[1] HURLEY ET, YASUI Y, GIANAKOS AL, et al. Limited evidence for adipose-derived stem cell therapy on the treatment of osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11):3499-3507.
[2] CHALY Y, BLAIR HC, SMITH SM, et al. Follistatin-like protein 1 regulates chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(7):1467-1473.
[3] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387.
[4] 赵志宏,王锐,国宇,等.膝关节骨关节炎患病率及与骨质疏松症相关性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(14):870-875.
[5] ALLEN KD, GOLIGHTLY YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(3):276-283.
[6] PELLETIER JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, RANNOU F, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral NSAIDs and analgesics in the management of osteoarthritis: Evidence from real- life setting trials and surveys. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016;45(4):S22-S27.
[7] DA COSTA BR, REICHENBACH S, KELLER N, et al. Effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of pain in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2017;390(10090):e21-e33.
[8] 王坤正.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018, 38(12):705-715.
[9] HESARI R, KESHVARINIA M, KABIRI M, et al. Comparative impact of platelet rich plasma and transforming growth factor-β on chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells. Bioimpacts. 2020; 10(1):37-43.
[10] TAKAHASHI A, TSUJINO T, YAMAGUCHI S, et al.Distribution of platelets, transforming growth factor-β1, platelet-derived growth factor-BB, vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloprotease-9 in advanced platelet-rich fibrin and concentrated growth factor matrices. J Investig Clin Dent. 2019;10(4):e12458.
[11] CHELLINI F, TANI A, VALLONE L, et al.Platelet-Rich Plasma Prevents In Vitro Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Induced Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition: Involvement of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-A/VEGF Receptor-1-Mediated Signaling †. Cells. 2018;7(9):E142.
[12] SARıKAYA B, YUMUŞAK N, YIGIN A, et al.Comparison of the effects of human recombinant epidermal growth factor and platelet-rich plasma on healing of rabbit patellar tendon. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2017;28(2):92-99.
[13] 罗毅,汪敏加,苏全生,等.富血小板血浆(PRP)凝胶联合TGF-β3对肌腱干细胞成软骨分化影响的实验研究[J].广西大学学报(自然科学版),2019,44(6):1781-1789.
[14] YIN N, WANG Y, DING L, et al.Platelet-rich plasma enhances the repair capacity of muscle-derived mesenchymal stem cells to large humeral bone defect in rabbits.Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6771.
[15] GILBERTIE JM, LONG JM, SCHUBERT AG, et al. Pooled Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate Therapy Increases Synoviocyte Proliferation and Hyaluronic Acid Production While Protecting Chondrocytes From Synoviocyte-Derived Inflammatory Mediators.Front Vet Sci. 2018;5:150.
[16] CHIU CH, LEI KF, YEH WL. Development of a co-culture device for the study of human tenocytes in response to the combined stimulation of electric field and platelet rich plasma (PRP). Biomed Microdevices. 2017;19(3):69.
[17] HULTH A, LINDBERG L, TELHAG H. Experimental osteoarthritis in rabbits: preliminary report. Acta Orthop Scand. 1970;41:552-553.
[18] 邬波,马旭,柳椰,等.膝关节骨关节炎患者软骨炎症因子表达与病变程度的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(2):236-241.
[19] 王锴,董雪,林剑浩,等.影响膝关节骨关节炎患者生活质量预后因素的队列研究[J] .中华骨科杂志,2019,39(18):1149-1156.
[20] ERDLE B, HERRMANN S, PORICHIS S, et al. Sporting Activity Is Reduced 11 Years After First-Generation Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation in the Knee Joint. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(12):2762-2773.
[21] YI LENG, GUANGKAI REN, YUTAO CUI, et al.Platelet-rich plasma-enhanced osseointegration of decellularized bone matrix in critical-size radial defects in rabbits. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(5):198.
[22] 陈玉泉,洪建明,徐俊.不同浓度富血小板血浆修复膝关节软骨损伤的疗效对比[J].医学理论与实践,2019,32(10):1550-1551.
[23] 王一帆,李小峰,罗道明,等.不同浓度富血小板血浆治疗膝关节骨性关节炎临床疗效研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2018,47(9):1113-1118.
[24] WANG Z, LI Z, LI Z, et al. Cartilaginous extracellular matrix derived from decellularized chondrocyte sheets for the reconstruction of osteochondral defects in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2018;81:129-145.
[25] MAYER U, BENDITZ A, GRÄSSEL S.miR-29b regulates expression of collagens I and III in chondrogenically differentiating BMSC in an osteoarthritic environment. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13297.
[26] 张圣扬,吕帅洁,丁权威,等.自体脂肪干细胞关节腔内注射治疗膝关节骨关节炎的随机对照研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(23): 1426-1434.
[27] JO CH, LEE YG, SHIN WH, et al. Intra-articular injection of mesen-chymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a proof-of-concept clinical trial. Stem Cells. 2014;32(5):1254-1266. |
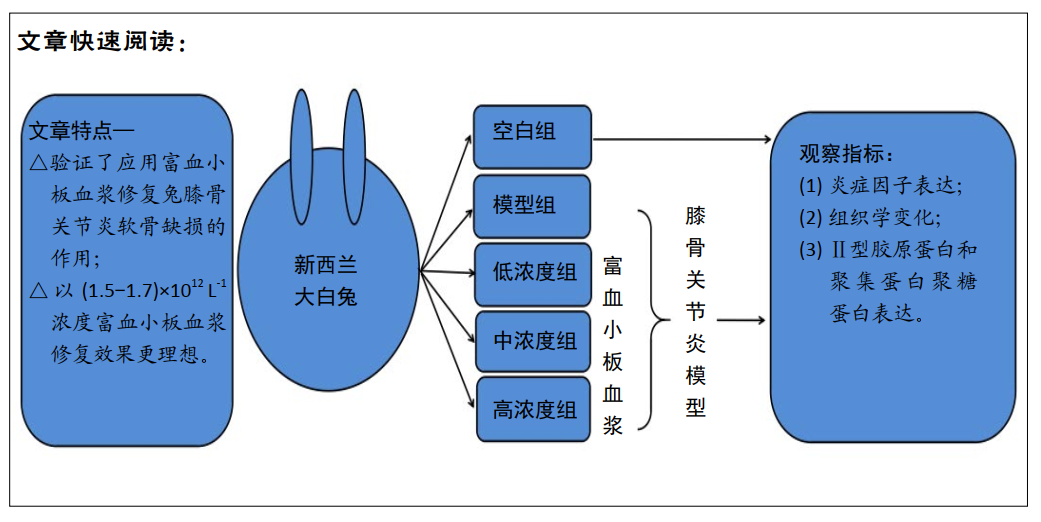
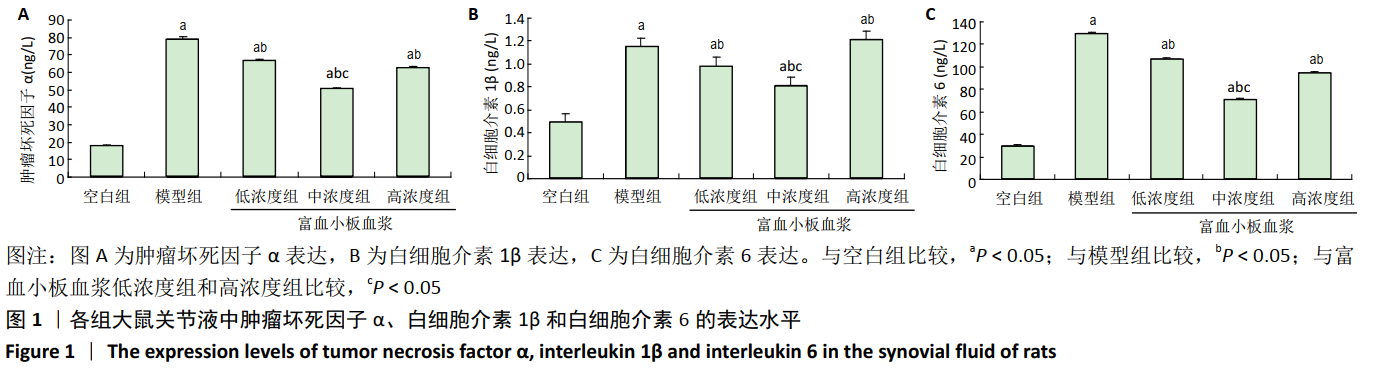
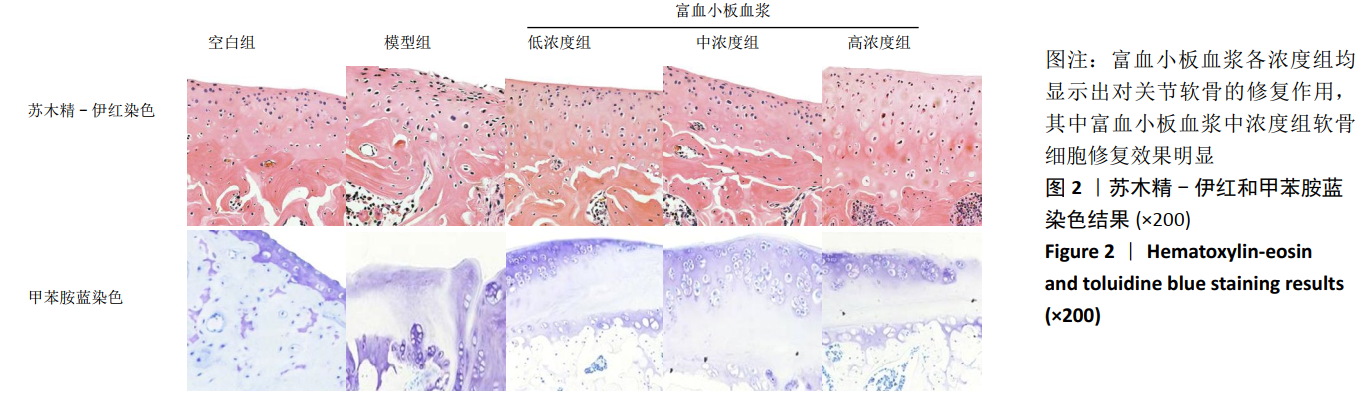
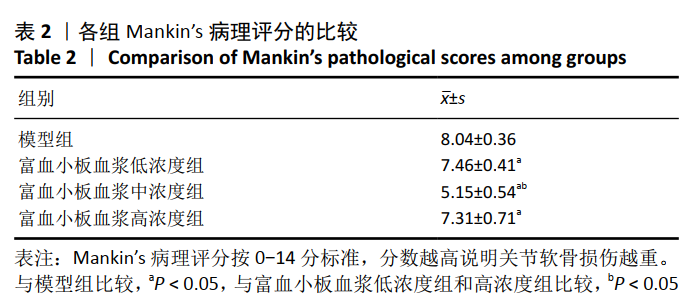
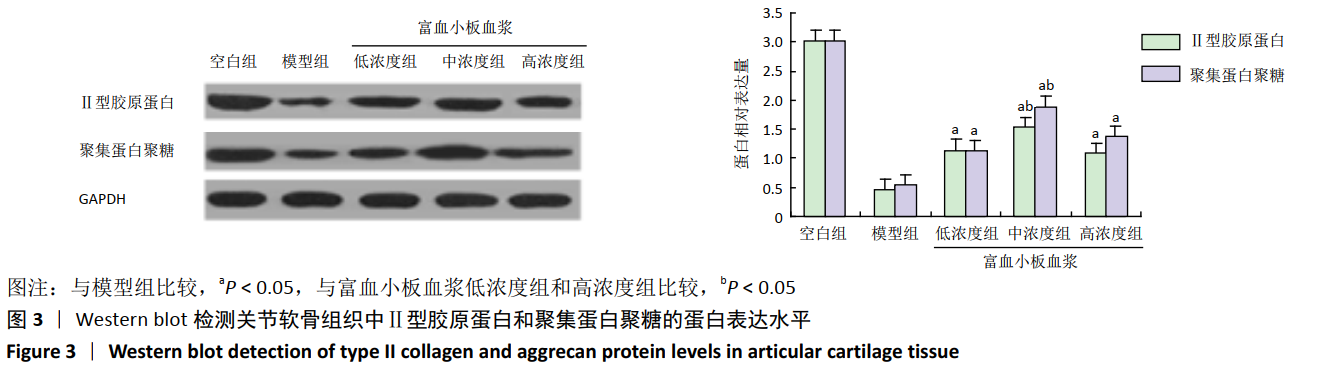


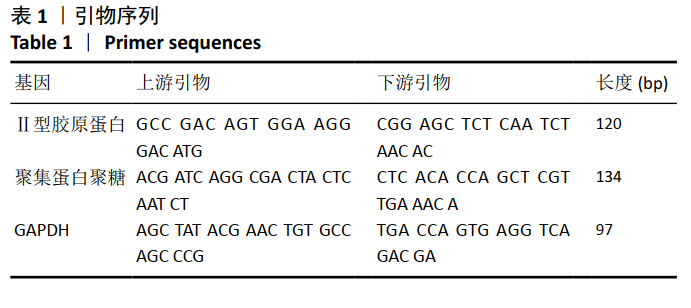 1.5 主要观察指标 ①兔软骨组织大体观察;②兔关节液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的表达;③关节软骨组织形态变化及Mankin’s病理评分;④关节软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的蛋白和mRNA表达水平。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①兔软骨组织大体观察;②兔关节液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的表达;③关节软骨组织形态变化及Mankin’s病理评分;④关节软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的蛋白和mRNA表达水平。