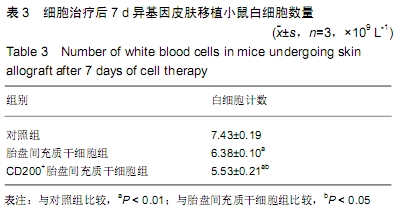
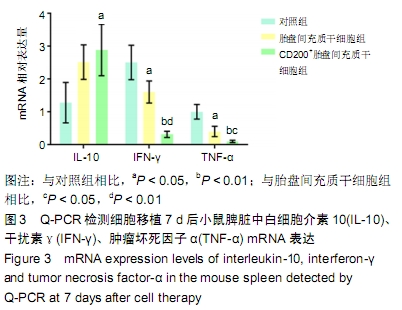
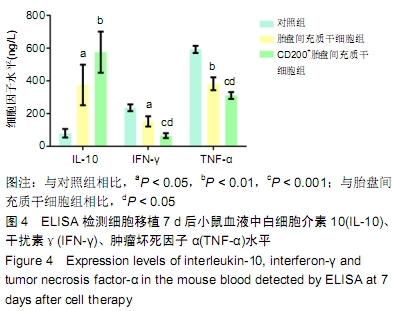
[1] REN X, LAUGEL MC. The next frontier in composite tissue allotransplantation. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013;19(1):1-4.
[2] SHECKTER CC, LI A, PRIDGEN B, et al. The impact of skin allograft on inpatient outcomes in the treatment of major burns 20-50% total body surface area - A propensity score matched analysis using the nationwide inpatient sample. Burns. 2019;45(1):146-156.
[3] COZZI E, VIAL C, OSTLIE D, et al. Maintenance triple immunosuppression with cyclosporin A, mycophenolate sodium and steroids allows prolonged survival of primate recipients of hDAF porcine renal xenografts. Xenotransplantation. 2003;10(4):300-310.
[4] CHUA AW, KHOO YC, TAN BK, et al. Skin tissue engineering advances in severe burns: review and therapeutic applications. Burns Trauma. 2016;4:3.
[5] VYAS KS, BURNS C, RYAN DT, et al. Prolonged Allograft Survival in a Patient With Chronic Immunosuppression: A Case Report and Systematic Review. Wounds. 2017;29(6): 159-162.
[6] VAN SANDWIJK MS, BEMELMAN FJ, Ten Berge IJ. Immunosuppressive drugs after solid organ transplantation. Neth J Med. 2013;71(6):281-289.
[7] BAJEK A, GURTOWSKA N, OLKOWSKA J, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Tool in Cell-Based Therapies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64(6): 443-454.
[8] MA T, WANG X, JIANG D. Immune Tolerance of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Induction of Skin Allograft Tolerance. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(5):409-415.
[9] LEE H, PARK JB, LEE S, et al. Intra-osseous injection of donor mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) into the bone marrow in living donor kidney transplantation; a pilot study. J Transl Med. 2013;11:96.
[10] KOIKE Y, ADACHI Y, SUZUKI Y, et al. Allogeneic intrabone marrow-bone marrow transplantation plus donor lymphocyte infusion suppresses growth of colon cancer cells implanted in skin and liver of rats. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):385-391.
[11] KANEDA H, ADACHI Y, SAITO Y, et al. Long-term observation after simultaneous lung and intra-bone marrow-bone marrow transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2005;24(9):1415-1423.
[12] FENG W, CUI Y, ZHAN H, et al. Prevention of premature ovarian failure and osteoporosis induced by irradiation using allogeneic ovarian/bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation. 2010;89(4):395-401.
[13] ROSENBLUM MD, YANCEY KB, OLASZ EB, et al. CD200, a "no danger" signal for hair follicles. J Dermatol Sci. 2006; 41(3):165-174.
[14] ROSENBLUM MD, WOODLIFF JE, MADSEN NA, et al. Characterization of CD 200-receptor expression in the murine epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125(6):1130-1138.
[15] WRIGHT GJ, CHERWINSKI H, FOSTER-CUEVAS M, et al. Characterization of the CD200 receptor family in mice and humans and their interactions with CD200. J Immunol. 2003; 171(6):3034-3046.
[16] GORCZYNSKI RM, CHEN Z, HE W, et al. Expression of a CD200 transgene is necessary for induction but not maintenance of tolerance to cardiac and skin allografts. J Immunol. 2009;183(3):1560-1568.
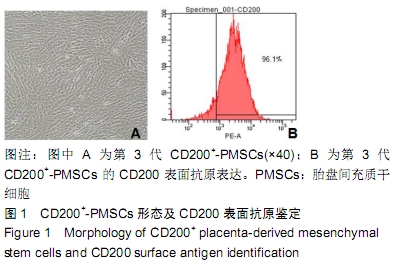
[17] 刘婷,马晓娜,马海滨,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞CD200+亚群细胞的免疫特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1):79-84.
[18] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[19] LE BLANC K, TAMMIK C, ROSENDAHL K, et al. HLA expression and immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2003;31(10):890-896.
[20] TSE WT, PENDLETON JD, BEYER WM, et al. Suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation by human marrow stromal cells: implications in transplantation. Transplantation. 2003; 75(3):389-397.
[21] CORNELISSEN AS, MAIJENBURG MW, Nolte MA, et al. Organ-specific migration of mesenchymal stromal cells: Who, when, where and why? Immunol Lett. 2015;168(2):159-169.
[22] SONG CG, ZHANG YZ, WU HN, et al. Stem cells: a promising candidate to treat neurological disorders.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(7):1294-1304.
[23] KAVANAGH H, MAHON BP. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells prevent allergic airway inflammation by inducing murine regulatory T cells. Allergy. 2011;66(4):523-531.
[24] LUZ-CRAWFORD P, KURTE M, BRAVO-ALEGRÍA J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells generate a CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell population during the differentiation process of Th1 and Th17 cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(3):65.
[25] KAUNDAL U, BAGAI U, RAKHA A. Immunomodulatory plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells: a potential key to successful solid organ transplantation. J Transl Med. 2018; 16(1):31.
[26] CHO KS, KIM YW, KANG MJ, et al. Immunomodulatory Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on T Lymphocyte and Cytokine Expression in Nasal Polyps. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;150(6):1062-1070.
[27] CAGLIANI J, GRANDE D, MOLMENTI EP, et al. Immunomodulation by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Clinical Applications. J Stem Cell Regen Biol. 2017;3(2):1-26.
[28] FRANQUESA M, HOOGDUIJN MJ, BESTARD O, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of mesenchymal stem cells on B cells. Front Immunol. 2012;3:212.
[29] SPAGGIARI GM, CAPOBIANCO A, ABDELRAZIK H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit natural killer-cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine production: role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E2. Blood. 2008;111(3): 1327-1333.
[30] VAN DEN BERK LC, JANSEN BJ, SNOWDEN S, et al. Cord blood mesenchymal stem cells suppress DC-T Cell proliferation via prostaglandin B2. Stem Cells Dev. 2014; 23(14):1582-1593.
[31] SPAGGIARI GM, ABDELRAZIK H, BECCHETTI F, et al. MSCs inhibit monocyte-derived DC maturation and function by selectively interfering with the generation of immature DCs: central role of MSC-derived prostaglandin E2. Blood. 2009; 113(26):6576-6583.
[32] HOEK RM, RUULS SR, MURPHY CA, et al. Down-regulation of the macrophage lineage through interaction with OX2 (CD200). Science. 2000;290(5497):1768-1771.
[33] JENMALM MC, CHERWINSKI H, BOWMAN EP, et al. Regulation of myeloid cell function through the CD200 receptor. J Immunol. 2006;176(1):191-199.
[34] WRIGHT GJ, PUKLAVEC MJ, WILLIS AC, et al. Lymphoid/neuronal cell surface OX2 glycoprotein recognizes a novel receptor on macrophages implicated in the control of their function. Immunity. 2000;13(2):233-242.
[35] GORCZYNSKI RM, LEE L, BOUDAKOV I. Augmented Induction of CD4+CD25+ Treg using monoclonal antibodies to CD200R. Transplantation. 2005;79(9):1180-1183.
[36] GORCZYNSKI RM, HU J, CHEN Z, et al. A CD200FC immunoadhesin prolongs rat islet xenograft survival in mice. Transplantation. 2002;73(12):1948-1953.
[37] GORCZYNSKI RM, CHEN Z, KHATRI I, et al. Graft-infiltrating cells expressing a CD200 transgene prolong allogeneic skin graft survival in association with local increases in Foxp3(+)Treg and mast cells. Transpl Immunol. 2011;25(4): 187-193.
[38] KONG T, PARK JM, JANG JH, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of CD200-positive human placenta-derived stem cells in the early phase of stroke. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(1):e425.
[39] OGAWA Y, DURU EA, AMEREDES BT. Role of IL-10 in the resolution of airway inflammation. Curr Mol Med. 2008;8(5): 437-445.
[40] FUJISAKI J, WU J, CARLSON AL, et al. In vivo imaging of Treg cells providing immune privilege to the haematopoietic stem-cell niche. Nature. 2011;474(7350):216-219.
[41] GURRAM RK, KUJUR W, MAURYA SK, et al. Caerulomycin A enhances transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-Smad3 protein signaling by suppressing interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) protein signaling to expand regulatory T cells (Tregs). J Biol Chem. 2014;289(25):17515-17528.
[42] BREHM MA, MANGADA J, MARKEES TG, et al. Rapid quantification of naive alloreactive T cells by TNF-alpha production and correlation with allograft rejection in mice. Blood. 2007;109(2):819-826.
[43] SHEN H, GOLDSTEIN DR. IL-6 and TNF-alpha synergistically inhibit allograft acceptance. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(5):1032-1040.
|