| [1] Bhatia M, Wong FL, Cao Y, et al. Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2005;5(2-3):132-144.
[2] Gravante G, Garcea G, Ong SL, et al. Prediction of mortality in acute pancreatitis: a systematic review of the published evidence. Pancreatology. 2009;9(5):601-614.
[3] Pezzilli R. Pharmacotherapy for acute pancreatitis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009;10(18):2999-3014.
[4] Steinle AU, Weidenbach H, Wagner M, et al. NF-kappaB/Rel activation in cerulein pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1999; 116(2):420-430.
[5] Yang YH, Szabat M, Bragagnini C, et al. Paracrine signalling loops in adult human and mouse pancreatic islets: netrins modulate beta cell apoptosis signalling via dependence receptors. Diabetologia. 2011;54(4):828-842.
[6] Sandoval D, Gukovskaya A, Reavey P, et al. The role of neutrophils and platelet-activating factor in mediating experimental pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1996;111(4): 1081-1091.
[7] Werner J, Dragotakes SC, Fernandez-del Castillo C, et al. Technetium-99m-labeled white blood cells: a new method to define the local and systemic role of leukocytes in acute experimental pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1998;227(1):86-94.
[8] Ly NP, Komatsuzaki K, Fraser IP, et al. Netrin-1 inhibits leukocyte migration in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(41):14729-14734.
[9] Rosenberger P, Schwab JM, Mirakaj V, et al. Hypoxia- inducible factor-dependent induction of netrin-1 dampens inflammation caused by hypoxia. Nat Immunol. 2009;10(2): 195-202.
[10] Mirakaj V, Thix CA, Laucher S, et al. Netrin-1 dampens pulmonary inflammation during acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181(8):815-824.
[11] Aherne CM, Collins CB, Masterson JC, et al. Neuronal guidance molecule netrin-1 attenuates inflammatory cell trafficking during acute experimental colitis. Gut. 2012;61(5): 695-705.
[12] Norman J. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1998;175(1):76-83.
[13] Pereda J, Sabater L, Aparisi L, et al. Interaction between cytokines and oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(23):2775-2787.
[14] Hughes CB, Grewal HP, Gaber LW, et al. Anti-TNFalpha therapy improves survival and ameliorates the pathophysiologic sequelae in acute pancreatitis in the rat. Am J Surg. 1996;171(2):274-280.
[15] Pereda J, Sabater L, Cassinello N, et al. Effect of simultaneous inhibition of TNF-alpha production and xanthine oxidase in experimental acute pancreatitis: the role of mitogen activated protein kinases. Ann Surg. 2004;240(1):108-116.
[16] Chen X, Ji B, Han B, et al. NF-kappaB activation in pancreas induces pancreatic and systemic inflammatory response. Gastroenterology. 2002;122(2):448-457.
[17] Rakonczay Z Jr, Jármay K, Kaszaki J, et al. NF-kappaB activation is detrimental in arginine-induced acute pancreatitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;34(6):696-709.
[18] Ethridge RT, Hashimoto K, Chung DH, et al. Selective inhibition of NF-kappaB attenuates the severity of cerulein- induced acute pancreatitis. J Am Coll Surg. 2002; 195(4): 497-505.
[19] Satoh A, Shimosegawa T, Fujita M, et al. Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activation improves the survival of rats with taurocholate pancreatitis. Gut. 1999;44(2):253-258.
[20] Algül H, Treiber M, Lesina M, et al. Pancreas-specific RelA/p65 truncation increases susceptibility of acini to inflammation-associated cell death following cerulein pancreatitis. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(6):1490-1501.
[21] Paradisi A, Maisse C, Bernet A, et al. NF-kappaB regulates netrin-1 expression and affects the conditional tumor suppressive activity of the netrin-1 receptors. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(4):1248-1257.
[22] Aherne CM, Collins CB, Masterson JC, et al. Neuronal guidance molecule netrin-1 attenuates inflammatory cell trafficking during acute experimental colitis. Gut. 2012;61(5): 695-705.
[23] Yuan L, Wu Y, Ren X, et al. Isoorientin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory responses through down-regulation of ROS-related MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in BV-2 microglia. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014; 386(1-2):153-165.
[24] Renard P, Ernest I, Houbion A, et al. Development of a sensitive multi-well colorimetric assay for active NFkappaB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29(4):E21.
[25] Yi D, Hou Y, Wang L, et al. Dietary N-acetylcysteine supplementation alleviates liver injury in lipopolysaccharide- challenged piglets. Br J Nutr. 2014;111(1):46-54.
[26] Qiu Y, Zhang J, Liu Y, et al. The combination effects of acetaminophen and N-acetylcysteine on cytokines production and NF-κB activation of lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglet mononuclear phagocytes in vitro and in vivo. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2013;152(3-4):381-388.
[27] Wang HW, Yang W, Lu JY, et al. N-acetylcysteine administration is associated with reduced activation of NF-kB and preserves lung dendritic cells function in a zymosan-induced generalized inflammation model. J Clin Immunol. 2013;33(3):649-660. |
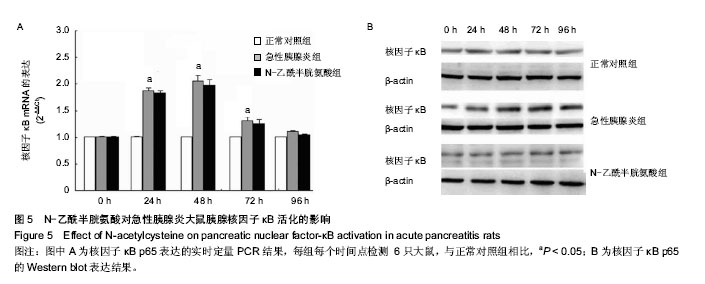
.jpg)
.jpg)