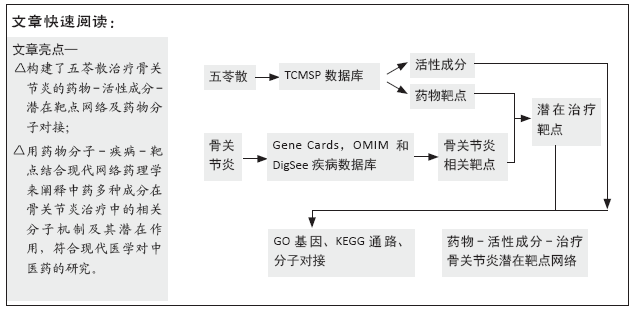
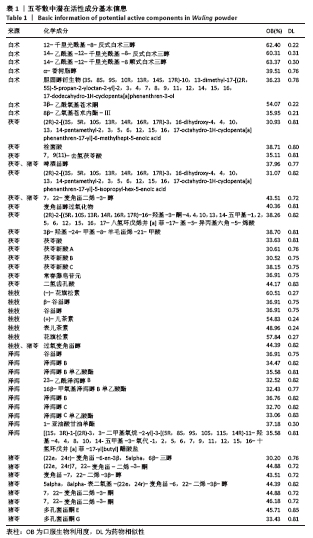
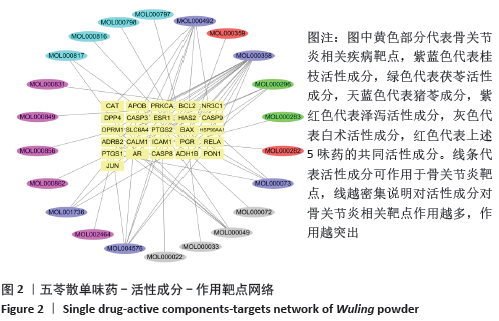
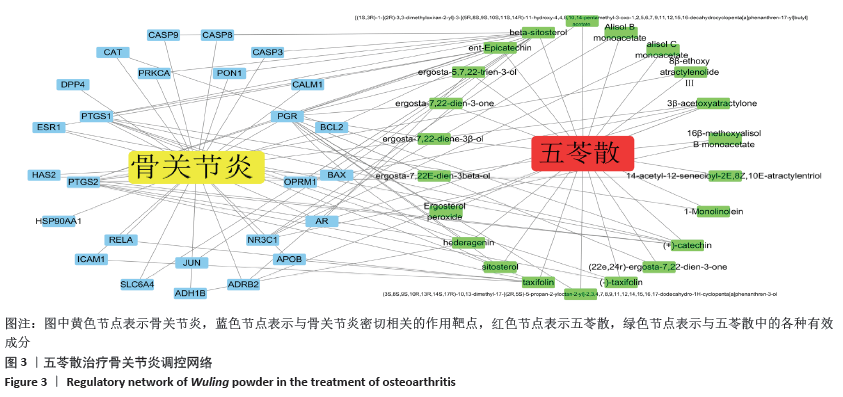
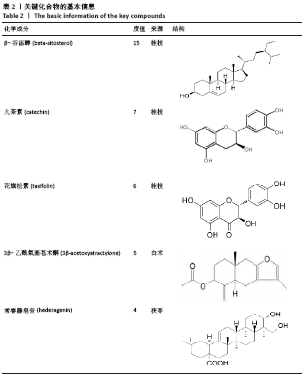
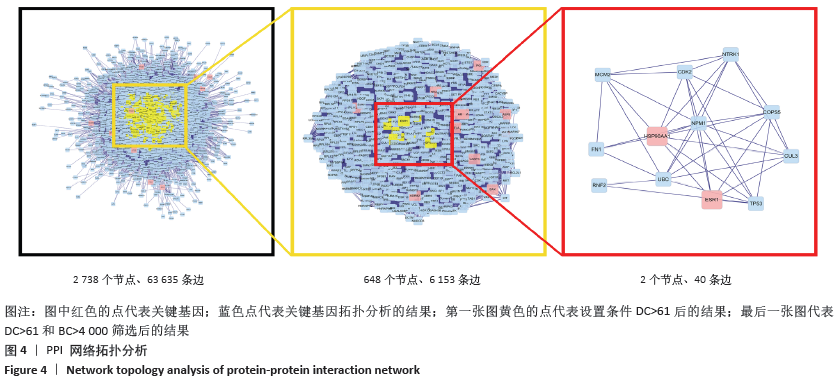
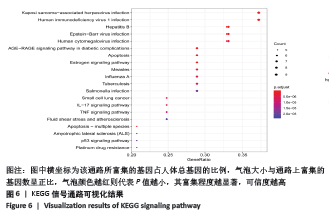
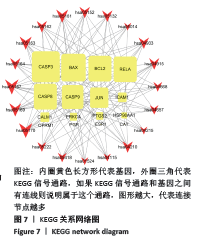
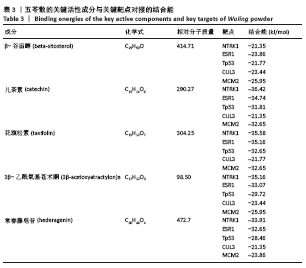
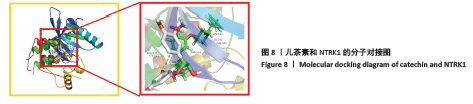
[1] 贺自克,王上增,沈锦涛.基于Hedgehog通路探讨补肾活血方对实验性膝骨性关节炎兔退变软骨的保护作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2020,36(4):700-706.
[2] 钱凯,杜彦仪,韩隆胤,等.基于网络药理学探讨五苓散治疗类风湿关节炎的作用机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019, 25(19):138-146.
[3] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2): 293-311.
[4] HAO DA C, XIAO PG. Network pharmacology: a Rosetta Stone for traditional Chinese medicine. Drug Dev Res. 2014;75(5): 299-312.
[5] 张彦琼,李梢.网络药理学与中医药现代研究的若干进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2015,29(6):883-892.
[6] 段贤春,黄石,彭代银,等.网络药理学在中药复方研究中的应用[J].中国药理学通报,2020,36(3):303-308.
[7] 曲凡,杨锡燕.五苓散合黄连解毒汤加减治疗难治性高血压的临床效果[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(4):692-694.
[8] 汝锦龙.中药系统药理学数据库和分析平台的构建和应用[D].咸阳:西北农林科技大学,2015.
[9] 胡聪,黎红维,吴琳静,等.基于网络药理学的苍耳散治疗鼻炎作用机制研究[J/OL].中华中医药学刊:1-19[2020-06-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R.20200108.1307.019.html.
[10] 浦冬青,刘政,梁佳玮,等.基于网络药理学及分子对接探讨热毒宁注射液抑制新型冠状病毒肺炎炎症风暴机制[J/OL].中药药理与临床:1-17[2020-06-14]. https://doi.org/10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20200603.001.
[11] 廖姿,张家琼,付先芸,等.基于网络药理学的“大黄-桃仁”配伍治疗子宫腺肌病的作用机制研究[J/OL].中国中药杂志:1-10[2020-06-14]. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200520.403.
[12] 耿玮,梁巍,叶智斌,等.苍术酮对结直肠癌细胞HT29凋亡的机制[J].中成药, 2018,40(4):937-940.
[13] 孙东东,程海波,沈卫星,等.补肾活血方中5种黄酮类成分的体外抗炎活性[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21(7):137-141.
[14] 曾莉萍,徐贤柱,饶华,等.杜仲叶β-谷甾醇对成骨细胞和卵巢颗粒细胞的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2012,23(5):1051-1053.
[15] 柳海平,周明旺,李盛华,等.骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖相关信号通路研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(23): 2163-2166.
[16] WANG YJ, ZHANG HQ, HAN HL, et al. Taxifolin enhances osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells partially via NF-κB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490(1):36-43.
[17] ZHANG HQ, WANG YJ, YANG GT, et al. Taxifolin Inhibits Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand-Induced Osteoclastogenesis of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages in vitro and Prevents Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Bone Loss in vivo. Pharmacology. 2019;103(1-2): 101-109.
[18] TIAN K, SU Y, DING J, et al. Hederagenin protects mice against ovariectomy-induced bone loss by inhibiting RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Life Sci. 2020;244:117336.
[19] 李健,姚玉龙,张磊磊,等.雌激素在软骨中作用机制研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(23):2156-2159.
[20] MA H, WU W, YANG X, et al. Genetic effects of common polymorphisms in estrogen receptor alpha gene on osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(8):13446-13454.
[21] HAYANO S, KOMATSU Y, PAN H, et al. Augmented BMP signaling in the neural crest inhibits nasal cartilage morphogenesis by inducing p53-mediated apoptosis. Development. 2015;142(7):1357-1367.
[22] 张国梁,王跃文,普日布苏荣,等.p53/miR-502-5p/TRAF2通路对骨关节炎软骨细胞损伤的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2018,34(7):1283-1290.
[23] 庞琳娜,徐连那,董红宇.p53基因在类风湿关节炎骨代谢中的作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(3):327-330, 337.
[24] ZHAO Y, XIONG X, SUN Y. Cullin-RING Ligase 5: Functional characterization and its role in human cancers. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. Doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.04.003.
[25] 程庆华. Cullin-1调节骨肉瘤细胞增殖及转移机制研究[D].南京:南京医科大学, 2018.
[26] 郭会芹,赵焕,李楠,等.MCM2免疫细胞化学检测在宫颈癌筛查中的意义[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2009,16(16): 1213-1216.
[27] 刘畅,王娜,李玉坤,等.晚期糖基化终末产物对骨组织细胞代谢的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(27):4376-4382.
[28] 黄文舟,王丽丽,殷嫦嫦,等.晚期糖基化终末产物通过氧化应激诱导大鼠软骨细胞损伤[J].中国病理生理杂志,2016, 32(11):2036-2042.
[29] 赵峻,马翅,杨娜娜,等.晚期糖基化终末产物致软骨细胞炎性反应的潜在机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(24): 3786-3791.
[30] LIU Y, PENG H, MENG Z, et al. Correlation of IL-17 level in synovia and severity of knee osteoarthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21: 1732-1736.
[31] CHEN B, DENG Y, TAN Y, et al. Association between severity of knee osteoarthritis and serum and synovial fluid interleukin 17 concentrations. J Int Med Res. 2014;42(1): 138-144.
[32] BAI Y, GAO S, LIU Y, et al. Correlation between Interleukin-17 gene polymorphism and osteoarthritis susceptibility in Han Chinese population. BMC Med Genet. 2019;20(1):20.
[33] WANG Z, ZHENG C, ZHONG Y, et al. Interleukin-17 Can Induce Osteoarthritis in Rabbit Knee Joints Similar to Hulth’s Method. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017: 2091325.
[34] KHOTIB J, UTAMI NW, GANI MA, et al. The change of proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor α level in the use of meloxicam in rat model of osteoarthritis. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2019. Doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2019-0331.
[35] ABDEL GALIL SM, EZZELDIN N, FAWZY F, et al. The single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of tumor necrosis factor α -308G/A gene is associated with early-onset primary knee osteoarthritis in an Egyptian female population. Clin Rheumatol. 2017; 36(11):2525-2530.
[36] KOU S, WU Y. Meta-analysis of tumor necrosis factor alpha -308 polymorphism and knee osteoarthritis risk. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:373.
[37] ZHU X, YANG S, LIN W, et al. Roles of cell cyle regulators cyclin d1, cdk4, and p53 in knee osteoarthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2016;20(9):529-534.
[38] 周绪昌,邹军,吴伟.p53调控骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2019,35(3):280-285. |