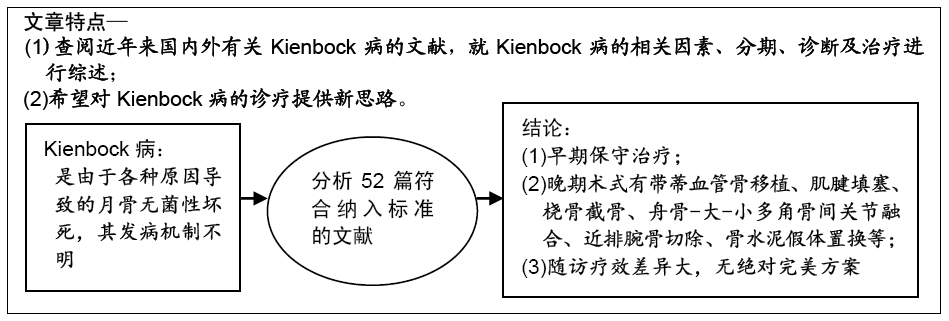
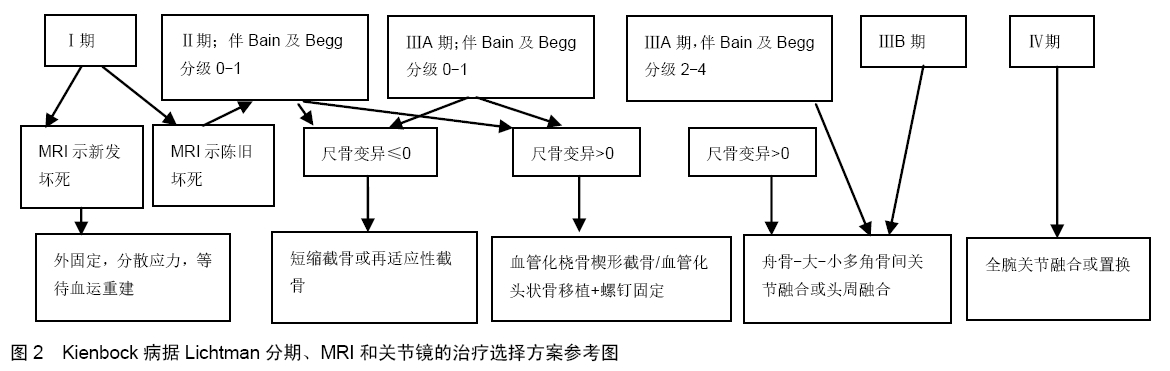
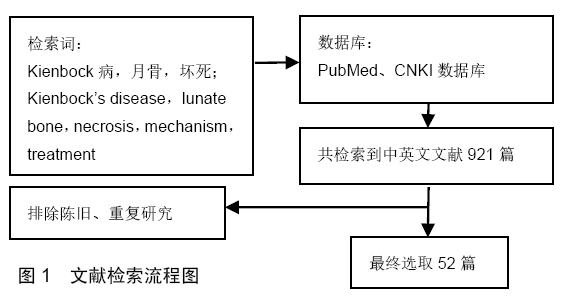
[1] LICHTMAN DM, PIENTKA WN, BAIN GI.Kienbock Disease: Moving Forward.J Hand Surg Am.2016;41(5):630-638.
[2] BAIN GI, MACLEAN SB, YEO CJ, et al.The Etiology and Pathogenesis of Kienbock Disease.J Wrist Surg. 2016;5(4): 248-254.
[3] VAN LEEUWEN WF, JANSSEN SJ, TER MEULEN DP, et al. What Is the Radiographic Prevalence of Incidental Kienbock Disease?. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2016;474(3):808-813.
[4] GOLAY SK, RUST P, RING D. The Radiological Prevalence of Incidental Kienbock Disease. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2016;4(3): 220-223.
[5] 王大伟,高飞,单贵霖,等.月骨滋养动脉应用解剖学研究及其临床意义[J].解剖学研究,2018,40(3):210-214.
[6] 田光磊,王澍寰,王海华.与月骨缺血性坏死有关的骨骼因素[J].中国实用手外科杂志,2000,14(2):35-38.
[7] KADAR A, ELHASSAN B, MORAN S L. Manifestations of Mucolipidosis III in the hand: avascular necrosis of multiple carpal bones.J Hand Surg Eur Vol.2017;42(6):645-646.
[8] LAMAS C, CARRERA A, PROUBASTA I, et al. The anatomy and vascularity of the lunate: considerations applied to Kienbock's disease.Chir Main.2007;26(1):13-20.
[9] RIKLI DA,REGAZZONI P.Fractures of the distal end of the radius treated by internal fixation and early function.A preliminary report of 20 cases.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1996;78(4):588-592.
[10] ADAMS JE.Forearm Instability: Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Treatment Options.J Hand Surg Am.2017;42(1):47-52.
[11] THOUVEREY C, CAVERZASIO J. Ablation of p38alpha MAPK Signaling in Osteoblast Lineage Cells Protects Mice From Bone Loss Induced by Estrogen Deficiency. Endocrinology. 2015; 156(12):4377-4387.
[12] 靳亮,于亚东,白延斌,等.月骨周围背侧脱位韧带损伤及手术修复后的生物力学研究[J].河北医药,2015,37(9):1337-1340.
[13] 路来金,贾晓燕. 腕月骨无菌性坏死的临床进展[J].遵义医学院学报,2016,39(4):333-339.
[14] VAN LEEUWEN WF, OFLAZOGLU K, MENENDEZ ME, et al. Negative Ulnar Variance and Kienbock Disease. J Hand Surg Am.2016;41(2):214-218.
[15] 于昆仑.月骨坏死与尺骨变异相关性X线分析及骨水泥成形术在月骨病变中的应用[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2016.
[16] 孙成.不同方法测量尺骨变异的对比研究[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学, 2016.
[17] LICHTMAN DM, PIENTKA WN, BAIN GI.Kienbock Disease: A New Algorithm for the 21st Century.J Wrist Surg.2017;6(1):2-10.
[18] SHINOHARA T, NAKAMURA R, NAKAO E, et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome associated with Kienbock disease. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2016;78(3):267-273.
[19] YESILOZ M,LOUIS M,DEVERBIZIER J,et al.Kienbock's disease: Role of cross-sectional imaging in treatment choice and patient follow-up.Eur J Radiol.2018;105:269-282.
[20] SALT O, SAYHAN MB. Avascular necrosis of lunate bone: Kienbock disease.Am J Emerg Med.2016;34(6):1185.
[21] FONTAINE C.Kienbock's disease.Chir Main.2015;34(1):4-17.
[22] LICHTMAN DM, MACK GR,MACDONALD RI,et al.Kienbock's disease: the role of silicone replacement arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1977;59(7):899-908.
[23] VAN LEEUWEN W F, JANSSEN S J, GUITTON T G, et al. Interobserver Agreement in Diagnosing Early-Stage Kienbock Disease on Radiographs and Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Hand (N Y).2017;12(6):573-578.
[24] KALB K, PILLUKAT T, SCHMITT R, et al. [Kienbock's disease in paediatric and juvenile patients]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2010;42(3):187-197.
[25] LOGTERS T,BUREN C,WINDOLF J.[Etiology, diagnostics and classification of lunate bone necrosis]. Unfallchirurg. 2018;121(5): 373-380.
[26] FIGUEIRA PJ,ALPUIM CD,BARBAGALLO N,et al.Stage III Kienbock's disease treated with hyperbaric oxygen: the role of an unusual approach to a rare condition.BMJ Case Rep. 2018;2018.
[27] RUETTERMANN M. Lunate excision, capitate osteotomy, and intercarpal arthrodesis should be used with caution for advanced Kienbock's disease.J Hand Surg Eur Vol.2019;44(1):112-113.
[28] 谭鸿,李锐.带血管豌豆骨移位治疗月骨坏死[A].呼和浩特:第二十四届中国中西医结合骨伤科学术年会论文汇编,2017.
[29] TAN Z, XIANG Z, HUANG F, et al. Long-term results of vascularized os pisiform transfer for advanced Kienbock disease after follow-up for at least 15 years: A case series.Medicine (Baltimore).2018;97(48):e13229.
[30] 梁再卿,吴宁,韦汉鹏,等.月骨摘除带血管蒂豌豆骨移位治疗月骨缺血性坏死[J].中医正骨,2017,29(4):50-52.
[31] NAKAGAWA M,OMOKAWA S,KIRA T, et al. Vascularized Bone Grafts from the Dorsal Wrist for the Treatment of Kienbock Disease.J Wrist Surg.2016,5(2):98-104.
[32] 谢德,朱仲伦,刘跃洪,等. 带血管桡骨瓣转移填塞治疗月骨缺血坏死效果及安全性分析[J].检验医学与临床,2017,14(16):2393-2394.
[33] DUTTA A, SIPANI AK, AGARWALA V, et al. Kienbock's Disease treated with Interposition Arthroplasty using Ipsilateral Palmaris Longus Tendon and Muscle Belly.J Orthop Case Rep.2012;2(1): 11-14.
[34] 朱勇.掌长肌腱团填塞术治疗月骨坏死的疗效研究[J].实用医技杂志, 2016,23(1):77-79.
[35] 王庆伟,唐运章,王华松,等.月状骨切除联合掌长肌腱填塞治疗中晚期月状骨无菌坏死[J].华南国防医学杂志, 2017,31(11):744-746.
[36] 周海振,杜娟娟,白杰,等. Herbert钉内固定联合植骨并肌腱团填塞治疗Lichtman Ⅲb期月骨缺血性坏死[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2018,33(01):36-38.
[37] ARORA R, LUTZ M, DEML C, et al. Long-term subjective and radiological outcome after reconstruction of Kienbock's disease stage 3 treated by a free vascularized iliac bone graft.J Hand Surg Am.2008;33(2):175-181.
[38] ARORA R,LUTZ M,ZIMMERMANN R, et al.[Free vascularised iliac bone graft for Kienbock's disease stage III].Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir.2010;42(3):198-203.
[39] LARAVINE J, LOUBERSAC T, GAISNE E, et al. Evaluation of a shape memory staple (Qual((R))) in radial shortening osteotomy in Kienbock's disease:A retrospective study of 30 cases.Hand Surg Rehabil. 2019;38(3):141-149.
[40] EBRAHIMZADEH MH,MORADI A,VAHEDI E,et al.Mid-term clinical outcome of radial shortening for kienbock disease.J Res Med Sci.2015;20(2):146-149.
[41] HONG IT,LEE S,JANG GC,et al. Kienbock's disease with non-negative ulnar variance : Treatment with combined radial wedge and shortening osteotomy.Orthopade.2019;48(1):96-101.
[42] SHIN YH,KIM J,GONG HS, et al.Clinical Outcome of Lateral Wedge Osteotomy of the Radius in Advanced Stages of Kienbock's Disease.Clin Orthop Surg.2017;9(3):355-362.
[43] LI J, PAN Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Capitate osteotomy and transposition for type III Kienbock's disease. J Hand Surg Eur Vol.2018;43(7): 708-711.
[44] CHEVROLLIER J, POMARES G, HUGUET S, et al. Intracarpal shortening osteotomy for Kienbock's disease: A retrospective study of 28 cases.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2017;103(2): 191-198.
[45] XU Y,LI C,ZHOU T,et al.Treatment of Aseptic Necrosis of the Lunate Bone (Kienbock Disease) Using a Nickel-Titanium Memory Alloy Arthrodesis Concentrator:A Series of 24 Cases. Medicine (Baltimore).2015;94(42):e1760.
[46] STAHL S,HENTSCHEL PJ, SANTOS SA,et al.Comparison of clinical and radiologic treatment outcomes of Kienbock's disease. J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10:133.
[47] CHEDAL-BORNU B, CORCELLA D, FORLI A, et al. Long-term outcomes of proximal row carpectomy: A series of 62 cases.Hand Surg Rehabil.2017;36(5):355-362.
[48] MARCUZZI A, COLANTONIO F, PETRELLA G, et al. Stage IV Kienbock's disease: Proximal row carpectomy and application of RCPI implant.Hand Surg Rehabil.2017;36(2):102-108.
[49] HOHENDORFF B,MUHLDORFER-FODOR M,KALB K,et al.STT arthrodesis versus proximal row carpectomy for Lichtman stage IIIB Kienbock's disease: first results of an ongoing observational study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2012;132(9):1327-1334.
[50] 李睿夫,缪旭东,闫乔生,等.骨水泥假体置换治疗月骨缺血性坏死的临床研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2017,27(01):107-110.
[51] PUIG-ZENTELLA M, RIVAS-MONTERO JA, HERNANDEZ- MENDEZ-VILLAMIL E, et al.Intercarpal fusion as a salvage procedure in Kienbock disease.Acta Ortop Mex.2016;30(6): 296-301.
[52] SEVIMLI R, ERTEM K, ASLANTURK O, et al. Mid term results of radial metaphyseal core decompression on Kienbock's disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2017;21(24):5557-5561.
|