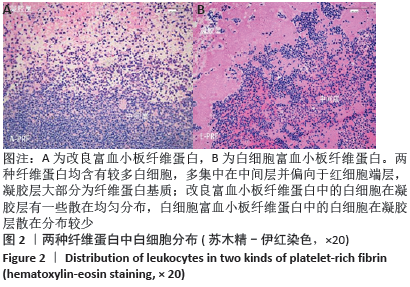
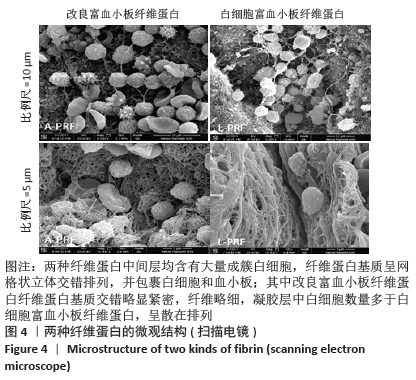
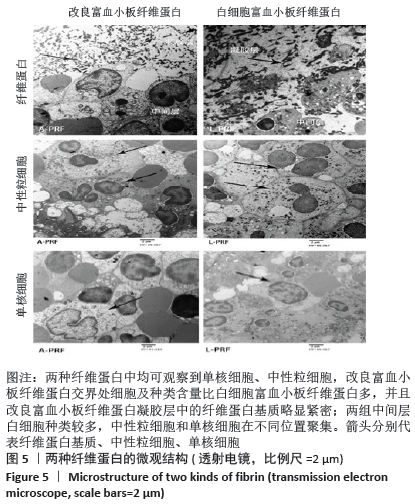
[1] ANFOSSI G, TROVATI M, MULARONI E, et al. Influence of propranolol on platelet aggregation and thromboxane B2 production from platelet-rich plasma and whole blood. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1989;36:1-7.
[2] FIJNHEER R, PIETERSZ RN, DE KORTE D, et al. Platelet activation during preparation of platelet concentrates:A comparison of the platelet-rich plasma and the buffy coat methods. Transfusion. 1990;30:634-638.
[3] MARX RE. Platelet-rich plasma: Evidence to support its use. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62:489-496.
[4] TOFFLER M. Guided bone regeneration (GBR) using cortical bone pins in combination with leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2014;35:192-198.
[5] LEKOVIC V, MILINKOVIC I, ALEKSIC Z, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin and bovine porous bone mineral vs. platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of intrabony periodontal defects. Periodontal Res. 2012;47:409-417.
[6] SHIVASHANKAR VY, JOHNS DA, VIDYANATH S, et al. Combination of platelet rich fibrin, hydroxyapatite and PRF membrane in the management of large inflammatory periapical lesion. Conserv Dent. 2013;16:261-264.
[7] KOBAYASHI E, FLÜCKIGER L, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, et al. Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(9):2353-2360.
[8] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, ANDIA I, ZUMSTEIN MA, et al. Classification of platelet concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for topical and infiltrative use in orthopedic and sports medicine: current consensus, clinical implications and perspectives. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4(1):3-9.
[9] SIMONPIERI A, DEL CORSO M, SAMMARTINO G, et al. The relevance of Choukrounan platelet-rich fibrin and metronidazole during complex maxillary rehabilitations using bone allograft. Part I: A new grafting protocol. Implant Dent. 2009;18:102-111.
[10] MARTINEZ CE, SMITH PC, PALMA ALVARADO VA. The influence of platelet-derived products on angiogenesis and tissue repair: a concise update. Front Physiol. 2015;6:290.
[11] EREN G, KANTARCI A, SCULEAN A, et al. Vascularization after treatment of gingival recession defects with platelet-rich fibrin or connective tissue graft. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20:2045-2053.
[12] CASTRO AB, MESCHI N, TEMMERMAN A, et al. Regenerative potential of leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin. Part A: intra-bony defects, furcation defects and periodontal plastic surgery. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Periodontol. 2017;44:67-82.
[13] PANDA S, DORAISWAMY J, MALAIAPPAN S, et al. Additive effect of autologous platelet concentrates in treatment of intrabony defects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Investig Clin Dent. 2016;7:13-26.
[14] SUTTAPREYASRI S, LEEPONG N. Influence of platelet-rich fibrin on alveolar ridge preservation. Craniofac Surg. 2013;24:1088e94.
[15] JEONG SM, LEE CU, SON JS, et al. Simultaneous sinus lift and implantation using platelet-rich fibrin as sole grafting material. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42:990e4.
[16] 王灿莉,焦志立,孙勇,等.两种富血小板纤维蛋白对人牙龈成纤维细胞增殖活性影响的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(7): 1007-1012.
[17] GHANAATI S,BOOMS P,ORLOWSKA A,et al. Advanced platelet-rich fibrin:a new concept for cell-based tissueengineering by means of inflammatorycells. J Oral Implant. 2014;40(6):679-689.
[18] DOHAN DM, CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part III: leucocyte activation: a new feature for platelet concentrates? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):e51-e55.
[19] CHOUKROUN J, ADDA F, SCHOEFFLER C, et al. Une opportuniteeit paro-implantologie: le PRF. Implantodontie. 2000;42: 55-62.
[20] 裴延平,林松杉.富血小板纤维蛋白的临床应用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2012,28(7):441-443.
[21] MASUKI H, OKUDERA T, WATANEBE T, et al. Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF), advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth factors(CGF). Int J Implant Dent. 2016;2:19.
[22] 李艳秋,周延民,孙晓琳,等.富血小板纤维蛋白体外释放TGF-G和PDGF-AB影响因素的探讨[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2012,26(6): 404-407.
[23] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, DISS A, ODIN G, et al. In vitroeffects of Choukrounro PRF(platelet-rich fibrin) on human gingival fibroblasts, dermal prekeratinocytes,preadipocytes, and maxillofacial osteoblasts in primary cultures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108(3):341-352.
[24] DAVID M, JOSEPH C, ANTOINE D, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: Technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):e37-44.
[25] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, DOGLIOLI GM, DEL CM, et al. Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) stimulates in vitro proliferation and differentiation of human oral bone mesenchymal stem cell in a dose-dependent way. Arch Oral Biol.2010;55(3):185.
[26] LIAO HT, CHEN CT, CHEN CH, et al. Combination of guided osteogenesis with autologous platelet-rich fibrin glue and mesenchymal stem cell for mandibular reconstruction. J Trauma. 2011;70(1):228.
[27] KNAFL D, THALHAMMER F, VOSSEN MG. In-vitro release pharmacokinetics of amikacin, teicoplanin and polyhexanide in a platelet rich fibrin-layer (PRF)-a laboratory evaluation of a modern, autologous wound treatment. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0181090.
[28] ASAKA T, OHGA N, YAMAZAKI Y, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin may reduce the risk of delayed recovery in tooth-extracted patients undergoing oral bisphosphonate therapy: a trial study. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;11:1-8.
[29] PARK JH, KIM JW, KIM SJ. Does the Addition of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 to Platelet-Rich Fibrin Improve Healing After Treatment for Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75(6):1176-1184.
[30] PATHAK H, MOHANTY S, URS AB. Treatment of Oral Mucosal Lesions by Scalpel Excision and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Membrane Grafting: A Review of 26 Sites. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;73(9):1865-1874.
[31] ÖNCÜ E. The Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Versus Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft in Treatment of Multiple Gingival Recessions: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2017; 37(2):265-271.
[32] DEL CORSO M, VERVELLE A, SIMONPIERI A, et al. Current knowledge and perspectives for the use of platelet-rich plasma(PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in oral and maxillofacial surgery part 1: Periodontal and dentoalveolar surgery. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(7):1207-1230.
[33] SIMONPIERI A, DEL CORSO M, VERVELLE A, et al. Current knowledge and perspectives for the use of platelet-rich plasma(PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in oral and maxillofacial surgery part 2: Bone graft, implant and reconstructive surgery. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(7):1231-1256.
[34] ZUMSTEIN MA, BERGER S, SCHOBER M, et al. Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) for long-term delivery of growth factorin rotator cuff repair: review, preliminary results and future directions. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(7):1196-1206.
[35] ZUMSTEIN MA, BIELECKI T, DOHAN EHRENFEST DM. The Future of Platelet Concentrates in Sports Medicine: Platelet-Rich Plasma,Platelet-Rich Fibrin, and the Impact of Scaffolds and Cells on the Long-term Delivery of Growth Factors. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2011;19(3): 190-197.
[36] MAJID E, MOHAMAD RM, AMIR HN, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin: An Autologous Fibrin Matrix in Surgical Procedures: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;24(69): 197-202.
[37] DOHAN DM, CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):e45-50.
[38] CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, SIMONPIERI A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF):a second-generationplatelet concentrate. Part V:histologic evaluations of PRFeffects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):299-303.
[39] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, PINTO NR, Pereda A, et al. The impact of the centrifuge characteristics and centrifugation protocols on the cells, growth factors, and fibrin architecture of a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) clot and membrane. Platelets. 2017;24:1-14.
[40] FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, MIRON RJ, HERNANDEZ M, et al. Optimized Platelet-Rich Fibrin With the Low-Speed Concept: Growth Factor Release, Biocompatibility, and Cellular Response. J Periodontol. 2017; 88(1):112-121.
[41] MARCHETTI E, MANCINI L, BERNARDI S, et al. Evaluation of Different Autologous Platelet Concentrate Biomaterials: Morphological and Biological Comparisons and Considerations. Materials. 2020:13(10): 2282.
[42] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, DEL CORSO M, DISS A, et al. Three-dimensional architecture and cell composition ofa Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin clot and membrane. J Periodontol. 2010;81(4): 546-555.
[43] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, DE PEPPO GM, DOGLIOLI P, et al. Slow release of growth factors and thrombospondin-1 inChoukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a gold standard to achieve for all surgical platelet concentrates technologies. Growth Factors. 2009;27(1):63-69. |