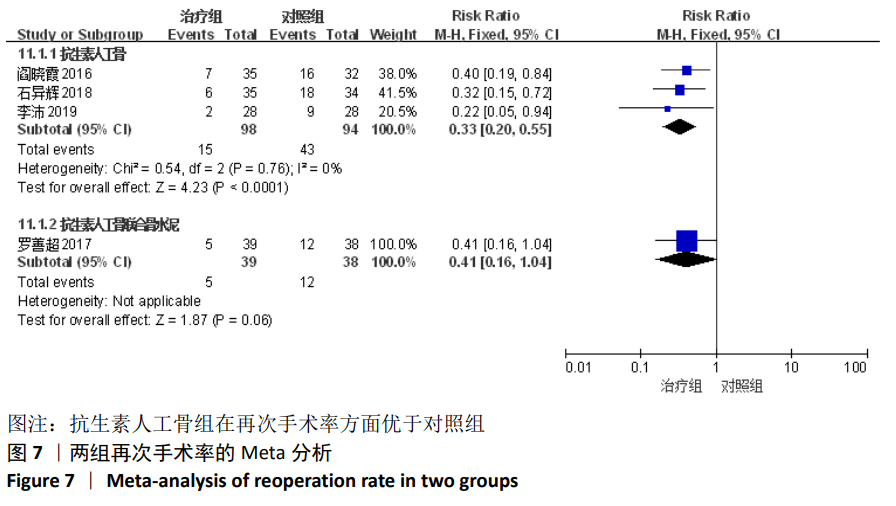
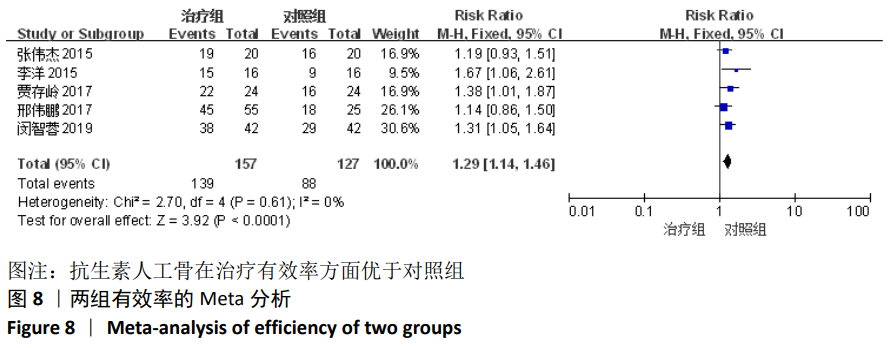
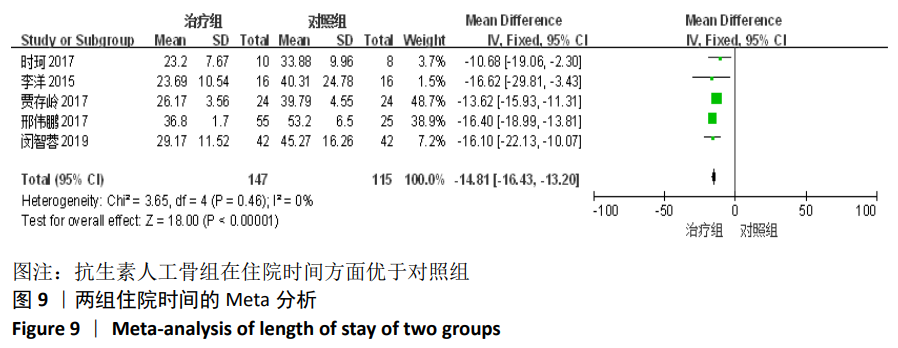
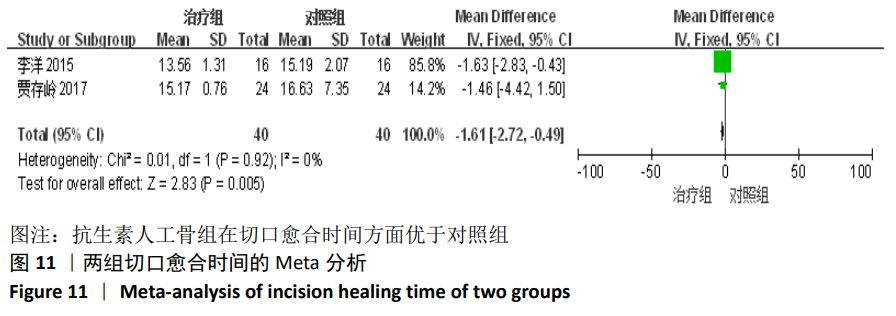
[1] TSCHUDIN-SUTTER S, FREI R, DANGEL M, et al. Validation of a treatment algorithm for orthopaedic implant-related infections with device-retention-results from a prospective observational cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(5):451-457.
[2] DYM H, ZEIDAN J. Microbiology of Acute and Chronic Osteomyelitis and Antibiotic Treatment. Dent Clin North Am. 2017; 61(2):271-282.
[3] 张震,魏屹东,季明华,等.胫骨慢性骨髓炎治疗进展[J].实用骨科杂志, 2019, 25(2):146-149.
[4] THABIT AK, FATANI DF, BAMAKHRAMA MS, et al. Antibiotic penetration into bone and joints: An updated review. Int J Infect Dis. 2019;81:128-136.
[5] BOYLE KK, SOSA B, OSAGIE L, et al. Vancomycin-laden calcium phosphate-calcium sulfate composite allows bone formation in a rat infection model. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e222034.
[6] 严伟.万古霉素硫酸钙联合负压封闭引流对慢性骨髓炎患者红细胞沉降率、C反应蛋白的影响[J].医疗装备, 2019, 32(14):115-116.
[7] 石异辉.抗生素缓释系统治疗创伤后及内固定相关骨感染的临床疗效[J].临床合理用药杂志,2018,11(24):54-56.
[8] 贾存岭,贾代良,吕琳,等.载抗生素硫酸钙人工骨治疗慢性骨髓炎及其细菌学分析[J].中国病原生物学杂志, 2017, 12(5):464-469.
[9] 阎晓霞,李康,朱明喜,等.万古霉素缓释系统与Wright硫酸钙对骨折内固定术后骨感染治愈率的分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2016,26(19):4491-4493.
[10] 时珂.万古霉素硫酸钙治疗慢性骨髓炎临床疗效分析[D].沈阳:中国医科大学, 2017.
[11] 闵智蓉.万古霉素与硫酸钙人工骨对跟骨骨折患者术后感染的疗效及其对骨折愈合的影响[J].抗感染药学, 2019,16(8):1468-1469.
[12] 邢伟鹏,李无阴,田涛涛,等.抗生素硫酸钙在胫骨慢性骨髓炎中的应用[J].皖南医学院学报,2017,36(1):58-60.
[13] 李沛,侯柯楠,唐锴,等.载万古霉素硫酸钙在慢性骨髓炎中的应用[J].武警后勤学院学报(医学版),2019,9:48-50.
[14] QIN CH, ZHOU CH, SONG HJ, et al. Infected bone resection plus adjuvant antibiotic-impregnated calcium sulfate versus infected bone resection alone in the treatment of diabetic forefoot osteomyelitis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):246.
[15] LUO S, JIANG T, YANG Y, et al. Combination therapy with vancomycin-loaded calcium sulfate and vancomycin-loaded PMMA in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):502.
[16] 罗善超.万古霉素硫酸钙与万古霉素PMMA缓释系统联合治疗慢性创伤性骨髓炎[D].桂林:广西医科大学,2017.
[17] 李洋.万古霉素硫酸钙与灌注冲洗治疗慢性骨髓炎的临床分析[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2015.
[18] 张伟杰.载万古霉素硫酸钙治疗慢性骨髓炎的临床研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2015.
[19] SENNEVILLE E, ROBINEAU O. Treatment options for diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017;18(8):759-765.
[20] WU ZQ, ZENG DL, YAO JL, et al. Research Progress on Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Osteomyelitis. Chin Med Sci J. 2019; 34(3): 211-220.
[21] 李文波,张超,石杰,等.慢性骨髓炎感染复发诱因的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志, 2017,23(12):1099-1102.
[22] GUPTA P, SARKAR S, DAS B, et al. Biofilm, pathogenesis and prevention--a journey to break the wall: a review. Arch Microbiol. 2016;198(1): 1-15.
[23] THADDEUS CA, EMEKA OM. Whole clavicle sequestration from chronic osteomyelitis in a 10 year old boy: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2016;6:92-95.
[24] 王步祥,杨铁翼,赵振群,等.组织工程技术在感染性骨缺损治疗中的应用及优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(28):4543-4549.
[25] 占华松,陈跃平,章晓云.骨组织工程技术治疗感染性骨缺损:优势与问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(30):4848-4854.
[26] SUN PQ, MA Y, ZHANG YC, et al. Application of antibiotic impregnated beads on the patients with tibial chronic osteomyelitis. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2018; 31(6(Special)):2783-2786.
[27] MASQUELET AC, KISHI T, BENKO PE. Very long-term results of post-traumatic bone defect reconstruction by the induced membrane technique. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(1):159-166.
[28] WENTAO Z, LEI G, LIU Y, et al. Approach to osteomyelitis treatment with antibiotic loaded PMMA. Microb Pathog. 2017;102:42-44. |