[1] JAVAN MR, KHOSROJERDI A, MOAZZENI SM. New Insights Into Implementation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cancer Therapy: Prospects for Anti-angiogenesis Treatment. Front Oncol. 2019;9:840.
[2] LI N, HUA J. Interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and the immune system. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(13):2345-2360.
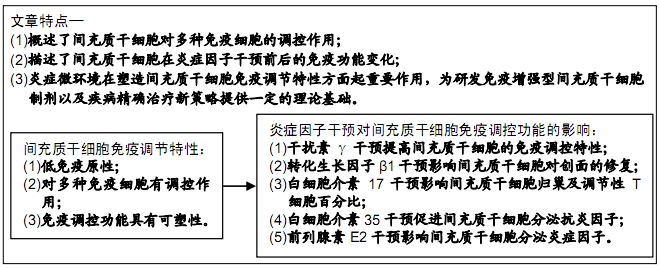
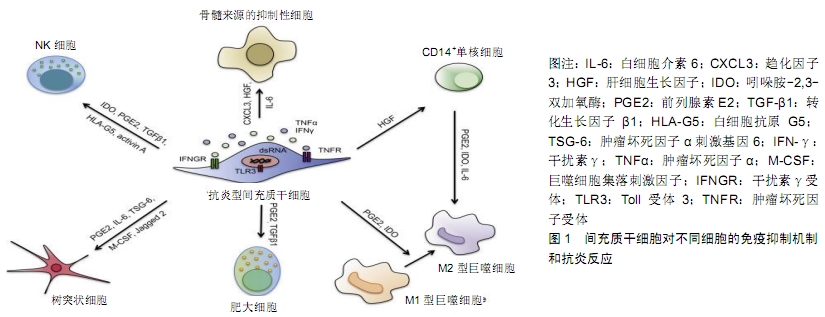
[3] 蒋珊珊,王峰,余丽梅. 间充质干细胞免疫调节特性及在器官移植中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1):103-109.
[4] LIN T, PAJARINEN J, KOHNO Y, et al. Trained murine mesenchymal stem cells have anti-inflammatory effect on macrophages, but defective regulation on T-cell proliferation. FASEB J. 2019;33(3): 4203-4211.
[5] WANG Y, CHEN X, CAO W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016.
[6] SZABÓ E, FAJKA-BOJA R, KRISTON-PÁL É, et al. Licensing by Inflammatory Cytokines Abolishes Heterogeneity of Immunosuppressive Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Population. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(18):2171-2180.
[7] KALAMEGAM G, SAIT KHW, ANFINAN N, et al. Cytokines secreted by human Wharton's jelly stem cells inhibit the proliferation of ovarian cancer (OVCAR3) cells in vitro. Oncol Lett. 2019;17(5):4521-4531.
[8] SOHNI A, VERFAILLIE CM. Mesenchymal stem cells migration homing and tracking. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:130763.
[9] LEE HY, HONG IS. Double-edged sword of mesenchymal stem cells: Cancer-promoting versus therapeutic potential. Cancer Sci. 2017; 108(10):1939-1946.
[10] HASS R, KASPER C, BÖHM S, et al. Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): A comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell Commun Signal. 2011;9:12.
[11] ELAHI KC, KLEIN G, AVCI-ADALI M, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Different Sources Diverge in Their Expression of Cell Surface Proteins and Display Distinct Differentiation Patterns. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:5646384.
[12] KRISTJÁNSSON B, HONSAWEK S. Mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. World J Orthop. 2017;8(9): 674-680.
[13] SATO K, OZAKI K, OH I, et al. Nitric oxide plays a critical role in suppression of T-cell proliferation by mesenchymal stem cells. Blood. 2007;109(1):228-234.
[14] RHEE KJ, LEE JI, EOM YW. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Effects of Tumor Support or Suppression. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(12): 30015-30033.
[15] LE BLANC K, DAVIES LC. Mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune response. Immunol Lett. 2015;168(2):140-146.
[16] MUNN DH. Blocking IDO activity to enhance anti-tumor immunity. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012;4:734-745.
[17] MEISEL R, ZIBERT A, LARYEA M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells inhibit allogeneic T-cell responses by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase- mediated tryptophan degradation. Blood. 2004;103(12):4619-4621.
[18] LING W, ZHANG J, YUAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use IDO to regulate immunity in tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(5):1576-1587.
[19] 朱雅姝,赵春华.间充质干细胞的免疫调节能力——临床治疗的希望[J].中国科学(C辑:生命科学),2009,39(8):727-735.
[20] CHAI HH, CHEN MB, CHEN GZ, et al. Inhibitory effect of TGF-β gene modified human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells on rejection after xenotransplantation of peripheral nerves. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(8):3198-3205.
[21] REN G, ZHANG L, ZHAO X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(2):141-150.
[22] 韩秋青,师帅南,王玉亮.脂肪来源间充质干细胞与免疫调节因子间作用的研究进展[J].天津医药,2018,46(1):109-112.
[23] HONG J, HUECKELHOVEN A, WANG L, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase mediates inhibition of virus-specific CD8(+) T cell proliferation by human mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(5):621-629.
[24] XISHAN Z, BIN Z, HAIYUE Z, et al. Jagged-2 enhances immunomodulatory activity in adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:14284.
[25] 何骁,黄宏,徐祥.间充质干细胞在炎症调节中的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2015,37(8): 1173-1179.
[26] SHENG H, WANG Y, JIN Y, et al. A critical role of IFNgamma in priming MSC-mediated suppression of T cell proliferation through up-regulation of B7-H1. Cell Res. 2008;18(8):846-857.
[27] 兰绍阳,谭梅傲,陶双友,等.沉默IFN-γR表达对大鼠BMMSCs免疫调节能力的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(3): 559-564.
[28] XU C, YU P, HAN X, et al. TGF-β promotes immune responses in the presence of mesenchymal stem cells. J Immunol. 2014;192(1):103-109.
[29] GHOSH D, MCGRAIL DJ, DAWSON MR. TGF-β1 Pretreatment Improves the Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Wound Bed. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017;5:28.
[30] LI D, LIU Q, QI L, et al. Low levels of TGF-β1 enhance human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell fibronectin production and extend survival time in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(2):1681-1692.
[31] SI X, LIU X, LI J, et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 promotes homing of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10):12368-12378.
[32] WU J, NIU J, LI X, et al. TGF-β1 induces senescence of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via increase of mitochondrial ROS production. BMC Dev Biol. 2014;14:21.
[33] LÓPEZ P, RODRÍGUEZ-CARRIO J, CAMINAL-MONTERO L, et al. A pathogenic IFNα, BLyS and IL-17 axis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20651.
[34] LORÈ NI, CIGANA C, RIVA C, et al. IL-17A impairs host tolerance during airway chronic infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25937.
[35] TIAN J, RUI K, TANG X, et al. IL-17 down-regulates the immunosuppressive capacity of olfactory ecto-mesenchymal stem cells in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(28): 42953-42962.
[36] TOY D, KUGLER D, WOLFSON M, et al. Cutting edge: interleukin 17 signals through a heteromeric receptor complex. J Immunol. 2006; 177(1):36-39.
[37] PARK H, LI Z, YANG XO, et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(11):1133-1141.
[38] BIE Q, ZHANG B, SUN C, et al. IL-17B activated mesenchymal stem cells enhance proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8(12):18914-18923.
[39] HE T, HUANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. Interleukin-17A-promoted MSC2 polarization related with new bone formation of ankylosing spondylitis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(57):96993-97008.
[40] MA T, WANG X, JIAO Y, et al. Interleukin 17 (IL-17)-Induced Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prolong the Survival of Allogeneic Skin Grafts. Ann Transplant. 2018;23:615-621.
[41] SIVANATHAN KN, ROJAS-CANALES DM, HOPE CM, et al. Interleukin- 17A-Induced Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Are Superior Modulators of Immunological Function. Stem Cells. 2015;33(9):2850-2863.
[42] BAI M, ZHANG L, FU B, et al. IL-17A improves the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in ischemic-reperfusion renal injury by increasing Treg percentages by the COX-2/PGE2 pathway. Kidney Int. 2018;93(4):814-825.
[43] COLLISON LW, CHATURVEDI V, HENDERSON AL, et al. IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T cell population. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(12):1093-1101.
[44] SHEN P, ROCH T, LAMPROPOULOU V, et al. IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature. 2014;507(7492):366-370.
[45] AMARI A, EBTEKAR M, MOAZZENI SM, et al. In Vitro Generation of IL-35-expressing Human Wharton's Jelly-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Lentiviral Vector. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015; 14(4):416-426.
[46] 张志强. IL-35修饰的间充质干细胞免疫调节性能初探[D]. 天津:天津医科大学, 2015.
[47] GUO H, ZHAO N, GAO H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Interleukin-35 Propagate Immunosuppressive Effects in Mice. Scand J Immunol. 2017;86(5):389-395.
[48] WANG W, GUO H, LI H, et al. Interleukin-35 Gene-Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Concanavalin A-Induced Fulminant Hepatitis by Decreasing the Interferon Gamma Level. Hum Gene Ther. 2018;29(2):234-241.
[49] HARRIS SG, PADILLA J, KOUMAS L, et al. Prostaglandins as modulators of immunity. Trends Immunol. 2002;23(3):144-150.
[50] BREYER RM, BAGDASSARIAN CK, MYERS SA, et al. Prostanoid receptors: subtypes and signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:661-690.
[51] WOOLARD MD, WILSON JE, HENSLEY LL, et al. Francisella tularensis-infected macrophages release prostaglandin E2 that blocks T cell proliferation and promotes a Th2-like response. J Immunol. 2007;178(4):2065-2074.
[52] ROZENBERG A, REZK A, BOIVIN MN, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Impact Th17 and Th1 Responses Through a Prostaglandin E2 and Myeloid-Dependent Mechanism. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016; 5(11):1506-1514.
[53] AN JH, SONG WJ, LI Q, et al. Prostaglandin E2 secreted from feline adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate DSS-induced colitis by increasing regulatory T cells in mice. BMC Vet Res. 2018;14(1):354.
[54] ZHUANG Y, ZHAO F, LIANG J, et al. Activation of COX-2/mPGES-1/ PGE2 Cascade via NLRP3 Inflammasome Contributes to Albumin-Induced Proximal Tubule Cell Injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2):797-807.
[55] LUZ-CRAWFORD P, JORGENSEN C, DJOUAD F. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Direct the Immunological Fate of Macrophages. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017;62:61-72.
[56] 曾宽,张露,邓保平,等. 前列腺素E1干预大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的旁分泌和迁移[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(17):2656-2660.
[57] HAN J, LU X, ZOU L, et al. E-Prostanoid 2 Receptor Overexpression Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cell Attenuated Lung Injury. Hum Gene Ther. 2016;27(8):621-630.
[58] 韩继斌. PGE2/EP2介导间充质干细胞向急性肺损伤小鼠肺组织归巢的效应和机制研究[D].南京:东南大学,2016.
|