中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (34): 5508-5513.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2319
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
桩核表面制备不同形式固位槽及使用不同黏结剂对固位力的影响
李 征1,王 媛2,田梦婷1,何惠宇1
1新疆医科大学第一附属医院口腔修复科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000;2乌鲁木齐市口腔医院口腔修复科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
Effect of different retentive grooves and adhesives on the retentive force between crown and post and core
Li Zheng1, Wang Yuan2, Tian Mengting1, He Huiyu1
1Department of Prosthodontics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Prosthodontics, Urumqi Stomatological Hospital, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
有限元分析法:是一种将求解区域看成是由许多小的互连子域组成,对每一单元假定一个合适的近似解,推导求解这个域总的满足条件,从而得到问题的解。其具有能够通过建立形态复杂的几何模型,输出所需模型任意部位的应力分布状态等,对应力的内部状态及其他力学性能的测定具有可信度高、重复性好、软件较成熟及数据处理较便捷等优点,此特点也使其成为分析牙体所受应力的常用手段。
固位力:指修复体在行使功能时能抵御外力而不发生移位或脱落的能力。增加固位力的方式有很多种,其中固位槽亦称固位沟或沟固位形,是常用方式之一。
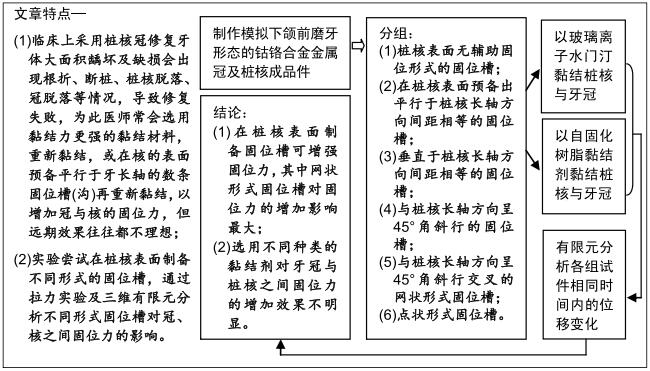
背景:临床中采用桩核冠修复牙体大面积龋坏及缺损后常出现根折、断桩、桩核脱落等情况,医师主要通过选择黏结力更强的黏结材料或在核表面制作平行于长轴的固位槽来提高固位力,但效果不理想。
目的:研究不同形式固位槽及两种黏结材料对桩核冠修复体冠与核黏结后固位力的影响。
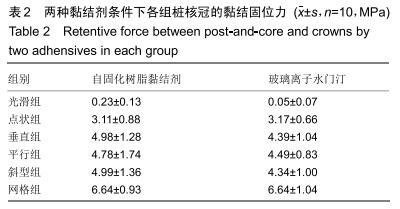
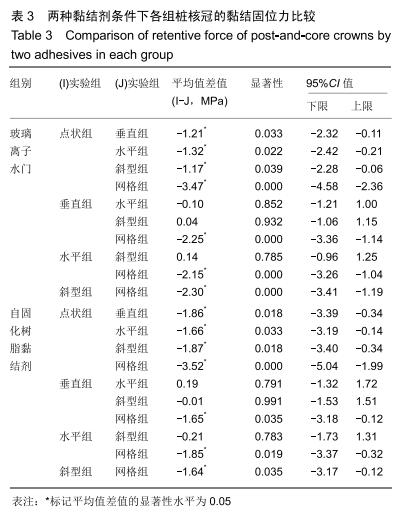
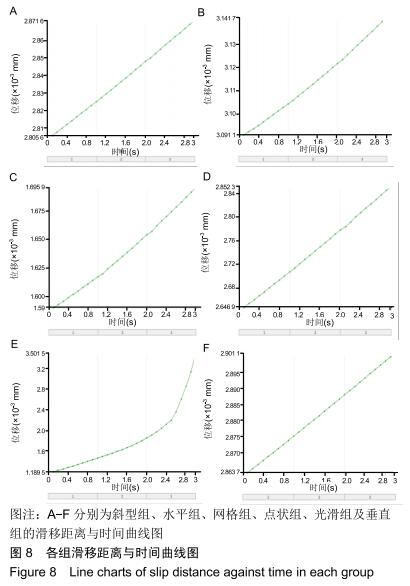
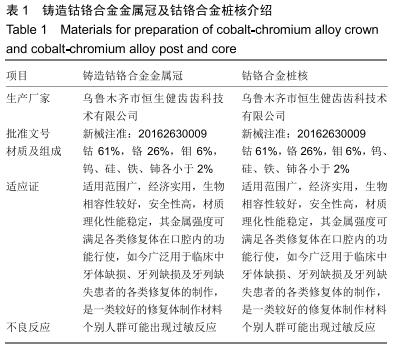
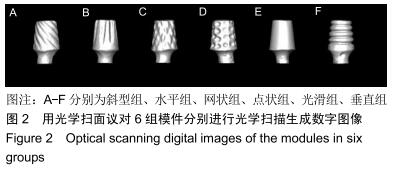
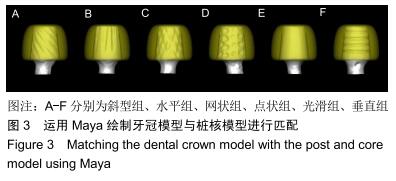
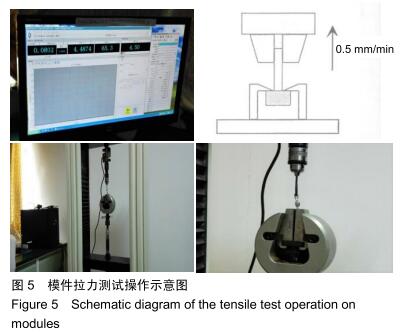
方法:制作模拟下颌前磨牙形态的钴铬合金金属冠及桩核成品件60个,核的轴向内聚角均为8°,随机分为6组,每组10个试件:光滑组桩核表面无辅助固位形式的固位槽;另5组分别在桩核表面预备出平行于桩核长轴方向间距相等的固位槽(平行组)、垂直于桩核长轴方向间距相等的固位槽(垂直组)、与桩核长轴方向呈45°角斜行的固位槽(斜型组)、与桩核长轴方向呈45°角斜行交叉的网状形式固位槽(网格组)、点状形式固位槽(点状组);6组再分别以玻璃离子水门汀和自固化树脂黏结剂黏结桩核与牙冠。拉力实验检测各组的黏结固位力,有限元分析各组试件相同时间内的位移变化。
结果与结论:①无论是使用玻璃离子水门汀还是自固化树脂黏结剂黏结,网格组的黏结固位力最大,点状组的黏结固位力最小;黏结剂和不同固位槽在增加固位力中不存在交互作用(F=0.26,P=0.91),不同黏结剂对固位力的影响不显著(F=1.04,P=0.31),不同辅助固位槽对固位力的影响显著(F=14.74,P < 0.05);②相同时间施以逐渐增加的相同力时,6组中网格组三维有限元模型位移变化较小;③结果表明,在桩核表面制备固位槽可增强固位力,其中网状形式固位槽对固位力的增加影响最大;选用不同种类的黏结剂对牙冠与桩核之间固位力的增加效果不明显。
ORCID: 0000-0003-4680-5843(李征)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: