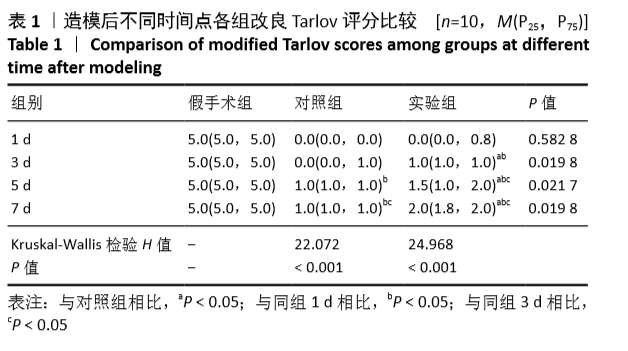
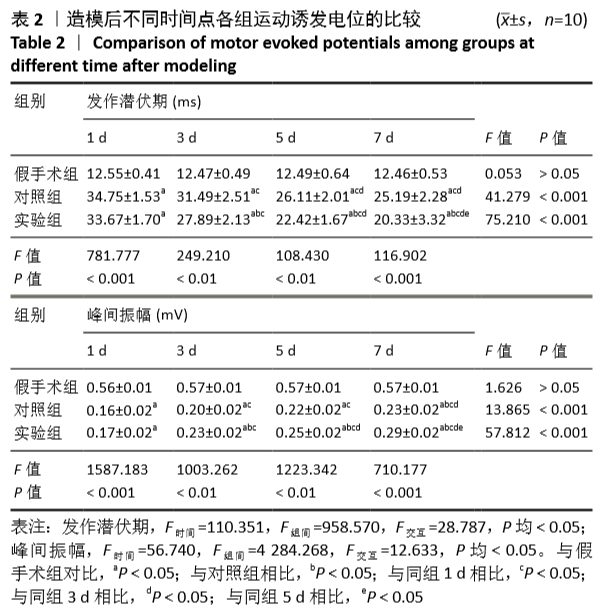
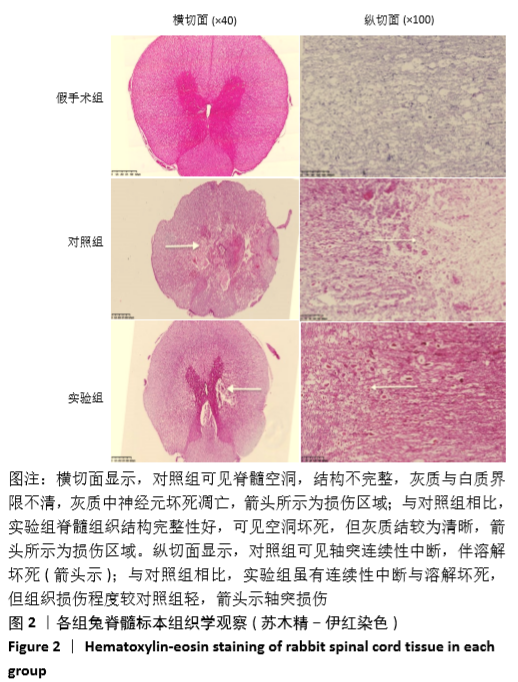
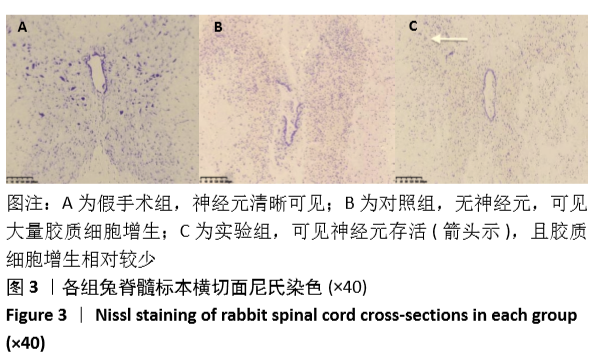
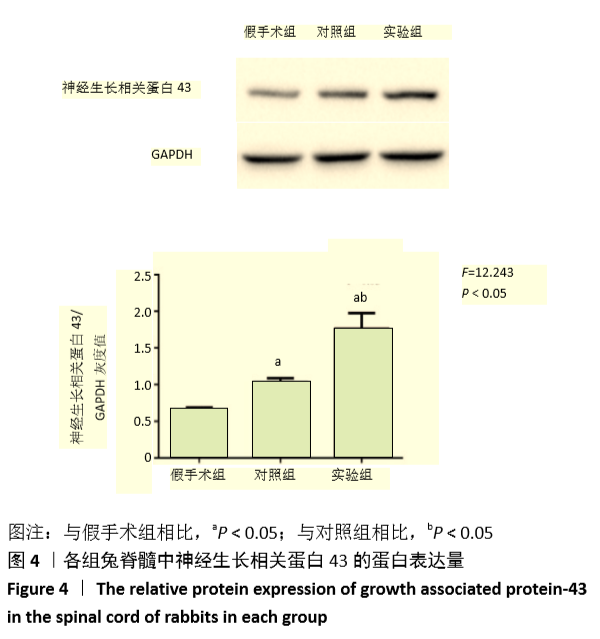
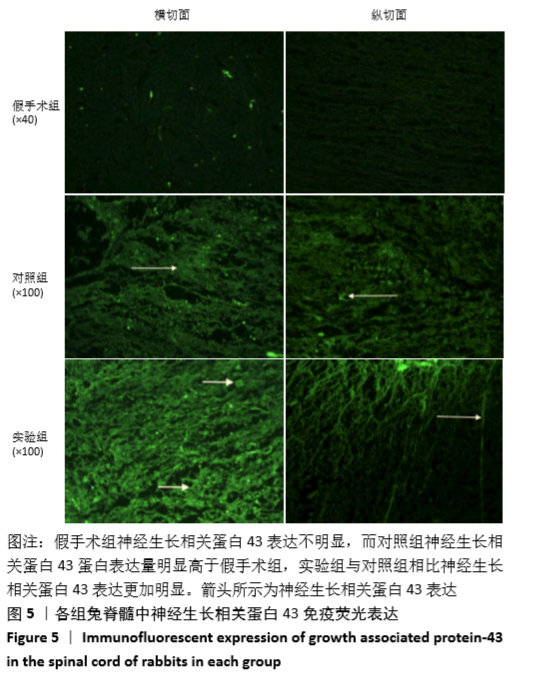
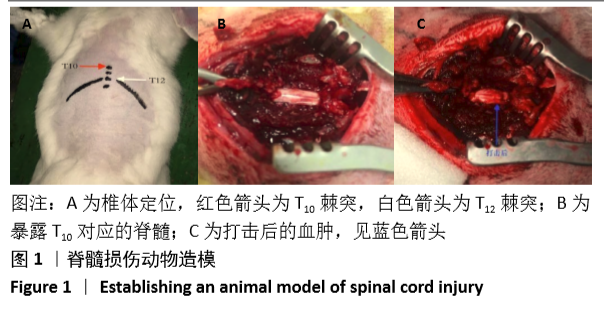
[1] 常有军,杨幼平,孙增春,等.脊髓损伤康复研究现状[J].临床医学进展,2019,9(3):354-358.
[2] Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) 2016 Facts and Figures at a Glance. J Spinal Cord Med. 2016;39(4):493-494.
[3] KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S, BILLAKANTI R. Reactive astrogliosis after spinal cord injury-beneficial and detrimental effects. Mol Neurobiol. 2012;46(2):251-264.
[4] ZHAO J, YAO Y, XU C, et al. Expression of the neural specific protein, GAP-43, dramatically lengthens the cell cycle in fibroblasts. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2009;27(6):531-537.
[5] ZHANG ZL, GAO YG, ZANG P, et al. Research progress on mechanism of gastrodin and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol on central nervous system. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020;45:312-320.
[6] LIU XC, WU CZ, HU XF, et al. Gastrodin Attenuates Neuronal Apoptosis and Neurological Deficits after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;29:104483.
[7] GRUNER JA. A monitored contusion model of spinal cordinjuryin the rat. J Neurotrauma. 1992;9(2):123-126.
[8] YOUNG W. Spinal cord contusion models. Prog. Brain Res. 2002;137: 231-255.
[9] 张瑞平.SPIO纳米颗粒标记BMSCs移植治疗兔脊髓损伤的MR活体示踪[D].太原:山西医科大学,2011.
[10] 何鹏,陈玉,高峰,等.失神经及制动后兔肱骨骨密度与生物力学性能的对比研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(12):1680-1684,1720.
[11] ZHANG RG, PENG ZW, WANG HH, et al. Gastrodin ameliorates depressive-like behaviors and up-regulates the expression of BDNF in the hippocampus and hippocampal-derived astrocyte of rats. Neurochem Res. 2014;39:172-179.
[12] TARLOV IM, KLINGER H. Spinal cord compression studies. II. Time limits for recovery after acute compression in dogs. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1954;71(3):271-290.
[13] REECET B, TRIBBLE CG, OKONKWO DO, et al. Early adenosine receptor activation ameliorates spinal cord reperfusion injury. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2008;9:363-367.
[14] FANG H, ZHANG JP, ZHANG JC, et al. The effects of REM-PCL on motor evoked potential in spinal cord ischemiare perfusion injury. J Hosp Pharm. 2015;35(12):5-11.
[15] ANWAR MA, Al SHEHABI TS, EID AH. Inflammogenesis of Secondary Spinal Cord Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:98.
[16] OYINBO CA. Secondary injury mechanisms in traumatic spinal cord injury: a nugget of this multiply cascade. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2011;71(2):281-299.
[17] MUKHAMEDSHINA YO, GRACHEVA OA, MUKHUTDINOVA DM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and the neuronal microenvironment in the area of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(2):227-237.
[18] GOMES ED, SILVA NA, SALGADO AJ. Combinatorial therapies for spinal cord injury: strategies to induce regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(1):69-71.
[19] LIU XH, BOTCHWAY BENSON OA, TAN XN, et al. Resveratrol treatment of spinal cord injury in rat model. Microsc Res Tech. 2019;82:296-303.
[20] FANG H, ZHANG JC, YANG M, et al. Perfusion of gastrodin in abdominal aorta for alleviating spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2016;9:688-693.
[21] DU F, WANG X, SHANG B, et al. Gastrodin ameliorates spinal cord injury via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Acta Biochim Pol. 2016; 63(3):589-593.
[22] DE OLIVEIRA MR, BRASIL FB, FURSTENAU CR. Nrf2 Mediates the Anti-apoptotic and Anti-inflammatory Effects Induced by Gastrodin in Hydrogen Peroxide-Treated SH-SY5Y Cells. J Mol Neurosci. 2019;69: 115-122.
[23] JIAO M, YIN KZ, ZHANG T, et al. Effect of the SSeCKS-TRAF6 interaction on gastrodin-mediated protection against 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced astrocyte activation and neuronal death. Chemosphere. 2019;226:678-686.
[24] JKUSIK BRANDON W, HAMMOND DENA R,UDVADIA AVA J, Transcriptional regulatory regions of gap43 needed in developing and regenerating retinal ganglion cells. Dev Dyn. 2010;239:482-495.
[25] ZHANG L, WANG ZJ, LI B, et al. The inhibition of miR-17-5p promotes cortical neuron neurite growth via STAT3/GAP-43 pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47:1795-1802.
|