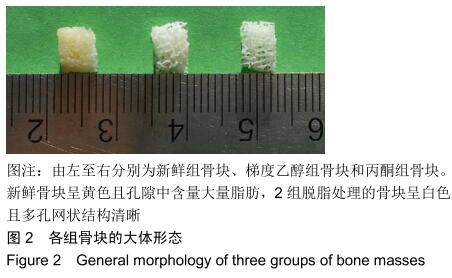
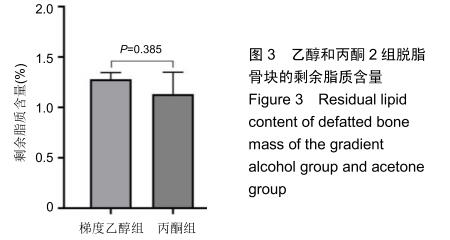
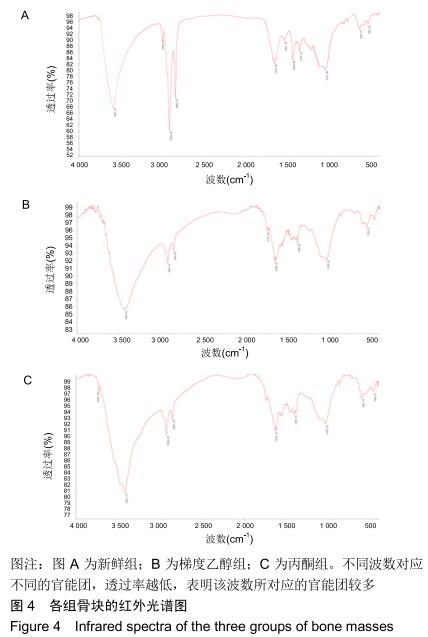
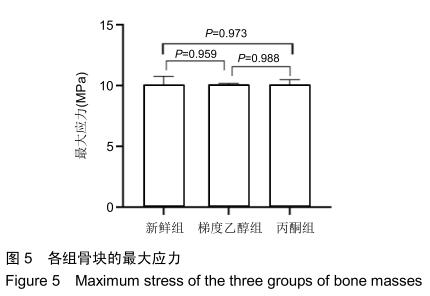
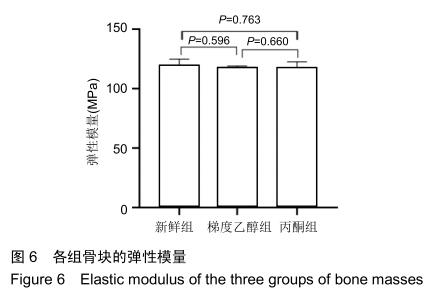
|
[1] DEVRIES JG, SCHARER B. Comparison and Use of Allograft Bone Morphogenetic Protein Versus Other Materials in Ankle and Hindfoot Fusions.J Foot Ankle Surg.2018;57(4):707-711.
[2] 张看,赵彦涛,白玉龙,等.不同脱脂方法对异种松质骨脱脂效果及免疫原性的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(6): 585-587.
[3] 田志超,蔡启卿,王鑫,等.四肢骨肿瘤大段同种异体骨移植术后骨愈合的分析[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2019,24(1):11-16.
[4] CZITROM AA. The Immune Response: The Afferent Arm.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1996; 326(326):11-24.
[5] HOROWITZ MC, FRIEDLAENDER GE, QIAN HY. The Immune Response: The Efferent Arm.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(326):25-34.
[6] URIST MR, MIKULSKI A, BOYD SD. A chemosterilized antigen-extracted autodigested alloimplant for bone banks. Arch Surg.1975;110(4):416-428.
[7] CHAPPARD D, FRESSONNET C, GENTY C, et al. Fat in bone xenografts: importance of the purification procedures on cleanliness,wettability and biocompatibility.Biomaterials.1993; 14(7):507-512.
[8] THORÉN K, ASPENBERG P, THORNGREN KG. Lipid extraction decreases the specific immunologic response to bone allografts in rabbits.Acta Orthop Scand. 1993;64(1): 44-46.
[9] NGUYEN H, MORGAN DAF, FORWOOD MR. Sterilization of allograft bone: effects of gamma irradiation on allograft biology and biomechanics.Cell Tissue Bank. 2007;8(2): 93-105.
[10] FRAYSSINET P, ROUQUET N, MATHON D, et al. Histological integration of allogeneic cancellous bone tissue treated by supercritical CO2 implanted in sheep bones. Biomaterials. 1998;19(24):2247-2253.
[11] PARHAMI F, MORROW AD, BALUCAN J, et al. Lipid oxidation products have opposite effects on calcifying vascular cell and bone cell differentiation. A possible explanation for the paradox of arterial calcification in osteoporotic patients.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997; 17(4):680-687.
[12] FAGES J, MARTY A, DELGA C, et al. Use of supercritical CO2 for bone delipidation.Biomaterials.1994;15(9):650-656.
[13] TADIC D, EPPLE M. A thorough physicochemical characterisation of 14 calcium phosphate-based bone substitution materials in comparison to natural bone. Biomaterials.2004;25(6):987-994.
[14] GARDIN C, RICCI S, FERRONI L, et al. Decellularization and Delipidation Protocols of Bovine Bone and Pericardium for Bone Grafting and Guided Bone Regeneration Procedures. PLoS One.2015; 10(7):e0132344.
[15] 中华人民共和国卫生健康委员会.人体捐献器官获取与分配管理规定[S]. 2019-01-28.
[16] 黄爱军,彭建强,陈丽萍,等.不同程度脱钙对皮质骨生物力学的影响[J].广东医学,2018,39(suppl):16-19.
[17] IORGI ND, ROSOL M, MITTELMAN SD, et al. Reciprocal Relation between Marrow Adiposity and the Amount of Bone in the Axial and Appendicular Skeleton of Young Adults.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2008;93(6):2281-2286.
[18] FRIEDLAENDER GE. Immune responses to osteochondral allografts. Current knowledge and future directions.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1983;174(174):58-68.
[19] HOROWITZ MC, FRIEDLAENDER GE. Induction of specific T-cell responsiveness to allogeneic bone.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1991;73(8):1157-1168.
[20] MUSCOLO DL, CALETTI E, SCHAJOWICZ F, et al. Tissue-typing in human massive allografts of frozen bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1987;69(4):583-595.
[21] MÖLLER E. Advances in and future of tissue typing. Transplant Proc. 1991;23(1 Pt 1):63-66.
[22] ECKELS DD. Alloreactivity: Allogeneic presentation of endogenous peptide or direct recognition of MHC polymorphism? A review.Tissue Antigens.1990;35(2):49-55.
[23] MUSCOLO DL, AYERZA MA, CALABRESE ME, et al. Human Leukocyte Antigen Matching, Radiographic Score, and Histologic Findings in Massive Frozen Bone Allografts.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1996;326(326):115-126.
[24] THORÉN K, ASPENBERG P, THORNGREN KG. Lipid extracted bank bone. Bone conductive and mechanical properties.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1995;311(311):232-246.
[25] SCHWARZ N, REDL H, SCHIESSER A, et al. Irradiation-sterilization of rat bone matrix gelatin.Acta Orthop Scand.1988;59(2):165-167.
[26] OSTROWSKI K, DZIEDZIC-GOCLAWSKA A, STACHOWICZ W, et al. Radiation-induced paramagnetic centers in research on bone physiopathology.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(272): 21-29.
[27] 王娴,崔龙,董威杰,等.电子束和γ射线对油料氧化及霉菌的影响[J].包装工程,2019,40(3):30-37.
[28] AKKUS O, BELANEY RM, DAS P. Free radical scavenging alleviates the biomechanical impairment of gamma radiation sterilized bone tissue.J Orthop Res.2005;23(4):838-845.
[29] BURGESS HW, MACKRELL J, TOMS D, et al. Response of Bone Subjected to Optimized High Dose Irradiation. J Biomater Appl.2010;24(5):387-400.
[30] MOREAU MF, GALLOIS Y, BASLE MF, et al. Gamma irradiation of human bone allografts alters medullary lipids and releases toxic compounds for osteoblast-like cells. Biomaterials.2000;21(4):369-376.
[31] KALUS U, HELGA MÜLLER, BAUDISCH H, et al. A method for the determination of the residual chloroform in defatted cancellous bone transplants.Cell Tissue Bank. 2005;6(1): 71-75.
|