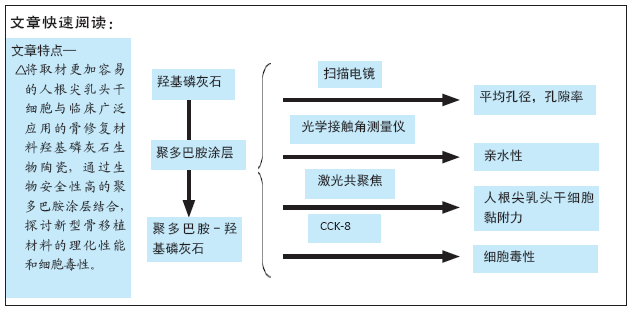
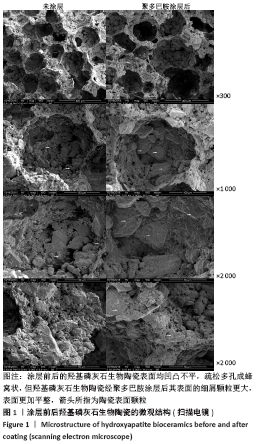
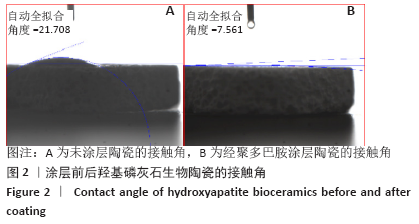
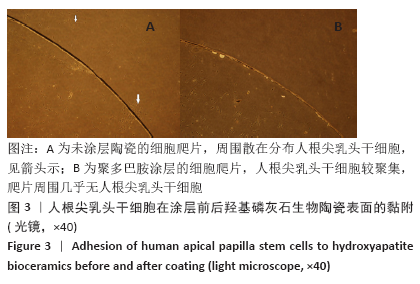
[1] 秦宇星,任前贵,沈佩锋.组织工程骨技术治疗骨缺损的优越性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(24):3877-3882.
[2] 赵灿灿.微纳米结构羟基磷灰石对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的调控研究[D].北京:中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所),2018.
[3] ATAK BH, BUYUK B, HUYSAL M, et al. Preparation and characterization of amine functional nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan bionanocomposite for bone tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;164: 200-213.
[4] SALGADO CL, GRENHO L, FERNANDES MH, et al. Biodegradation, biocompatibility,and osteoconduction evaluation of collagen-nanohydroxyapatite cryogels for bone tissue regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(1):57-70.
[5] KAMALI A, ORYAN A, HOSSEINI S, et al. Cannabidiol-loaded microspheres incorporated into osteoconductive scaffold enhance mesenchymal stem cell recruitment and regeneration of critical-sized bone defects. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:64-75.
[6] SHEN X, ZHANG Y, GU Y, et al. Sequential and sustained release of SDF-1 and BMP-2 from silk fibroin-nanohydroxyapatite scaffold for the enhancement of bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;106: 205-216.
[7] AMJADIAN S, SEYEDJAFARI E, ZEYNALI B, et al. The synergistic effect of nano-hydroxyapatite and dexamethasone in the fibrous delivery system of gelatin and poly(l-lactide) on the osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Pharm. 2016;507(1-2):1-11.
[8] SIMON JD, PELES DN. The red and the black. Accounts Chem Res. 2010; 43(11):1452.
[9] WATT AAR, BOTHMA JP, MEREDITH P. The supramolecular structure of melanin. Soft Matter. 2009;5(19):3754.
[10] LIU YL, AI KL, LIU JH, et al. Dopamine-melanin colloidal nanospheres:An efficient near-infrared photothermal the rapeutic agent for in vivo cancer therapy. Adv Mater. 2013;25(9):1353.
[11] LUO RF, TANG LL, WANG J, et al. Improved immobilization of biomolecules to quinone-rich polydopamine for efficient surface functionalization. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;106:66.
[12] CHO HJ, PERIKAMANA SK, LEE JH, et al. Effective immobilization of BMP-2mediated by polydopamine coating on biodegrDAable nanofibers for enhanced in vivo bone formation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;6(14):11225.
[13] LEE JS, LEE K, MOON SH, et al. Mussel-inspired cell-adhesionpeptide modification for enhanced endothelialization of decellularized blood vessels. Macrol Biosci. 2014;14(8):1181.
[14] 李琰.基于生物粘附分子表面改性的组织修复材料研究[D].北京:北京化工大学,2013.
[15] RIM NG, KIM SJ, SHIN YM, et al. Mussel-inspired surface modification of poly(L-lactide) electrospun fibers for modulation of osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;91:189-197.
[16] KAO CT, LIN CC, CHEN YW, et al. Poly (dopamine) coating of 3D printed poly (lactic acid) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;56:165-173.
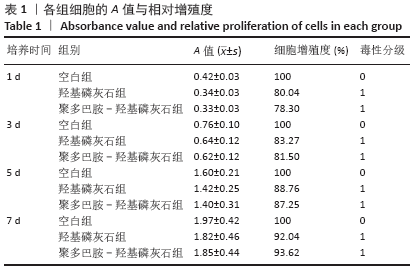
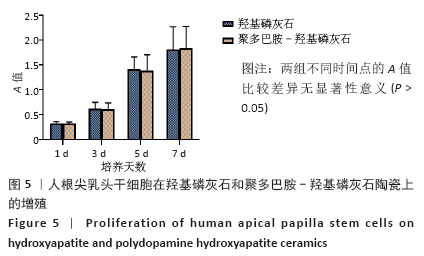
[17] 何林,何淞,吴稀,等.人根尖乳头干细胞在羟基磷灰石和聚多巴胺-羟基磷灰石上的粘附、增殖及成骨分化[J].口腔医学研究, 2020,36(6):523-526.
[18] 王振兴.基于多巴胺的聚偏氟乙烯膜表面亲水化改性及性能研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2017.
[19] 奚江波.高性能负载型钯基纳米催化剂的制备及其应用[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2015.
[20] 高军凯.新型吸附材料的制备及其对溶液中铀的净化研究[D].天津:天津大学,2015.
[21] 陈丽娟.抗蛋白质吸附聚合物接枝聚多巴胺涂层的设计及其应用[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学,2013.
[22] KO CC, WANG Z, TSENG HC, et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of polydopamine-laced gelatinous hydroxyapatite nanocomposites for orthopedic applications. Advances in Bioceramics and Biotechnologies II: Ceramic Transactions. 2014:135-148.
[23] YANG H, XU Y, ZHU M, et al. Inhibition of titanium-particle-induced inflammatory osteolysis after local administration of dopamine and suppression of osteoclastogenesis via D2-like receptor signaling pathway. Biomaterials. 2016;80: 1-10.
[24] LEE DJ, TSENG HC, WONG SW, et al. Dopaminergic effects on in vitro osteogenesis.Bone Res. 2015;3: 15020.
[25] BUIZER AT, VELDHUIZEN AG, BULSTRA SK, et al. Static versus vacuum cell seeding on high and low porosity ceramic scaffolds. Biomater Appl. 2014;29(1):3-13.
[26] 聂姗姗,刘佳,张瑞涵,等.牙髓干细胞MHC分子表达与体外混合淋巴细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(50):8162-8167.
[27] 任俊臣.多孔羟基磷灰石支架表面微纳米结构的构建及其表征[D].成都:西南交通大学,2016.
[28] TU MG, HO CC, HSU TT, et al. Mineral Trioxide Aggregate with Mussel-inspired Surface Nanolayers for Stimulating Odontogenic Differentiation of Dental Pulp Cells. J Endod. 2018;44(6):963-970.
|