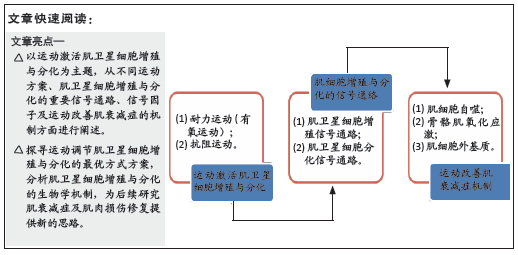
[1] SOUSA-VICTOR P, MUNOZ-CANOVERS P. Regenerative decline of stem cells in sarcopenia. Mol Aspects Med. 2016;50:109-117.
[2] SUZMAN R, BEARD JR, BOERMA T, et al. Health in an ageing world--what do we know. Lancet. 2015;385(9967):484-486.
[3] MAURO A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers.J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961;9:493-495.
[4] BENGAL E, PERDIGUERO E, SERRANO AL, et al. Rejuvenating stem cells to restore muscle regeneration in aging. F1000 Res. 2017;6:76.
[5] SAMPATH SC, SAMPATH SC, HO A, et al. Induction of muscle stem cell quiescence by the secreted niche factor Oncostatin. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1531.
[6] DINULOVIC I, FURRER R, HANDSCHIN C. Plasticity of the muscle stem cell microenvironment. AdvExp Med Biol. 2017;1041:141-169.
[7] NEDERVEEN JP, JOANISSE S, SNIJDERS T, et al. The influence of capillarization on satellite cell pool expansion and activation following exercise-induced muscle damage in healthy young men. J Physiol. 2018;596(6):1063-1078.
[8] BOLDRIN L, ROSS JA, WHITMORE C, et al. The effect of calorie restriction on mouse skeletal muscle is sex, strain and time -dependent. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5160-5168.
[9] PALLAFACCHINA G, BLAAUW B, SCHIAFFION S. Role of satellite cells in muscle growth and maintenance of muscle mass. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23:12-18.
[10] 史仍飞,刘子青,袁海平,等.机械生长因子对骨骼肌卫星细胞增殖及MGFmRNA表达的影响[J].临床医学工程,2012,19(1):18-21.
[11] KOOK SH, SON YO, CHOI KC, et al. Cyclic mechanical stress suppresses myogenic differentiation of adult bovine satellite cells through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Mol Cell Bioch. 2008;309(1-2):133-141.
[12] TIERNEY MT, STEC MJ, RULANDS S, et al. Muscle stem cells exhibit distinct clonal dynamics in response to tissue repair and homeostatic aging. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(1):119-127,e3.
[13] GAYRAUD-MOREL B, CHRETIEN F, JORY A, et al. Myf5 haploinsufficiency reveals distinct cell fate potentials for adult skeletal muscle stem cells. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(7):1738-1749.
[14] KOOPMAN R, GEHRIG SM, LEGER B, et al. Cellular mechanisms underlying temporal changes in skeletal muscle protein synthesis and breakdown during chronic β-adrenoceptor stimulation in mice. J Physiol. 2019;588(Pt 23):4811-4823.
[15] MACKEY AL, KJAER M, CHARIFI N, et al. Assessment of satellite cell number and activity status in human skeletal muscle biopsies. Muscle Nerve. 2009;40(3):455-465.
[16] SNIJDERS T, NEDERVEEN JP, JOANISSE S, et al. Musclefibrecapillarization is a critical factor in muscle fibre hypertrophy during resistance exercise training in older men. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2016;8(2):267-276.
[17] 金晶,卢健.肌卫星细胞代谢重编程研究进展及其展望[J].中国体育科技,2017,53(6):65-70.
[18] NEDERVEEN JP, JOANISSE S, SNIJDERS T, et al. The influence of capillarization on satellite cell pool expansion and activation following exercise-induced muscle damage in healthy young men. J Physiol. 2018;596(6):1063-1078.
[19] APPELL HJ, FORSBERG S, HOLLMANN W. Satellite cell activation in humanskeletal muscle after training:Evidence for muscle fiber neoformation. Int J Sports Med. 1988;9(4):297-299.
[20] SMITH HK, MAXWEL LL, RODGERS CD, et al. Exercise-enhanced satellite cell proliferation and new myonuclear accretion in rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 2001;90(4):1407-1414.
[21] MILANESI A, LEE JW, YANG A, et al. Thyroid Hormone Receptor alpha is Essential to Maintain the Satellite Cell Niche during Skeletal Muscle Injury and Sarcopenia of Aging. Thyroid. 2017;27(10):1316-1322.
[22] 赵昱,刘庆午,卢健.有氧运动对小鼠肌肉干细胞衰减的影响—基于单肌纤维分析技术的研究[J].西安体育学院学,2019,36(3): 91-98.
[23] RÖSCH T. Satellite Cell Activation in Human Skeletal Muscle After Training: Evidence for Muscle Fiber Neoformation. Int J Sports Med. 1988;9(4):297-299.
[24] SMITH HK, MAXWELL L, RODGERS CD, et al. Exercise-enhanced satellite cell proliferation and new myonuclear accretion in rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 2001;90(4):1407-1414.
[25] MANGAN G, BOMBARDIER E, MITCHELL AS, et al. Oestrogen-dependent satellite cell activation and proliferation following a running exercise occurs via the PI3K signalling pathway and not IGF-1. Acta Physiologica. 2014;212(1):75-85.
[26] VYVER M, MYBURGH KH. Cytokine and satellite cell responses to muscle damage: interpretation and possible confounding factors in human studies. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2019;33(3-4):177-185.
[27] FRY CS, NOEHREN B, MULA J, et al. Fibre type-specific satellite cell response to aerobic training in sedentary adults. J Physiol. 2014; 592(12):2625-2635.
[28] SHEFER G, RAUNER G, STUELSATZ P, et al. Moderate-intensity treadmill running promotes expansion of the satellite cell pool in young and old mice. FEBS J. 2013;280(17):4063-4073.
[29] 余群,翁锡全,王丽平.骨骼肌衰减症与运动训练对肌卫星细胞影响的研究现状及展望[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(15): 2248-2254.
[30] KUROSAKA M, NAITO H, OGURA Y.Effects of voluntary wheel running on satellite cells in the rat plantaris muscle. J Sports Sci Med. 2009;8(1): 51-57.
[31] PARISE G, MCKINNELL IW, RUDNICKI MA. Muscle satellite cell and atypical myogenic progenitor response following exercise. Muscle Nerve. 2008;37(5):611-619.
[32] VERNEY J, KADI F, CHARIFI N, et al. Effects of combined lower body endurance and upper body resistance training on the satellite cell pool in elderly subjects. Muscle Nerve. 2008;38(3):1147-1154.
[33] ADAMS G. Satellite cell proliferation and skeletal muscle hypertrophy.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2006;31(6):782-790.90
[34] 薄海,王逊,陈放祥,等.耐力运动促进骨骼肌卫星细胞线粒体能量代谢及其对成肌分化的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,5(7): 402-408.
[35] 卜凡.耐力运动经AMPK介导的自噬维持老年小鼠骨骼肌卫星细胞干细胞属性[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2019.
[36] 邱守涛.不同强度耐力训练对SAMP6小鼠AMPK/Sirt1信号轴及骨骼肌质量的影响[D].上海:华东师范大学,2015.
[37] 陈涛,陈彩珍,卢健.耐力、力量和混合运动对成年C57BL/6小鼠骨骼肌卫星细胞激活信号通路的影响[J].体育科学,2010,31(9): 69-76.
[38] FAWZI K, PETER S, LARS L,et al.The effects of heavy resistance training and detraining on satellite cells in human skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 2004;558(3):1005-1012.
[39] XIAO W, CHEN P, DONG J. Effects of overtraining on skeletal muscle growth and gene expression. Int J Sports Med. 2012;33(10): 846-853.
[40] CRAMERI RM, LANGBERG H, MAGNUSSON P, et al. Changes in satellite cells in human skeletal muscle after a single bout of high intensity exercise. J Physiol. 2004;558(1):333-340.
[41] PETRELLA JK, KIM JS, MAYHEW DL, et al. Potent myofiber hypertrophy during resistance training in humans is associated with satellite cell-mediated myonuclear addition: a cluster analysis. J Appl Physiol. 2008;104(6):1736-1742.
[42] SNIJDERS T, NEDERVEEN JP, JOANISSE S, et al. Musclefibrecapillarization is a critical factor in muscle fibre hypertrophy during resistance exercise training in older men. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017;8(2):267-276.
[43] NEDERVEEN JP, SNIJDERS T, JOANISSE S, et al. Altered muscle satellite cell activation following 16 weeks of resistance training in young men.Am J Physiol RegulIntegr Comp Physiol. 2017;312(1):R85-R92.
[44] BELLAMY LM, JOANISSE S, GRUBB A, et al. The acute satellite cell response and skeletal muscle hypertrophy following resistance training. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109739.
[45] PETREL LA JK, KIM JS, MAYHEW DL, et al. Potentmyofiber hypertrophy during resistance training in humans is associated with satellite cell-mediated myonuclearaddition:a cluster analysis. J Appl Physiol. 2008;104(6):1736-1742.
[46] 林文弢,王震,翁锡全,等.抗阻训练对衰老大鼠腓肠肌Bcl-2 BaxmRNA及线粒体膜电位的影响[J].天津体育学院学报,2013, 28(5):419-421.
[47] 景少元.抗阻训练、耐力训练对SD大鼠骨骼肌氧化还原及肌卫星细胞增殖影响的研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2017.
[48] MACKEY AL, HOLM L, REITELSEDER S, et al. Myogenic response of human skeletal muscle to 12 weeks of resistance training at light loading intensity. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011;21(6):773-782.
[49] MACKEY AL, KJAER M, CHARIFI N, et al. Assessment of satellite cell number and activity status in human skeletal muscle biopsies. Muscle Nerve. 2009;40(3):455-465.
[50] NIELSEN JL, AAGAARD P, BECHR D, et al. Proliferation of myogenic stem cells in human skeletal muscle in response to low-load resistance training with blood flow restriction. J Physiol. 2012;590(17):4351-4361.
[51] WERNBOM M, APRO W, PAULSEN G, et al. Acute low-load resistance exercise with and without blood flow restriction increased protein signalling and number of satellite cells in human skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(12):2953-2965.
[52] 冯燕.有氧、抗阻运动对衰老小鼠骨骼肌毛细血管生成和卫星细胞的影响研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2019.
[53] ARIEL A, TIMOR O. Hanging in the balance: endogenous anti-inflammatory mechanisms in tissue repair and fibrosis. J Pathol. 2013; 229(2):250-263.
[54] CHEN YT, WEI JD, WANG JP, et al. Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Human Ligamentum Flavum. Spine. 2011;36(18):E1193-1200.
[55] 贺舟,常青,唐成林,等.大鼠骨骼肌急性损伤后早期运动训练和按摩对肌卫星细胞增殖相关因子的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2020,26(1):49-54.
[56] BERNET JD, DOLES JD, HALL JK, et al. p38 MAPK signaling underlies a cell autonomous loss of stem cell self-renewal in aged skeletal muscle. Nat Med. 2014;20(3):265-271.
[57] TROY A, CADWALLADER AB, FEDOROV Y, et al. Coordination of satellite cell activation and self-renewal by Par-complex-dependent asymmetric activation of p38alpha/beta MAPK. Cell Stem Cell. 2012; 11(4):541-553.
[58] ROMMEL C, BODINE SC, CLARKE BA, et al. Mediation of IGF-1-induced skeletal myotube hypertrophy by PI(3)K/Akt/mTOR and PI(3)K/Akt/GSK3 pathways. Nature Cell Biol. 2001;3(11):1009.
[59] HITACHI K, TSUCHIDA K. Myostatin-deficiency in mice increases global gene expression at the Dlk1-Dio3 locus in the skeletal muscle. Oncotarget. 2017;8(4):5943-5953.
[60] WANG DT, YANG YJ, HUANG RH, et al. Myostatin activates the ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosome systems contributing to muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:684-965.
[61] SCIMECA M, PICCIRILLI E, MASTRANGELI F, et al. Bonemor-phogenetic proteins and myostatin pathways: key mediator of human sarcopenia. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1): 34.
[62] YIN H, PRICE F, RUDNICKI MA. Satellite cells and the muscle stem cell niche. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(1):23-67.
[63] GRAND F, JONES AE, SEALE V, et al. Wnt7a activates the planar cell polarity pathway to drive the symmetric expansion of satellite stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;4(6):535-547.
[64] 仝昕炜.力竭运动及钝挫伤各时相大鼠骨骼肌PTRF/MG53/Pax7/β-catenin的变化及其机制研究[D].扬州: 扬州大学, 2019.
[65] HARA M, TABATA K, SUZUKI T, et al. Calicum influx through a possible coupling of cation channels impacts skeletal muscle satellite cell activation in response to mechanical stretch. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018;302(12):1741-1750.
[66] HAN T, ZHANG P, XIONG Y, et al. Lkb1 deletion up-regulates Pax7 expression through activating Notch signaling pathway in myoblasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;76:31-88.
[67] 刘晓光,徐苗苗,陈佩杰,等.IGF-1 在治疗骨骼肌损伤中的应用潜能及其相关机制[J].生命的化学,2017,36(4): 496-502.
[68] 陶志云,邹剑敏,宋迟,等.鸭胚骨骼肌生肌调节因子Myo D1和Myf5 发育性变化研究[J].中国家禽,2012,34(17): 16-19.
[69] GAYRAUD MB, CHRETIEN F, JORY A, et al. Myf5 haploinsufficiency reveals distinct cell fate potentials for adult skeletal muscle stem cells. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(7):1738-1749.
[70] MICHAEL A, RUDNICKI, PATRICK NJ, et al. MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 1994;75(7):1351-1359.
[71] COOPER RN, TAJBAKHSH S, MOULY V, et al. In vivo satellite cell activation via Myf5 and MyoD in regenerating mouse skeletal muscle. Journal of Cell Science. 1999;112(17):2895.
[72] 刘芳,费菁,陈敏,等.肌肉发育中肝细胞生长因子(HGF)生物学作用研究进展[J].中国畜牧兽医,2010,37(12):63-67.
[73] 邓启烈,莫伟彬.骨骼肌卫星细胞在组织工程与运动损伤修复中的应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(10):2899-2901.
[74] 吴国梁,李娜.抗阻和被动拉伸联合训练对大鼠腓肠肌卫星细胞激活相关因子基因表达的影响[J].广州体育学院学报,2016,36(6): 104-107.
[75] 陈彩珍,卢健.抗阻训练与耐力训练对小鼠腓肠肌卫星细胞激活作用的影响[J].成都体育学院学报,2014,40(4):55-59.
[76] MAOKA Y, KAWAI M, MORI F, et al. Effect of eccentric contraction on satellite cell activation in human vastuslateralis muscle. J Physiol Sci. 2015;65(5):461-469.
[77] 王洪玲,刘东旭,袁晓.周期性张应力对肌卫星细胞成肌细胞增殖的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(20):3242-3245.
[78] SNIJDERS T, VERDIJK LB, BEELEN M, et al. A single bout of exercise activates skeletal muscle satellite cells during subsequent overnight recovery. Exp Physiol. 2012;97(6):762-773.
[79] TIDBALL JG, VILLALTA SA. Regulatory interactions between muscle and the immune system during muscle regeneration. Am J Physiol RegulIntegr Comp Physiol. 2016;298(5): 1173-1187.
[80] HODGSON B, MAFI R, MAFI P, et al. The regulation of differentiation of mesenchymal stem-cells into skeletal muscle: a look at signalling mole-cules involved in myogenesis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(5): 384-407.
[81] CORNELISON DD, OLWIN BB, RUDNICKI MA, et al. Myo D–/–sat-ellite cells in single-fiber culture are differentiation defective and MRF4 deficient. Dev Biol. 2000;224(2):122-137.
[82] ODELBERG SJ, KOLLHOFF A, KEATING MT. Dedifferentiation of mammalian myotubes induced by msx1. Cell. 2017;103(7): 1099-10109.
[83] CRIST CG, MONTARRAS D, BUCKINGHAM M. Muscle satellite cells are primed for myogenesis but maintain quiescence with sequestration of Myf5 m RNA targeted by micro RNA-31 in m RNP granules. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11(1):118-126.
[84] LUO W, LI E, NIE Q, et al. Myomaker, Regulated by MYOD, MYOG and mi R-140-3p, promotes chicken myoblast fusion. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):26186-26201.
[85] FENG X, WANG Z, WANG F, et al. Dual function of VGLL4 in muscle regeneration. EMBO J. 2019;38(17):e101051.
[86] SEBASTIAN D, SORIANELLO E, SEGALES J, et al. Mfn2 deficiency links age-related sarcopenia and impaired autophagy to activation of an adaptive mitophagy pathway. EMBO J. 2016;35(15):1677-1693.
[87] 李恩,叶魁,孙君志,等. 8周游泳运动对高脂饮食诱导胰岛素抵抗大鼠骨骼肌细胞自噬的影响[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2019,45(4): 121-126.
[88] 卜凡.耐力运动经AMPK介导的自噬维持老年小鼠骨骼肌卫星细胞干细胞属性[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2019.
[89] FAN J, YANG X, LI J, et al. Spermidine coupled with exercise rescues skeletal muscle atrophy from D-gal-induced aging rats through enhanced autophagy and reduced apoptosis via AMPK-FOXO3a signal pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(11):17475-17490.
[90] KIM YA, KIM YS, OH SL, et al. Autophagic response to exercise training in skeletal muscle with age. J Physiol Biochem. 2013;69(4):697-705.
[91] KWON I, LEE Y, COSIO-LIMA LM, et al. Effects of long-term resistance exercise training on autophagy in rat skeletal muscle of chloroquine-induced sporadic inclusion body myositis. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2015;19(3):225-234.
[92] SZENTESI P, CSERNOCH L, DUX L, et al. Changes in redox signaling in the skeletal muscle with aging. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019; 2019:4617801.
[93] 付绍婷, 邱守涛, 李茜,等.不同强度耐力训练对衰老小鼠骨骼肌线粒体抗氧化及生物发生相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2014,33(11):1069-1074.
[94] 孙磊,李方晖.长期高强度间歇训练对增龄大鼠骨骼肌脂联素/AMPK信号途径和细胞自噬的影响[J].体育科学,2018,38(11):52-61.
[95] ABRUZZO PM, ESPOSITO F, MARCHIONNI C, et al. Moderate exercise training induces ROS-related adaptations to skeletal muscles. Int J Sports Med. 2013;34(8):676-687.
[96] MILLER CJ, GOUNDER SS, KANNAN S, et al. Disruption of Nrf2/ARE signaling impairs antioxidant mechanisms and promotes cell degradation pathways in aged skeletal muscle. BiochimBiophysActa. 2012;1822(6):1038-1050.
[97] RADAK Z, CHUNG HY, KOLTAI E, et al. Exercise, oxidative stress and hormesis. Ageing Res Rev. 2008;7(1):34-42.
[98] THOMAS K, ENGLER AJ, MEYER GA. Extracellular matrix regulation in the muscle satellite cell niche. Connect Tissue Res. 2015;56(1):1-8.
[99] CZARKOWSKA B, ZENDZIAN M, BARTLOMIEJCZYK I, et al. The effect of acute and prolonged endurance exercise on transforming growth factor-beta1 generation in rat skeletal and heart muscle. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;60(4):157-162.
[100] BENTZINGER CF, WANG YX, MALTZAHN J, et al. Fibronectin regulates Wnt7a signaling and satellite cell expansion. Cell Stem Cell. 2013; 12(1):75-87.
|