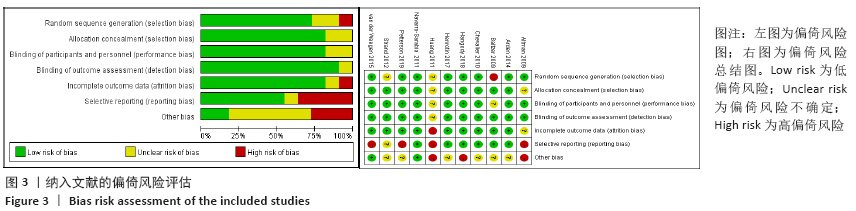
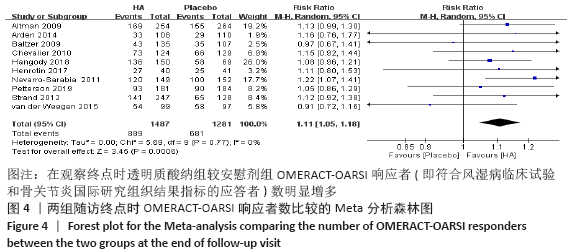
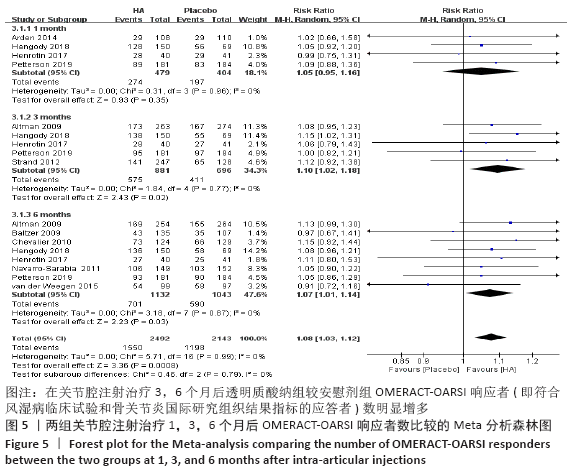
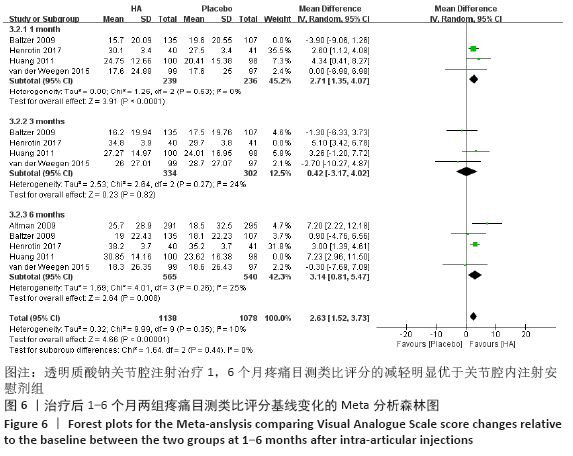
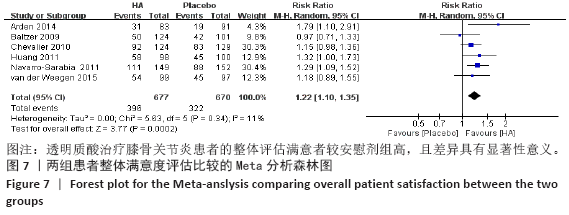
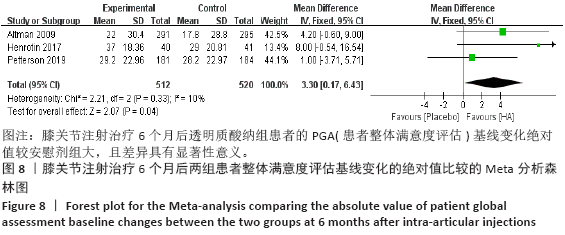
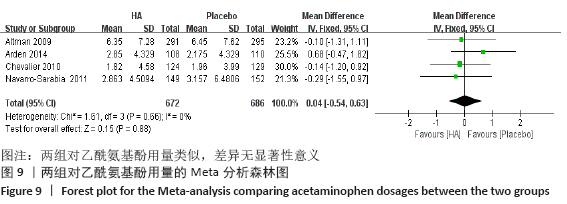
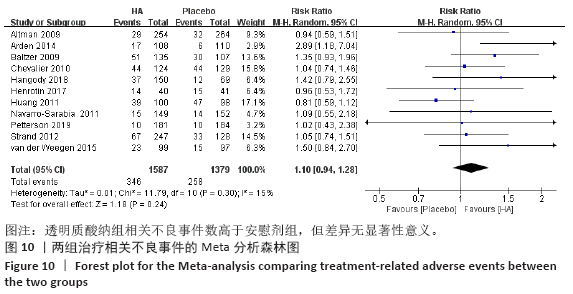
[1] KOLASINSKI SL, NEOGI T, HOCHBERG MC, et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(2):220-233.
[2] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759.
[3] MILLER RE, SCANZELLO CR, MALFAIT AM. An emerging role for Toll-like receptors at the neuroimmune interface in osteoarthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41(5):583-594.
[4] 中华医学会骨科分会关节外科学组,吴阶平医学基金会骨科学专家委员会.膝骨关节炎阶梯治疗专家共识(2018年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):124-130.
[5] KNUDSON W, ISHIZUKA S, TERABE K, et al. The pericellular hyaluronan of articular chondrocytes. Matrix Biol. 2019;78-79:32-46.
[6] GUO YL, YANG PY, LIU L. Origin and Efficacy of Hyaluronan Injections in knee osteoarthritis: Randomized, Double-Blind Trial. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:4728-4737.
[7] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018, 38(12):705-715.
[8] 王斌,邢丹,林剑浩,等.关节腔内注射治疗膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2018,12(6):59-63.
[9] FERREIRA DE ACA, GENOV IR, PEREIRA SRN, et al. Viscossuplementation for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a protocol for an umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(37):e21813.
[10] HIGGINS JP, GREEN S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Hoboken: John Wiley &Sons, USA. 2011.
[11] LIBERATI A, ALTMAN DG, TETZLAFF J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies thatevaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Int Med. 2009;151(4):W65-W94.
[12] PHAM T, VAN DER HEIJDE D, ALTMAN RD, et al.OMERACT-OARSI initiative: osteoarthritis Research Society International set of responder criteria for osteoarthritis clinical trials revisited. Osteo Arthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(5):389-399.
[13] HIGGINS JPT, SAVOVIĆ J, PAGE MJ, et al. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial//HIGGIN JPT, THOMAS J, CHANDLER J, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updaeptemted Sber 2020). Cochrane, 2020. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/ handbook.
[14] 汪鑫,林晓东,刘洪亮,等.全膝置换应用固定平台与活动平台假体疗效随访比较的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(12):1924-1929.
[15] HAN YH, HUANG H,PAN JK, et al. Meta-analysis comparing platelet-rich plasma vs hyaluronic acid injection in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Pain Med. 2019;20(7):1418-1429.
[16] 陈泽华,叶翔凌,陈伟健,等.系统回顾和量化倒走治疗膝骨关节炎的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(26):4251-4256.
[17] ALTMAN RD, ROSEN JE, BLOCH DA, et al. A double-blind, randomized, saline-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of EUFLEXXA for treatment of painful osteoarthritis of the knee, with an open-label safety extension (the FLEXX trial). Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2009;39(1):1-9.
[18] ARDEN NK, AKERMARK C, ANDERSSON M, et al. A randomized saline-controlled trial of NASHA hyaluronic acid for knee osteoarthritis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014;30(2):279-286.
[19] BALTZER AWA, MOSER C, JANSEN SA, et al. Autologous conditioned serum (Orthokine) is an effective treatment for knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(2):152-160.
[20] CHEVALIER X, JEROSCH J, GOUPILLE P, et al. Single, intra-articular treatment with 6 ml hylan G-F 20 in patients with symptomatic primary osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomised, multicentre, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(1):113-119.
[21] HANGODY L, SZODY R, LUKASIK P, et al. Intraarticular injection of a cross-linked sodium hyaluronate combined with triamcinolone hexacetonide (cingal) to provide symptomatic relief of osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trial. Cartilage. 2018;9(3):276-283.
[22] HENROTIN Y, BERENBAUM F, CHEVALIER X, et al. Reduction of the Serum Levels of a Specific Biomarker of Cartilage Degradation (Coll2-1) by Hyaluronic Acid (KARTILAGE(R) CROSS) Compared to Placebo in Painful Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: the EPIKART Study, a Pilot Prospective Comparative Randomized Double Blind Trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):222.
[23] HUANG TL, CHANG CC, LEE CH. Intra-articular injections of sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan®) in osteoarthritis of the knee.a randomized, controlled, double-blind, multicenter trial in the asian population. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2011;12(221):1-8.
[24] NAVARRO-SARABIA F, CORONEL P, COLLANTES E, et al. A 40-month multicentre, randomised placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy and carry-over effect of repeated intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid in knee osteoarthritis: the AMELIA project. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(11):1957-1962.
[25] PETTERSON SC, PLANCHER KD. Single intra-articular injection of lightly cross-linked hyaluronic acid reduces knee pain in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(6):1992-2002.
[26] STRAND V, BARAF HSB, LAVIN PT, et al. A multicenter, randomized controlled trial comparing a single intra-articular injection of Gel-200, a new cross-linked formulation of hyaluronic acid, to phosphate buffered saline for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(5):350-356.
[27] VAN DER WEEGEN W, WULLEMS JA, BOS E, et al. No difference between intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid and placebo for mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(5):754-757.
[28] Maheu E, Bannuru RR, Herrero-Beaumont G, et al. Why we should definitely include intra-articular hyaluronic acid as a therapeutic option in the management of knee osteoarthritis: Results of an extensive critical literature review. Semin Arthritis rheum. 2019;48(4):563-572.
[29] ALTMAN RD, MANJOO A, FIERLINGER A, et al. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:321.
[30] 潘正烽,林奕鹏,李棋.玻璃酸钠分子量差异影响骨关节炎临床治疗获益的效应及机制分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(3):183-188.
[31] CARLESSO LC, SEGAL NA, FREY-LAW L, et al. Pain susceptibility phenotypes in those free of knee pain with or at risk of knee osteoarthritis: the multicenter osteoarthritis study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(4):542-549.
[32] 荀杨芹,张元元,王建成,等.透明质酸钠治疗膝骨关节炎的临床实践指南质量评价[J].中国医药导刊,2018,20(10):584-589.
[33] 管红珍,彭智聪,傅鹰.循证医学中文献证据等级标准的系统性综述[J].药物流行病学杂志, 2002,11(3):145-148.
|