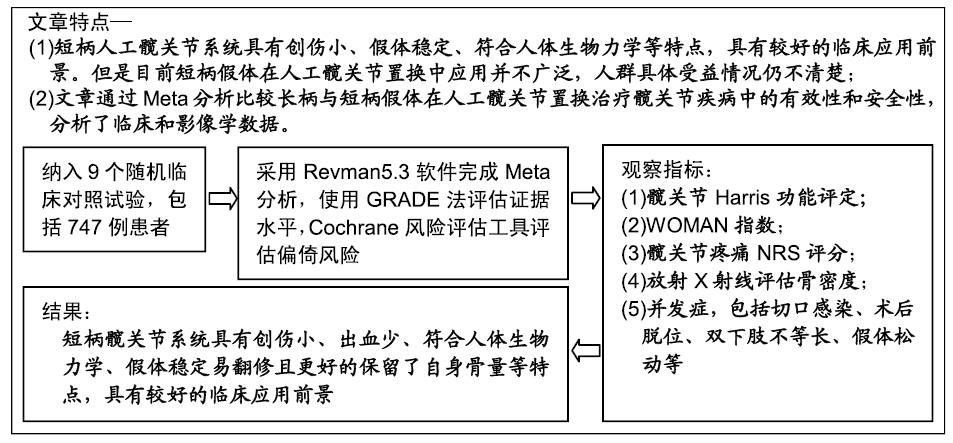
背景:短柄人工髋关节系统具有创伤小、假体稳定、符合人体生物力学、更好的保留骨量等特点,但是目前短柄假体在人工髋关节置换术中应用并不广泛,人群具体受益情况仍不清楚。
目的:评价长柄及短柄人工髋关节置换治疗股骨头坏死的疗效及安全性。
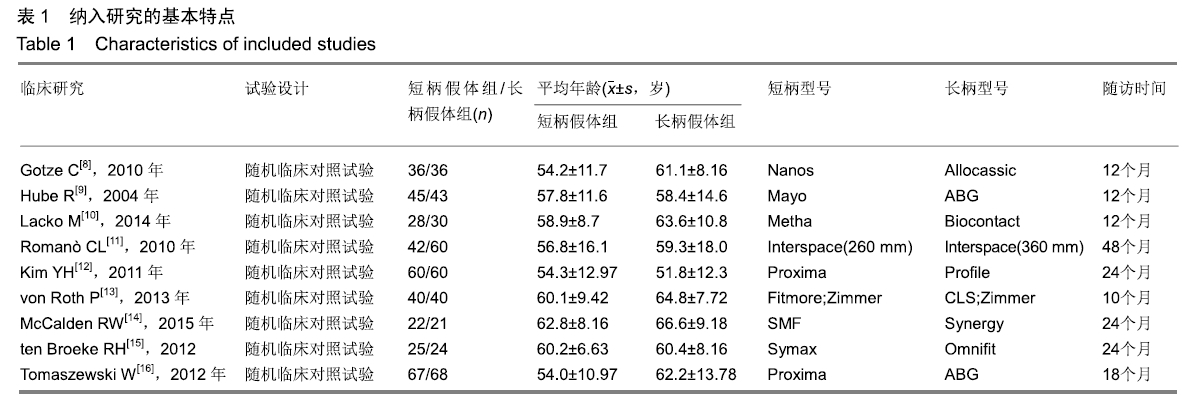
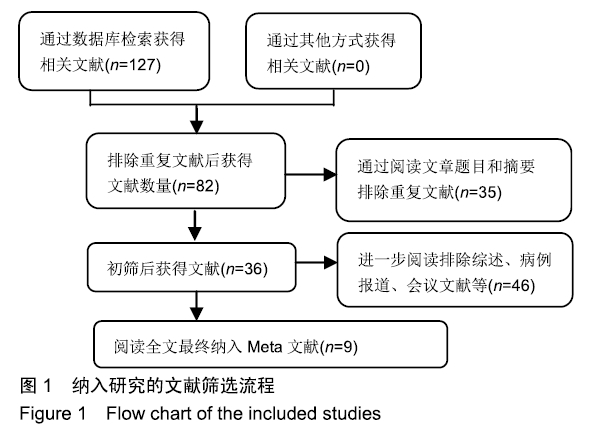
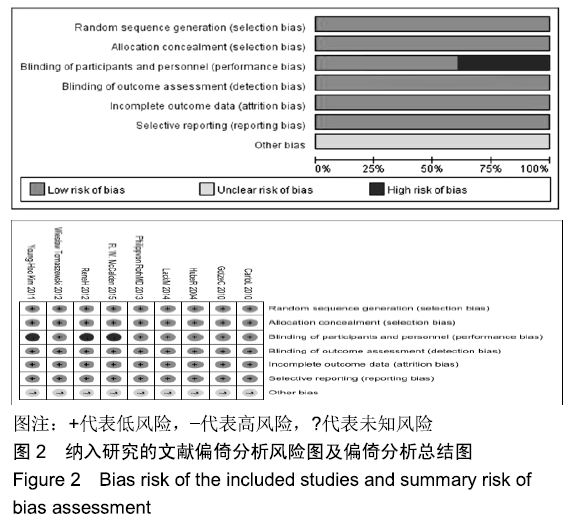
方法:应用计算机检索PubMed数据库、Embese数据库、Medline数据库、Web of Science和Cochrane图书馆数据库,收集关于长柄及短柄髋关节置换的临床随机对照试验,对符合纳入标准的研究采用RevMan 5.3软件进行Meta分析。
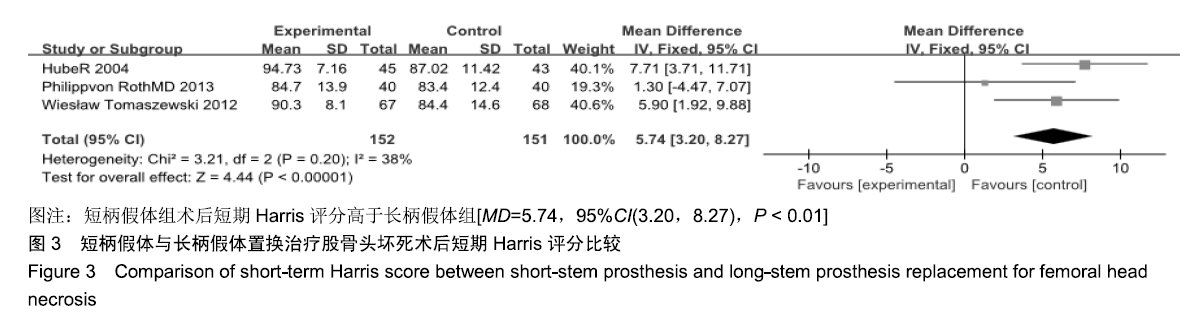
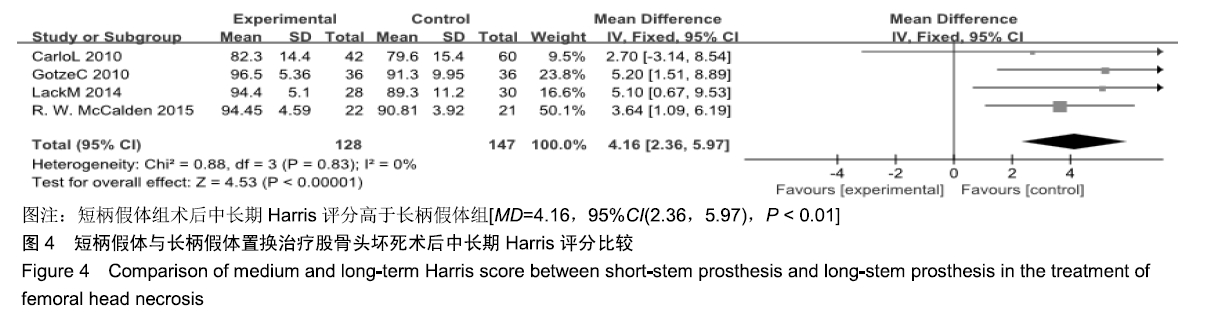
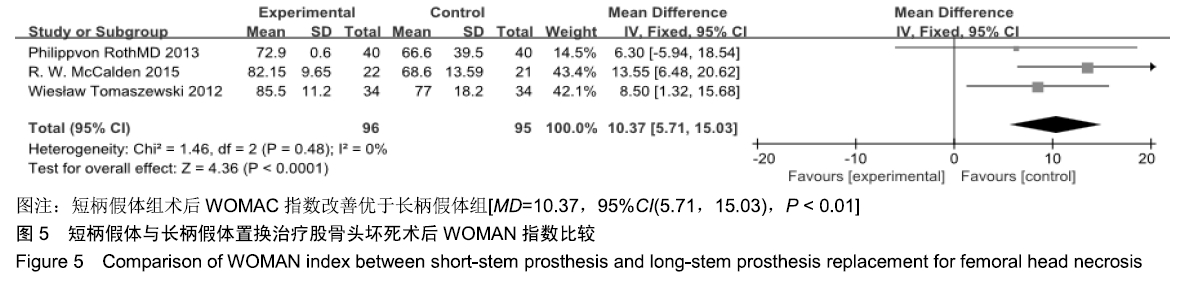
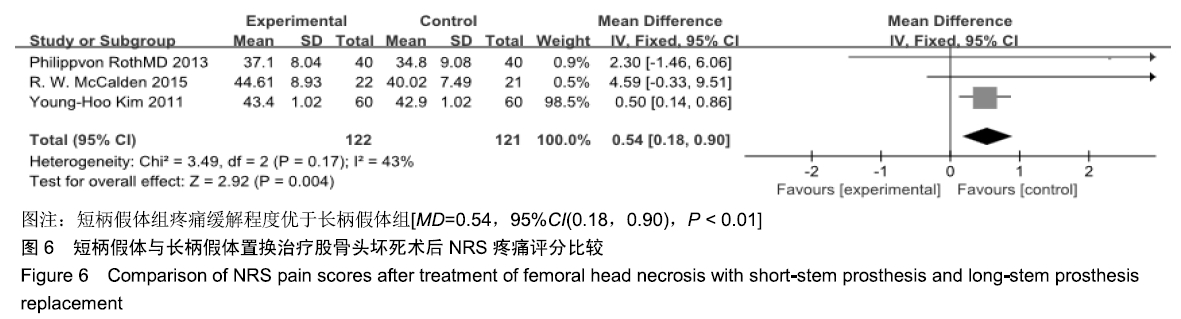
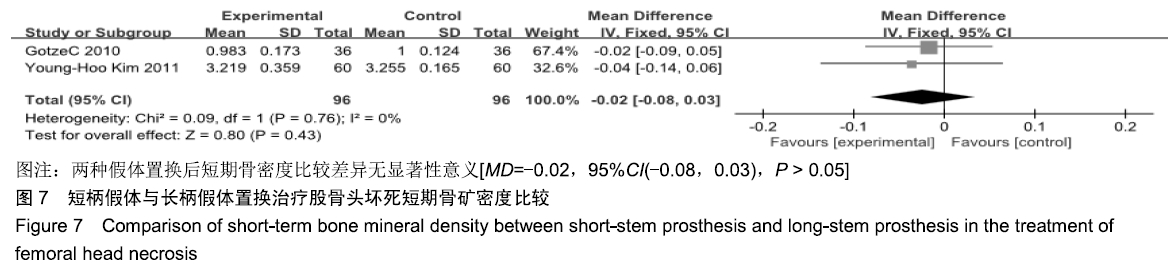
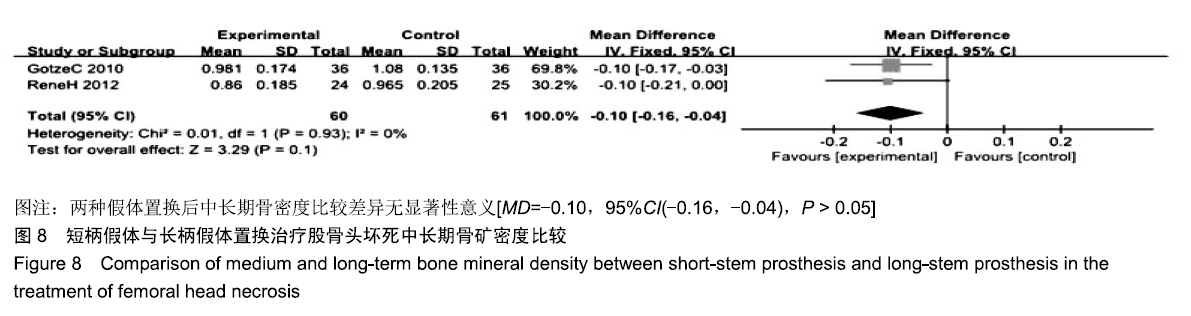
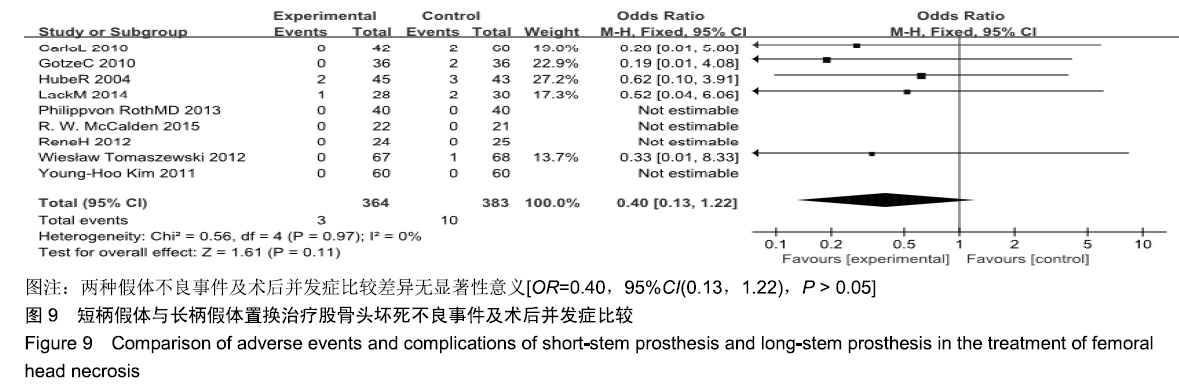
结果与结论:①共纳入9项随机临床对照试验、747例患者,其中长柄假体组383例和短柄假体组364例;②Meta分析显示:短柄假体组术后6个月及6个月以上的髋关节Harris评分高于长柄假体组[MD=5.74,95%CI(3.20,8.27),P < 0.05;MD=4.16,95%CI(2.36,5.97),P < 0.05],术后WOMAN指数评分较长柄假体组明显改善[MD=10.37,95%CI(5.71,15.03),P < 0.05],术后NRS疼痛评分较长柄假体组明显改善[MD=0.54,95%CI(0.18,0.90),P < 0.01];两组切口感染、术后脱位、双下肢不等长、假体松动等并发症发生率与术后6个月及6个月以上的骨密度比较差异均无显著性意义[OR=0.40,95%CI(0.13,1.22),P > 0.05;MD=-0.02,95%CI(-0.08,0.03),P > 0.05;MD=-0.10,95%CI(-0.16,0.04),P > 0.05];③结果表明,短柄人工髋关节置换是治疗股骨头坏死的有效方法,可缓解疼痛、尽早恢复关节功能、提高手术效果,尤其适用于骨质较好的年轻患者。ORCID: 0000-0003-2405-476X(刘长路)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: