中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 752-758.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.05.017
• 器官移植动物模型 organ transplantation and animal model • 上一篇 下一篇
复方血竭对结肠炎模型大鼠Toll样受体4/核因子κB及树突状细胞表型的影响
李 楠1,王雪明2,稽 杨3,石玉玲1,王 欣1,李 娜1,苏 丽1,沙丽娜1
- 解放军总参谋部总医院(309),1消化科,2药剂科,北京市 100091;3解放军总后勤部药品仪器检验所药理室,北京市 100071
-
修回日期:2014-12-17出版日期:2015-01-30发布日期:2015-03-02 -
通讯作者:李楠,解放军总参谋部总医院,北京市 100091 -
作者简介:李楠,男,1957年生、山东省青岛市人、1996年于解放军第三军医大学毕业,博士、主任医师、博士生导师。主要从事炎症性肠病的基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:北京市自然科学基金(717329)
Effects of resina draconis on Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB and dendritic cell phenotypes in colitis rats
Li Nan1, Wang Xue-ming2, Ji Yang3, Shi Yu-ling1, Wang Xin1, Li Na1, Su Li1, Sha Li-na1
- 1 Department of Gastroenterology, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100091, China
2 Department of Pharmacy, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100091, China
3 Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Drug and Instrument Control, General Logistics Department of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100071,
China
-
Revised:2014-12-17Online:2015-01-30Published:2015-03-02 -
Contact:Li Nan, Department of Gastroenterology, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100091, China -
About author:Li Nan, M.D., Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Gastroenterology, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100091, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing, No. 717329
摘要:
背景:树突状细胞可调节肠道内环境的免疫反应,这一功能缺陷会导致炎症性肠病,Toll样受体4/核因子κB通路与上述反应密切相关。 目的:构建实验性结肠炎模型大鼠,观察复方血竭对其树突状细胞及Toll样受体4/核因子κB表达的影响并探讨其作用机制。 方法:将大鼠随机抽样法分为空白对照组、模型组、复方血竭组和5-氨基水杨酸治疗组。除空白对照组外,其他3组大鼠建立2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸诱导的实验性结肠炎模型。造模成功后,复方血竭组和5-氨基水杨酸治疗组分别给予复方血竭[0.75 g/(kg•d)]和5-氨基水杨酸 [(100 mg/(kg•d)]灌胃治疗10 d。 结果与结论:复方血竭组较模型组大鼠的疾病活动指数评分、大体形态损伤评分、病理组织学评分均显著降低(P < 0.05),5-氨基水杨酸治疗组、复方血竭组的症状、结肠组织损害均较模型组明显减轻。模型组大鼠肠系膜淋巴结CD80和CD86的表达率,Toll 样受体4,核因子κB表达较其他3组均显著升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。复方血竭组Toll样受体4及核因子κB表达明显低于5-氨基水杨酸治疗组。结果证实,复方血竭可部分缓解实验性结肠炎模型大鼠的症状,有效抑制其肠系膜淋巴结中树突状细胞的活化。复方血竭可能通过抑制大鼠肠黏膜细胞Toll 样受体4和核因子κB的表达而缓解肠道的炎症反应。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李 楠,王雪明,稽 杨,石玉玲,王 欣,李 娜,苏 丽,沙丽娜. 复方血竭对结肠炎模型大鼠Toll样受体4/核因子κB及树突状细胞表型的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(5): 752-758.
Li Nan, Wang Xue-ming, Ji Yang, Shi Yu-ling, Wang Xin, Li Na, Su Li, Sha Li-na. Effects of resina draconis on Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB and dendritic cell phenotypes in colitis rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(5): 752-758.
All the involved 44 rats entered the final analysis without any dropout. The process of model establishment is shown in Figure 1.

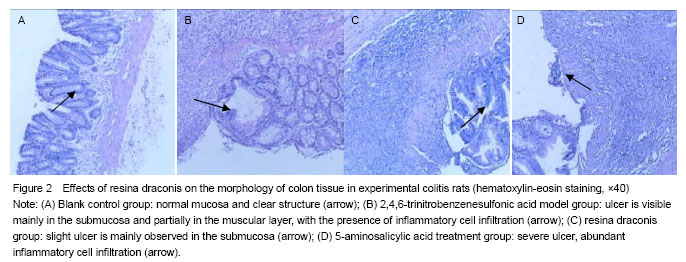
In the TNBS model group, rat colitis specimens exhibited mucosal hyperemia, edema, erosions, necrosis, thickening intestinal wall and ulcer. Ulcer, inflammatory exudates and lymphoid hyperplasia were visible in the mucosa, submucosa and muscular layer. In the blank control group, intact smooth mucosa and clear structure of glandular organ were observed, without erosion or ulcer, with the presence of slight neutrophil infiltration. In the resina draconis and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment groups, there were slight ulcer and partially intact glandular organ (Figure 2).
Ulcer size was observed according to colonic mucosal damage index. Significant differences in weight changes were detected between the resina draconis and blank control groups (P=0.017, P=0.022, P=0.027), but there was no significant difference as compared TNBS model group with resina draconis and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment groups (P=0.067, P=0.077). Disease activity index, macroscopic colonic damage score and histopathological score were significantly decreased in the resina draconis group compared with the model group (P < 0.05). Symptoms and tissue damages were obviously lessened in the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment and resina draconis groups compared with the model group. Within 10 days, disease activity index scores were higher in the TNBS model group than those in the resina draconis and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment groups (P=0.008, P=0.001; Table 1).
Expression rates of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 were the lowest in the blank control group. Expression rates of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 were greater in the TNBS model group than those in the blank control group (P=0.006, P=0.007). Expression rates of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 in the resina draconis group were significantly lower than those in the TNBS model group (P=0.021, P= 0.019), but still higher than those in the blank control group (P=0.006, P=0.001). Expression rates of major histocompatibility complex class II and CD86 in the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group were significantly lower than those in the TNBS model group (P=0.015, P= 0.014), but higher than those in the blank control group (P= 0.077, P=0.032) (Table 2).
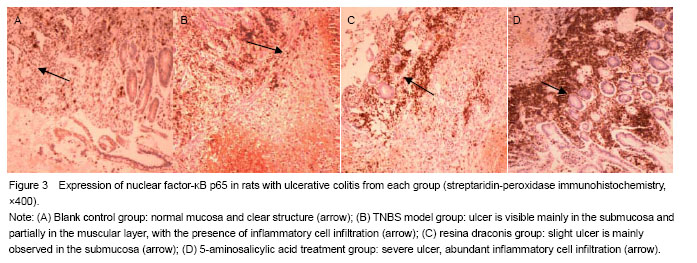
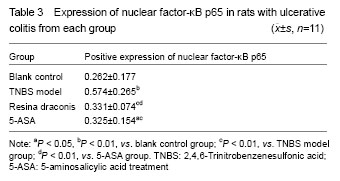
Yellow particles in the cytoplasm and/or nuclei were positive cells (Figure 3). Compared with the control group, nuclear factor-κB p65 expression was significantly higher in the TNBS model group, resina draconis group and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group (P < 0.01, P < 0.05). Compared with the TNBS model group, nuclear factor-κB p65 expression was significantly lower in the resina draconis group and 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group (P < 0.01). Compared with the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group, nuclear factor-κB p65 expression was lower in the resina draconis group (P < 0.01; Table 3).
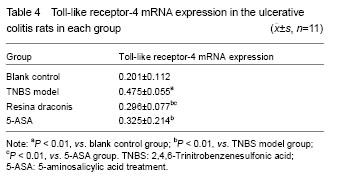
Compared with the blank control group, Toll-like receptor-4 mRNA expression was significantly higher in the TNBS model group (P < 0.01). Compared with the TNBS model group, Toll-like receptor-4 mRNA expression was significantly lower in the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group and resina draconis group (P < 0.01). Compared with the 5-aminosalicylic acid treatment group, Toll-like receptor-4 mRNA expression was significantly lower in the resina draconis group (P < 0.01) (Table 4).
| [1] Carrera E, Manzano R, Garrido E. Efficacy of the vaccination in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(9):1349-1353. [2] Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448(7152):427-434. [3] Diamante G, Dikstein R. Transcriptional control by NF-κB: elongation in focus. Biochim Biophysics Acta. 2013;1829 (9):937-945. [4] Lzcue A, Coombes JL, Powrie F. Regulatory T cells suppress systemic and mucosal immune activation to control intestinal inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:256-271. [5] Chen S, Zeng ZP, Li HZ, et al. Relationship between plasma level of leptin and the expression of leptin receptor in human adrenal tissues and tumors. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;19;90(38):2667-2670. [6] Petvises SO, Neill HC. Characterisation of dendritic cells arising from progenitors endogenous to murine spleen. PLoS One. 2014;14;9(2):e88311. [7] Li N, Wang XM, Wu K, et al. Influence of Compound Xuejie Enema on the Blood Rheology of Chronic Nonspecific Ulcerative Colitis. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue. 2006;9(24): 2073-2074. [8] Wang XM, Wu K, Shi YL, et al. Preparation and Clinical Application of Compound Xuejie enema. Zhongguo Yiyuan Yaoxue Zazhi. 2005;25(3):281. [9] Sobczak M, Zakraewski, Zakrzewski PK, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive action of the dimeric enkephalin peptide biphalin in the mouse model of colitis: New potential treatment of abdominal pain associated with inflammatory bowel diseases. Peptides. 2014;60:102-106. [10] Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, et al. Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 1993;69(2):238-249. [11] Tu P, Tsaip L, Lin Y, et al. Expression profile of Toll-like receptor mRNA in pigs co-infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and porcine circovirus type 2. Res Vet Sci. 2014;14(3):1-9. [12] Brenan M, Rees DJ. Sequence analysis or rat integrin alphaE1 and alphaE2 subunits: tissue expression reveals phenotypic similarities between intraepithelial lymphocytes and dendritic cells in lymph. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30(6): 1527-1537. [13] Tanaka K. Expression of Toll-like receptors in the intestinal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;2(2):193-196. [14] Arasaradnam R, Nwokolo CU. Epiphenomenon of telomere lengths lessons from ulcerative colitis. Gut. 2012;61(10):1516. [15] Pulli B, Ali M, Forghani R, et al. Measuring myeloperoxidase activity in biological samples. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):1-10. [16] Zhang X, Ma J, Xu M, et al. Imbalance between CD205 and CD80/CD86 in dendritic cells in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Thromb Res. 2014;19(14):1-10. [17] Haider J, Marisavljevic D, Stanisavljevicn, et al. BCL10 aberations and NF-kappa B activation involving p65 are absent or rare in primary gastric MALT lymphoma. Vojnosanit Preql. 2014;7(11):1040-1044. [18] Dimitrakopoulos GN, Dimtrakopoulou K, Maraziotis IA, et al. Supervised method for construction of microRNA-mRNA networks: application in cardiac tissue aging dataset. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;26(30):318-321. [19] Wang H, Ouyang Q, Hu RW. Establishment of rat colitis model induced by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Weichang Bingxue. 2001;6(1):7-10. [20] Yang XY, Yao L. Pharmacological action and clinical experience of dragon’s blood. Heilongjiang Yiyao. 2011; 24(2): 265-266. [21] Xia PF, Ding LY. The research progress of dragon's blood. Hebei Zhongyiyao Xuebao. 2006;21(1):40-43. [22] Li N, Wang XM, Gao LC, et al. Experimental study of resina draconis in protecting intestinal mucous membrane barrier in burned rats. Zhongguo Zhongxuyi Jiehe Xiaohua Zazhi. 2010;18(6):351-354. [23] Li N, Wang XM, Wu K, et al. Experimental study of resina draconis on rats with ulcerative colitisin. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xiaohua Yiyuan. 2007;15(6):377-379. [24] Creticos PS. Advances in synthetic peptide immuno- regulatory epitopes. World Allergy Organ J. 2014;7(1):30. [25] Wang J, Wang X, Hussain S, et al. Distinct roles of different NF-κB subunit s in regulating inflammatory and T cell stimulatory gene expression in dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2007;178(11):6777-6788. [26] Zhou HG, Chen HB, Wu MH. Viewing from the toll-like receptor/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway to explore the immunomodulatory mechanism of Chinese drugs. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2010;30(8):884-888. [27] Yu S, Tang S, Mayer GD, et al. Interactive effects of ultraviolet-B radiation and pesticide exposure on DNA photo-adduct accumulation and expression of DNA damage and repair genes in Xenopus laevis embryos. Aquat Toxicol. 2014;12(4):256-266. [28] Tan W, Huang W, Gu X, et al. IL-17F/IL-17R interaction stimulates granulopoiesis in mice. Exp Hematol. 2008; 36(11): 1417-1427. [29] Ahmed S, Shaffer A, Geddes T, et al. Evaluation of optimal RNA extraction method from human carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2014;5(14):1-9. |
| [1] | 贺茜, 万瑀, 唐玉婷, 杨安宁, 吴凯, 焦运, 白志刚, 姜怡邓, 沈江涌. 铁死亡诱导剂抑制增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞的增殖[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 杨芷姗, 唐正龙. Hippo信号通路中的核心因子YAP/TAZ参与骨形成的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [3] | 王 继, 张 敏, 杨中亚, 张 龙. 体力活动干预2型糖尿病肌少症的研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [4] | 孙佳佳, 朱海迪, 卢 赟, 张 凯. 髋部骨折合并2型糖尿病和非2型糖尿病患者骨代谢标志物的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [5] | 唐 亮, 李熙恒, 牛瑞娟, 李欣悦, 邹馨颖, 毛天骄, 李 江. 柚皮苷通过调控RAW264.7细胞功能影响MC-3T3-E1细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [6] | 李梦菲, 仉 红, 赵少剑, 殷广浩, 王其宝. 叉头样转录因子3在粪肠球菌感染模型大鼠难治性根尖周炎病变中的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1187-1192. |
| [7] | 张永强, 潘 凤, 孙 鹏, 谭明辉, 轩留明, 王勤章. Gja1基因重组慢病毒对糖尿病豚鼠膀胱病变模型中缝隙连接蛋白43蛋白及mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1161-1165. |
| [8] | 赵 璐, 赵逸菲, 高 达, 刘艳芳, 付婷婷, 徐江雁. Zeste基因抑制子基因12在糖尿病肾脏病模型大鼠肾组织中的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [9] | 张 伟, 黄致超, 赵锐锋, 梁 欢, 马玉峰, 申艳光, 钟红刚, 陈兆军, 张继川, 陈卫衡. 杜仲胶夹板固定兔骨折模型的疗效评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1055-1061. |
| [10] | 王书祥, 伍 权, 周小淞, 况现桃. 钛合金全冠选择性激光熔化成形工艺及变形实验[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1012-1016. |
| [11] | 刘文涛, 冯兴超, 杨 毅, 白生宾. M2型巨噬细胞外泌体诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [12] | 龙燕鸣, 谢梦生, 黄加洁, 薛文利, 荣 慧, 李晓捷. 酪蛋白激酶2相互作用蛋白1调控骨质疏松大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [13] | 廖益东, 明 江, 宋文学, 王梓力, 张 宇, 廖一飞, 徐卡娅, 杨 华. 一种同时培养原代皮质及海马神经元的实验方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 897-902. |
| [14] | 李晓寅, 杨晓青, 陈淑莲, 李正超, 王梓琪, 宋 震, 朱达仁, 陈旭义. 胶原/丝素蛋白支架联合神经干细胞治疗创伤性脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [15] | 闫 乐, 张慧萍, 戴林桐. 间充质干细胞治疗变应性鼻炎:一项基于动物实验的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 977-984. |
Resina draconis (dragon’s blood, common bletilla tuber) is a compound Chinese medicine[8]. Stock solution per milliliter contains resina draconis crude drug 2.0 g (adult dose: [1.45 g/(kg·d)], which is provided by the Manufacturing Laboratory, the 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA. Resina draconis dose (5.0 g/kg) was equal to 3.5 times the daily dose of adult in clinic.
.jpg)
Isolation of dendritic cells with immunomagnetic beads: Mesenteric lymph node was sterilely obtained from the rats to prepare single cell suspension. In accordance with the method of Brenan et al [12], dendritic cells were isolated from the rat mesenteric lymph node using a MiniMACS immunomagnetic separation system (MihenyiBiotec, Germany). Totally seven sets of rats received immunomagnetic bead separation technique.
Data were analyzed using SPSS 13.0 software, and measurement data were expressed as the mean±SD. Intergroup comparison was conducted using one-way analysis of variance. Intergroup comparison of numeration data was done using Chi-square test. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||