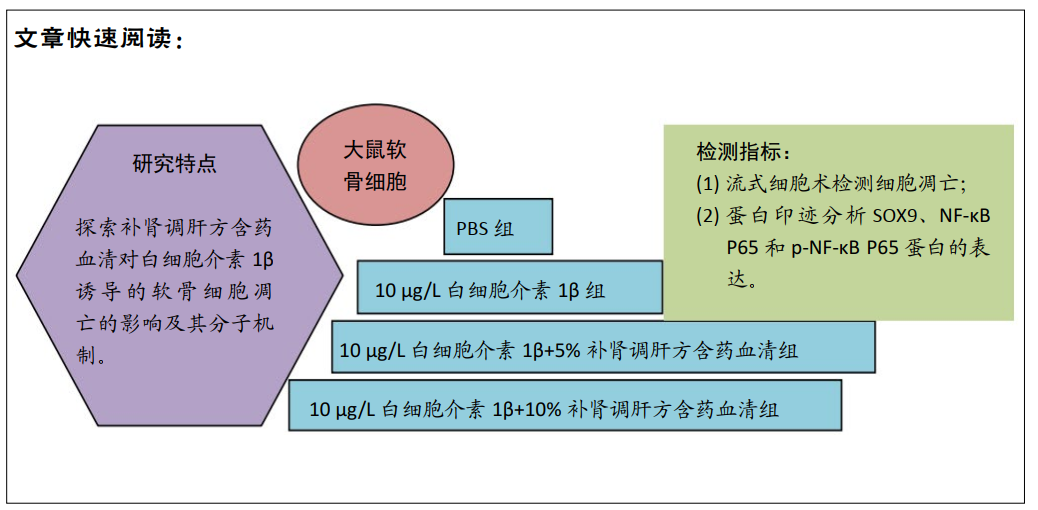
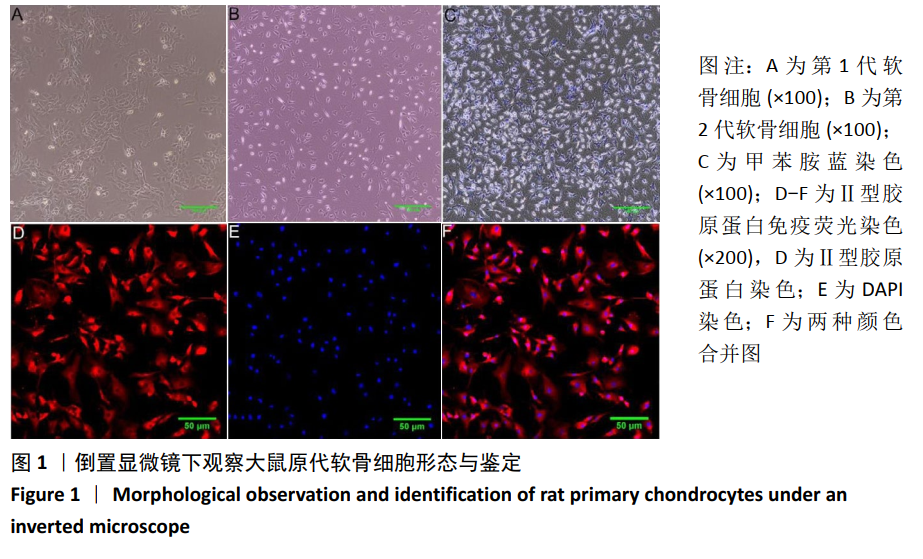
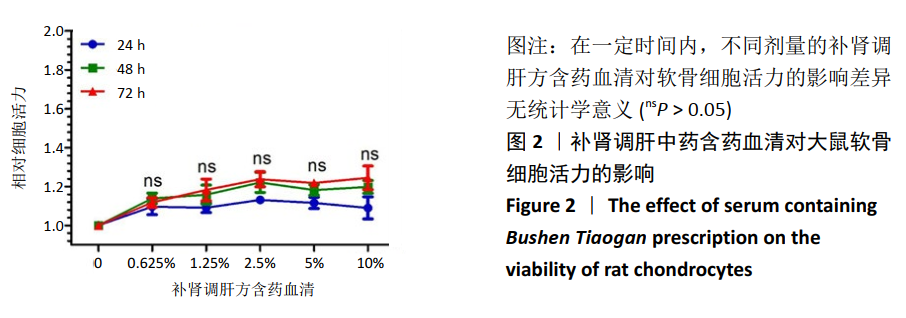
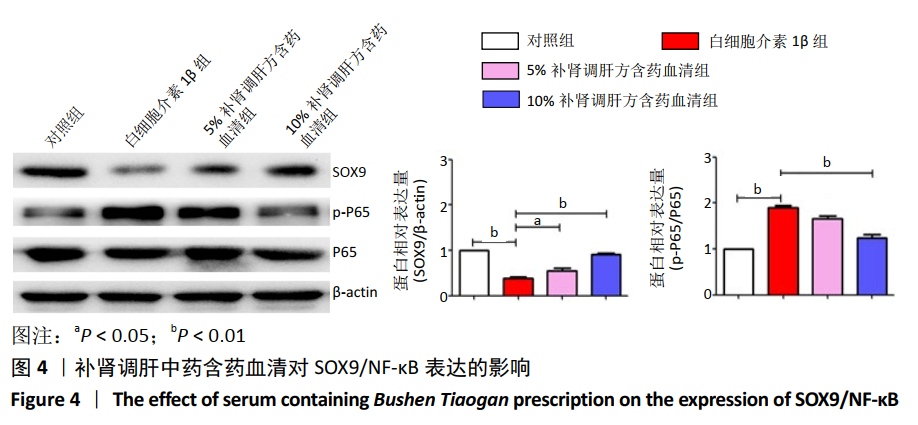
[1] CROSS M, SMITH E, HOY D, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73(7):1323-1330.
[2] 陆艳红, 石晓兵.膝骨关节炎国内外流行病学研究现状及进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(6):81-84.
[3] LEI Z, SHI H, LI W, et al. miR-185 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion through targeting of SOX9 and regulation of Wnt signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1):1742-1752.
[4] KANG S, ZHANG J, YUAN Y. Abietic acid attenuates IL-1beta-induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Int immunopharmacol. 2018;64:110-115.
[5] WANG J, CHEN L, JIN S, et al. Altered expression of microRNA-98 in IL-1beta-induced cartilage degradation and its role in chondrocyte apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(3):3208-3216.
[6] HUANG Z, ZHOU M, WANG Q, et al. Mechanical and hypoxia stress can cause chondrocytes apoptosis through over-activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Arch Oral Biol. 2017;84:125-132.
[7] PAN T, CHEN R, WU D, et al. Alpha-Mangostin suppresses interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis in rat chondrocytes by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway and delays the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;52:156-162.
[8] ZHANG W, CHENG P, HU W, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-384-5p alleviates osteoarthritis through its effects on inhibiting apoptosis of cartilage cells via the NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting SOX9. Cancer Gene Ther. 2018;25(11-12):326-338.
[9] 吴春飞,易俊,梁桂洪,等.补肾调肝方治疗肝郁肾虚膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J].中医临床研究,2017,9(36):74-76.
[10] FELSON DT. Osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(23):841-848.
[11] YANG S, DUBE CE, EATON CB, et al. Longitudinal use of complemen-tary and alternative medicine among older adults with radiographic knee osteoarthritis.Clin Therapeut. 2013;35(11):1690-1702.
[12] 杨建辉,吕建国,聂会勇,等.白藜芦醇对白细胞介素-1β诱导的软骨细胞凋亡及增殖能力的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(21):6151-6153.
[13] JUNYI L, NING H, NIAN Z, et al. Sox9 Potentiates BMP2-Induced Chondrogenic Differentiation and Inhibits BMP2-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation. Plos One. 2014;9(2):e89025.
[14] SUN Q, WU G, CHEN H, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen protects type II collagen in interleukin-1β-induced mandibular condylar chondrocyte via inhibiting the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(36):60312-60323.
[15] YAO B, WANG Q, LIU CF, et al. The SOX9 upstream region prone to chromosomal aberrations causing campomelic dysplasia contains multiple cartilage enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(11):5394-5408.
[16] 汤晓晨,俞峰,孙书龙,等.黄芪甲苷对人膝骨关节炎退变关节软骨IL-1β表达的影响[J].南京中医药大学学报,2013,29(1):48-52.
[17] 姚丽,赵婧,周强,等.祛痰化瘀利湿方对大鼠膝骨关节炎滑膜组织和血清IL-1β,MMP-1及COMP,CTX-Ⅱ的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(11):5-8.
[18] 贺牡丹,王小平,陈同生.白细胞介素-1β诱导关节软骨细胞凋亡的分子机理[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2011,33(1):49-54.
[19] GOLDRING MB, OTERO M, PLUMB DA, et al.Roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism: signals and multiple effectors converge upon MMP-13 regulation in osteoarthritis. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;21(24):202-220.
[20] 季卫锋,童培建,袁小凤,等.补肾法与活血法对SD大鼠膝骨性关节炎滑膜IL-1β、TNF-α及软骨MMP-13、ADAMTS-5的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2012,20(2):1-5.
[21] ZHENG W, ZHANG H, JIN Y, et al. Butein inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and slows the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;42:1-10.
[22] LI W, ZHANG L, GUO B, et al. Exosomal FMR1-AS1 facilitates maintaining cancer stem-like cell dynamic equilibrium via TLR7/NFκB/c-Myc signaling in female esophageal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):22.
[23] RAO Z, WANG S, WANG J. Protective effects of psoralidin on IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(2):3418-3424.
[24] 罗珊,霍永鑫,刘英,等.连翘苷对IL-1β诱导的人关节软骨细胞凋亡及细胞外基质降解的影响[J].免疫学杂志,2019,35(8):645-652.
[25] LIU YX, WANG GD, WANG X, et al. Effects of TLR-2/NF-κB signaling pathway on the occurrence of degenerative knee osteoarthritis: an in vivo and in vitro study. Oncotarget. 2017;8(24):38602-38617.
[26] JEONG JW,LEE HH,LEE KW,et al. Mori folium inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators by suppressing the activation of nf- kappab and p38 mapk in sw1353 human chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(2):452-460.
[27] YU G, WAN R, YIN G, et al. Diosmetin ameliorates the severity of cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice by inhibiting the activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(5):2133-2142.
[28] JEONG JW, LEE HH, CHOI EO, et al. Schisandrae fructus inhibits il- 1beta-induced matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators production in sw1353 human chondrocytes by suppressing NF-kappa B and mapk activation. Drug Dev Res. 2015;76(8):474-483.
[29] YANG Y, GONG XB, HUANG LG, et al. Diosmetin exerts anti- oxidative,anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects to protect against endotoxin-induced acute hepatic failure in mice. Oncotarget. 2017;8(19):30723-30733.
[30] 鲁宏, 宋俊, 孟京红,等. 香叶木素通过NF-κB通路缓解IL-1β诱导的新生大鼠骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡和免疫反应[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(3):292-297. |