1.1 设计 体外细胞观察实验及动物实验。
1.2 时间及地点 于2018年1月至2019年2月在南通大学附属吴江医院(苏州市第九人民医院)中心实验室进行。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 8周龄C57/BL6雌性小鼠24只,SPF级,体质量20-22 g,购自上海灵畅生物科技有限公司。
1.3.2 实验试剂及仪器 葡聚糖硫酸钠(MW=36 000- 50 000,MP Biomedicals,美国);鼠抗人CD29-PE、CD90-PE、CD105-PE、CD146-PE、CD34-PE、CD45-PE及小鼠Treg流式检测试剂盒[True-Nuclear™ One
Step Staining Mouse Treg Flow™ Kit(FOXP3 Alexa Fluor® 488/CD25 PE/CD4 PerCP)]
(BioLegend,美国);兔抗人FasL单克隆抗体(CST,美国);α-MEM培养基及胎牛血清(Hyclone,美国);人FasL基因的shRNA慢病毒干扰载体试剂套装(吉凯基因公司);人白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α检测ELISA试剂盒(联科生物);CCK-8细胞增殖检测试剂盒及蛋白提取试剂盒(碧云天);40 μm及100 μm孔径的细胞滤网(BD,美国);倒置荧光显微镜(奥林巴斯,日本);UVP Chem Studio Plus多功能化学发光成像系统(Analytik
Jena,德国);流式细胞分析仪(BD Calibur,美国)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 根尖牙乳头干细胞的分离、培养
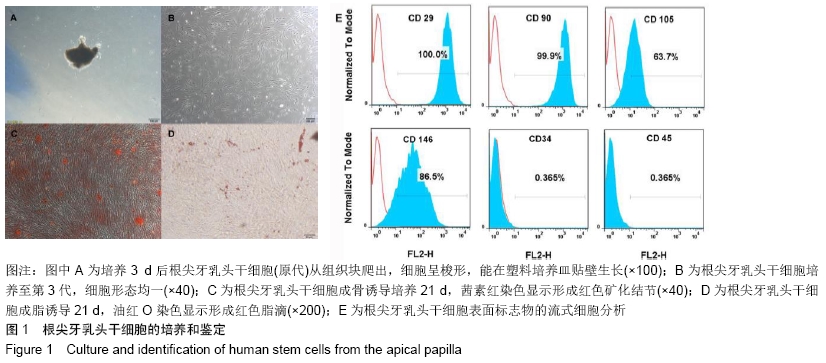
临床采集因正畸拔除的根尖尚未发育完成的健康前磨牙。无菌条件下分离根尖牙乳头,采用组织块培养法将根尖乳头组织碎块放入含体积分数为15%胎牛血清的α-MEM培养基中,于37 ℃,体积分数为5% CO2条件下进行培养,每周换液2次,细胞融合达80%时用2.5 g/L胰酶消化传代,取第3代细胞用于以下实验。
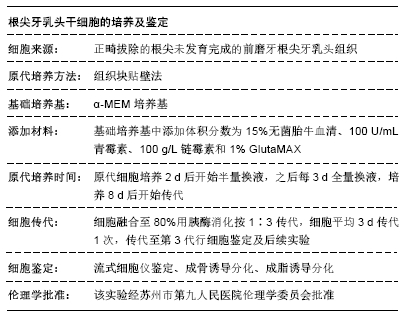
1.4.2 根尖牙乳头干细胞表面标志物鉴定 用PBS将第3代根尖牙乳头干细胞重悬为2×109 L-1的细胞悬液,分装于离心管,每管100 μL。每管分别加入2 μL鼠抗人CD29-PE、CD34-PE、CD45-PE、CD90-PE、CD105-PE、CD146-PE单克隆抗体,并设1管空白对照,4 ℃避光孵育30 min,PBS洗3次,1 600 r/min离心6 min后重悬于含0.5% BSA的PBS溶液中,流式细胞仪检测细胞表面标志物的阳性表达率。
1.4.3 成骨、成脂诱导培养 将第3代根尖牙乳头干细胞接种于6孔培养板进行细胞培养,到50%-60%融合时,将完全培养液换为含50 mg/L抗坏血酸、0.1 mol/L地塞米松、10 mmol/L β-甘油酸钠的成骨培养液进行成骨诱导3周,茜素红染色观察矿化结节,评估根尖牙乳头干细胞的成骨能力。
将第3代根尖牙乳头干细胞接种于6孔培养板进行细胞培养,到50%-60%融合时,将完全培养液换为含 0.5 mmol/L IBMX、60 μmol/L吲哚美辛、0.5 μmol/L氢化可的松,10 mg/L胰岛素的成脂诱导液诱导培养3周,油红O染色评估根尖牙乳头干细胞的成脂能力。
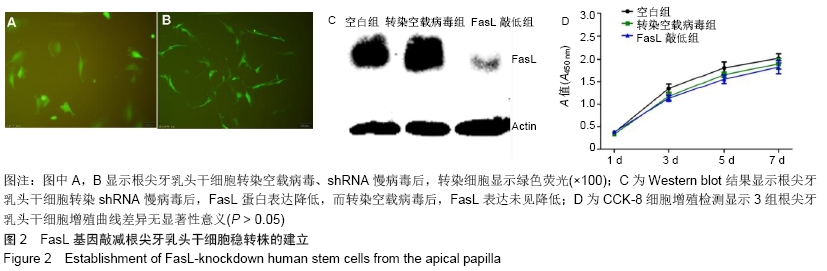
1.4.4 FasL的基因敲减 第3代根尖牙乳头干细胞的FasL基因敲减稳转株的建立按照试剂盒说明书进行操作。转染后24 h倒置荧光显微镜下观察转染效率。细胞发出明亮的绿色荧光为转染阳性细胞,用1%嘌呤霉素杀死未感染细胞,从而获得FasL敲减根尖牙乳头干细胞;对照组细胞转染空载慢病毒,空白组未进行转染。
1.4.5 CCK-8检测细胞增殖 将空白组、转染空载病毒组及FasL 敲低组根尖牙乳头干细胞接种到96孔板,接种密度均为3×103/孔,接种量为 100 μL/孔,每3 d更换培养液,分别在1,3,5,7 d各时间点加入CCK-8孵育2 h,酶标仪450 nm波长检测吸光度值,绘制增殖曲线。
1.4.6 Western blot检测各组根尖牙乳头干细胞的FasL表达水平 提取细胞蛋白,BCA法定量后,将20 μg蛋白加样到含0.1% SDS的10%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶上,电泳分离蛋白并转移到硝酸纤维素膜上;5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭1 h,用抗FasL和GAPDH蛋白抗体4 ℃孵育过夜,用过氧化物酶缀合的二抗孵育1 h。使用UVP ChemStudio Plus化学发光成像系统显示及分析蛋白条带。
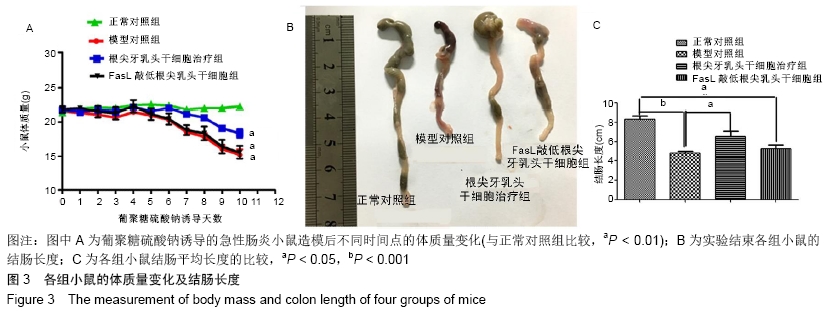
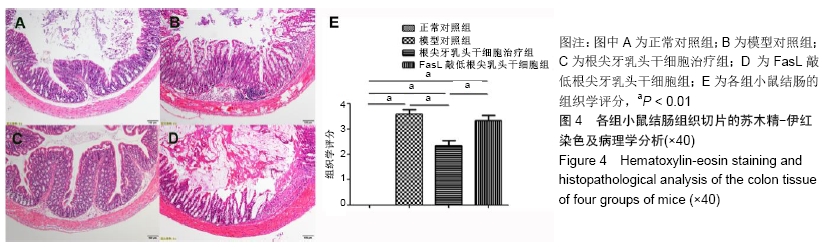
1.4.7 小鼠急性肠炎模型的诱导及细胞治疗 将24只小鼠随机平均分为4组(n=6):正常对照组正常饮水,其余3组(模型对照组、根尖牙乳头干细胞治疗组及FasL敲低根尖牙乳头干细胞组)小鼠饮水中给予3%葡聚糖硫酸钠以诱导实验性肠炎,此时记为第0天。根尖牙乳头干细胞治疗组在第3天一次性腹腔注射空载病毒转染的根尖牙乳头干细胞 2×106个(200 μL PBS);FasL敲减根尖牙乳头干细胞组则注射FasL敲低的根尖牙乳头干细胞2×106个(200 μL PBS);模型对照组注射200 μL PBS。每日记录各组小鼠的体质量、大便性状、便血及死亡情况。第10天麻醉后断颈处死小鼠,完整剖取结肠(从回盲部到肛门)并测量其长度,PBS冲洗去除结肠内容物,然后在上、中、下3个部位截取一小段结肠做苏木精-伊红染色及病理组织分析;剪取靠近肛门上方2.0-3.0 mm段结肠,用冷PBS清洗后-80 ℃冰箱冻存用于炎症相关细胞因子的ELISA分析。
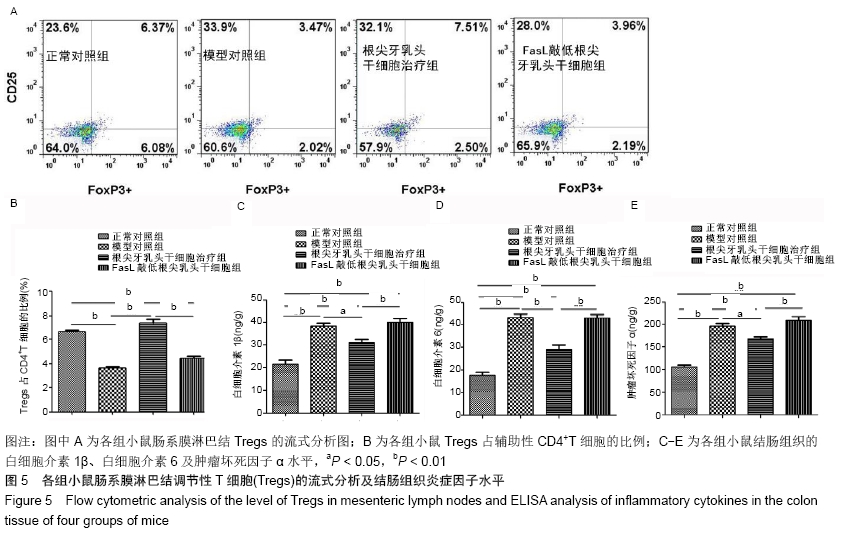
1.4.8 流式细胞分析 采集肠系膜淋巴结,通过100 μm孔径的滤网研磨,40 μm孔径的滤网过滤获得淋巴细胞单细胞悬液。为了分析调节性T细胞(Tregs)在CD4+辅助性T细胞中的比例,取1×106/管细胞先用小鼠Treg流式检测试剂盒中的试剂对细胞进行固定、打孔,然后加入20 μL鼠抗人Alexa Fluor® 488
FOXP3/CD25 PE/CD4 PerCP抗体混合液或20 µL
Alexa Fluor® 488小鼠IgG1同型对照/CD25 PE/CD4 PerCP抗体混合液在冰上避光条件下孵育 60 min;再用流式分析清洗缓冲液(PBS加0.5% BSA配置)清洗细胞,最后用流式细胞分析仪及FlowJo 10软件进行流式分析。
1.4.9 结肠组织病理学分析 40 g/L多聚甲醛溶液固定结肠组织,常规石蜡包埋,6 μm厚度切片做苏木精-伊红染色。显微镜下观察形态特点并进行组织病理学评分(参照COOPER等[17]的报道):共分为5个等级,0级:少量炎细胞;1级:黏膜固有层和黏膜下层轻度炎症;2级:黏膜固有层和黏膜下层重度炎症;3级:全结肠壁轻度炎症;4级:全结肠壁重度炎症。
1.4.10 ELISA分析炎症相关细胞因子水平 取50 mg左右结肠组织,PBS冲洗后剪碎,冰上用匀浆器制成匀浆;蛋白提取试剂盒提取细胞蛋白。BCA法检测蛋白浓度,再按照ELISA试剂盒说明书检测白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①各组小鼠的体质量变化及结肠长度;②各组小鼠结肠组织病理学评分;③各组小鼠肠系膜淋巴结Tregs比例及结肠组织炎症因子水平。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 13.0进行统计学分析。吸光度值、体质量、结肠长度、Tregs比例、炎症因子水平多组间均数比较进行单因素方差分析,Tukey检验比较两两组间差异;病理学评分采用Student-t 检验比较两组间均值的差异。P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。