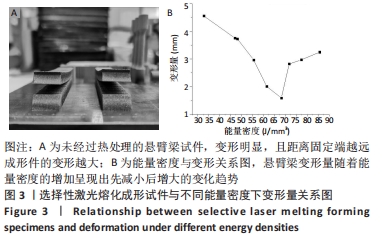
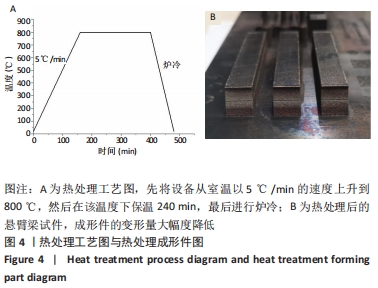
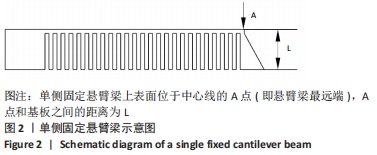
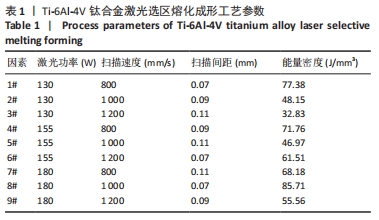
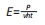[1] 张杰,李宗义.基于MJM技术的3D打印牙冠蜡型制作工艺研究[J].南方农机,2019,50(24):199-200.
[2] 姚路,胡培鑫,刘武,等.3D打印技术在牙科制造领域中的应用及未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):637-642.
[3] 魏青松,宋波,文世峰,等.金属粉床激光增材制造技术[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2021:2-5.
[4] BAGHI AD, NAFISI S, HASHEMI R, et al. Effective post processing of SLM fabricated Ti-6Al-4 V alloy: Machining vs thermal treatment J Manuf Process. 2021;68(1):1031-1046.
[5] ZHANG P, HE AN, LIU F, et al. Evaluation of low cycle fatigue performance of selective laser melted titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Metals. 2019;9(10):1041.
[6] ABOUTALEB AM, MAHTABI MJ, TSCHOPP MA, et al. Multi-objective accelerated process optimization of mechanical properties in laser-based additive manufacturing: case study on selective laser melting (SLM) Ti-6Al-4V. J Manuf Process. 2019;38:432-444.
[7] WANG H, XU JB, NIE Z, et al. Preparation and properties of Co-Cr alloy denture by selective laser melting. Mater Res Express. 2018;6(2):026552.
[8] HONG JK, KIM SK, HEO SJ, et al. Mechanical properties and metal-ceramic bond strength of co-cr alloy manufactured by selective laser melting. Materials. 2020;13(24):5745.
[9] ZHOU Y, WEI W, YAN J, et al. Microstructures and metal-ceramic bond properties of Co-Cr biomedical alloys fabricated by selective laser melting and casting. Mat Sci Eng A. 2019;759:594-602.
[10] HUSSEIN A, HAO L, YAN CZ, et al. Finite element simulation of the temperature and stress fields in single layers built without-support in selective laser melting. Mater Design. 2013;52(5):638-647.
[11] SONG B, DONG SJ, LIAO HL, et al. Process parameter selection for selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V based on temperature distribution simulation and experimental sintering. Int J Adv Manuf Tech. 2012; 61(9-12):967-974.
[12] HONG SP, ANSARI MJ. Estimation of residual stress and deformation in selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V alloy. Procedia CIRP. 2020;93:44-49.
[13] LI H, RAMEZANI M, CHEN Z, et al. Effects of process parameters on temperature and stress distributions during selective laser melting of Ti–6Al–4V. T Indian I Metals. 2019;72(12):3201-3214.
[14] 祝彬彬. 选择性激光熔化金属零件翘曲变形的研究[D].杭州:浙江工业大学,2017.
[15] PAL S, LOJEN G, GUBELJAK N, et al. Melting, fusion and solidification behaviors of Ti-6Al-4V alloy in selective laser melting at different scanning speeds. Rapid Prototyping J. 2020;26(7):1209-1215.
[16] SALEM M, ROUX SL, HOR A, et al. A new insight on the analysis of residual stresses related distortions in selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V using the improved bridge curvature method. Addit Manuf. 2020; 36:101586.
[17] ZHANG XC, KANG JW, RONG YM, et al. Effect of scanning routes on the stress and deformation of overhang structures fabricated by SLM. Materials. 2019;12(1):47.
[18] 蔡振毅.激光选区熔化Ti-6Al-4V合金翘曲变形研究[D].武汉:武汉轻工大学,2020.
[19] MARQUES BM, ANDRADE CM, NETO DM, et al. Numerical analysis of residual stresses in parts produced by selective laser melting process. Procedia Manuf. 2020;47:1170-1177.
[20] SHARMA RS, KUMAR A. Numerical analysis of thermal stresses in selective laser melting. Springer, Singapore, 2020.
[21] TATIANA M, SANDRA C, KATIA A, et al. An assessment of subsurface residual stress analysis in SLM Ti-6Al-4V. Materials. 2017;10(4):348.
[22] 张凯,刘婷婷,张长东,等.基于熔池数据分析的激光选区熔化成形件翘曲变形行为研究[J].中国激光,2015,42(9):135-141.
[23] LI L, PAN T, ZHANG X, et al. Deformations and stresses prediction of cantilever structures fabricated by selective laser melting process. Rapid Prototyping J. 2021;27(3):453-464.
[24] CHEN C, ZHU H, XIAO Z, et al. The residual stress distribution of Ti-6Al-4V thin wall in the selective laser melting. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng. 2019;538:012020.
[25] 唐超兰,温竟青,张伟祥等.钛合金3D打印成形技术及缺陷[J].航空材料学报,2019,39(1):38-47.
[26] LI C, LIU JF, GUO YB. Prediction of residual stress and part distortion in selective laser melting. Procedia CIRP. 2016;45:171-174.
[27] 李俊峰,魏正英,卢秉恒.钛及钛合金激光选区熔化技术的研究进展[J].激光与光电子学进展,2018,55(1):29-46.
[28] 张升,桂睿智,魏青松,等.选择性激光熔化成形TC4钛合金开裂行为及其机理研究[J].机械工程学报,2013,49(23):21-27.
[29] 边培莹,尹恩怀.选区激光熔化激光功率对316L不锈钢熔池形貌及残余应力的影响[J].激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(1):129-135.
[30] CHAO Q, THOMAS S, BIRBILIS N, et al. The effect of post-processing heat treatment on the microstructure, residual stress and mechanical properties of selective laser melted 316L stainless steel. Mat Sci Eng A-Struct. 2021;821:141611.
[31] PONNUSAMY P, MASOOD SH, RUAN D, et al. Investigating the effects of post-heat treatment on residual stress in AlSi12 parts processed with Selective Laser Melting. IOP Conf Ser: Mater. Sci Eng. 2021;1067(1):012117.
[32] COSMA C, KESSLER J, GEBHARDT A, et al. Improving the Mechanical Strength of Dental Applications and Lattice Structures SLM Processed. Materials. 2020;13(4):905.
[33] SINGLA AK, BANERJEE M, SHARMA A, et al. Selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V alloy: process parameters, defects and post-treatments. J Manuf Process. 2021;64:161-187.
[34] YAKOUT M, ELBESTAWI MA, VELDHUIS SC. A study of the relationship between thermal expansion and residual stresses in selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V. J Manuf Process. 2020;52:181-192.
[35] 冯庆晓,李多生,宋胜利,等.SLM成形义齿支架在模拟口腔环境下的耐腐蚀性能[J].材料导报,2021,35(6):6107-6113.
[36] YAMAMOTO S, AZUMA H, SUZUKI S, et al. Melting and solidification behavior of Ti-6Al-4V powder during selective laser melting. Int J Adv Manuf Tech. 2019;103:4433–4442.
[37] 巩建强,杜文强,张璐,等.经SLM打印成型的TC4合金热处理研究[J].应用激光,2020,40(3):404-408.
[38] JAVIDRAD HR, GHANBARI M, JAVIDRAD F. Effect of scanning pattern and volumetric energy density on the properties of selective laser melting Ti-6Al-4V specimens. J Mater Res Technol. 2021;12:989-998.
[39] 姜歆,孙凯博,谢能.钛合金(Ti-6Al-4V)义齿激光选区熔化工艺验证研究[J].中国医疗器械信息,2020,26(9):25-26+39.
[40] VALENTE EH, GUNDLACH C, CHRISTIANSEN TL, et al. Effect of Scanning Strategy During Selective Laser Melting on Surface Topography, Porosity, and Microstructure of Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Appl Sci-Basel. 2019;9(24):5554.
[41] 张雯,谢文强,郑美华,等.激光选区熔化钛合金可摘局部义齿支架的临床应用[J].口腔疾病防治,2020,28(4):231-235.
[42] MAHDAVI M, MIRKOOHI E, HOAR E, et al. Prediction of the deformation behavior of a selective laser-melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy as a function of process parameters. Int J Adv Manuf Tech. 2020;107(9-10): 4069-4076.
[43] 倪达. 选择性激光熔融打印支撑角度对可摘局部义齿支架适合性的影响及力学性能研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2020.
[44] KASPEROVICH G, HAUBRICH J, GUSSONE J, et al. Correlation between porosity and processing parameters in TiAl6V4 produced by selective laser melting. Mater Design. 2016;105:160-170.
[45] YANG J, YU H, YIN J, et al. Formation and control of martensite in Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by selective laser melting. Mater Design. 2016;108:308-318.
[46] 王俊飞,袁军堂,汪振华,等.激光选区熔化成形TC4钛合金薄壁件变形与残余应力[J].激光技术,2019,43(3):411-416.
[47] COTTAM R, PALANISAMY S, AVDEEV M, et al. Diffraction Line Profile Analysis of 3D Wedge Samples of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated Using Four Different Additive Manufacturing Processes. Metals. 2019; 9(1):60.
[48] 洪法廉,李颖超,史俊南,等.牙齿的显微硬度和元素成分[J].口腔医学纵横,1991(1):10-12.
|