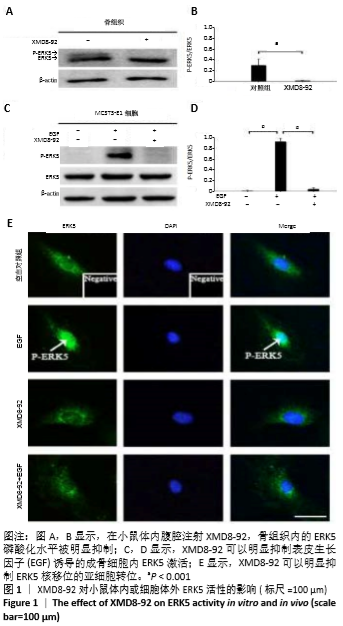
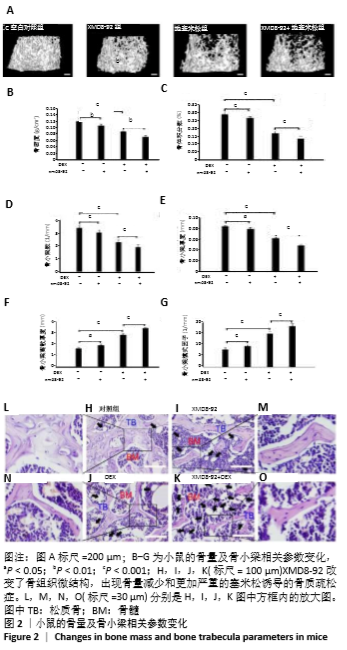
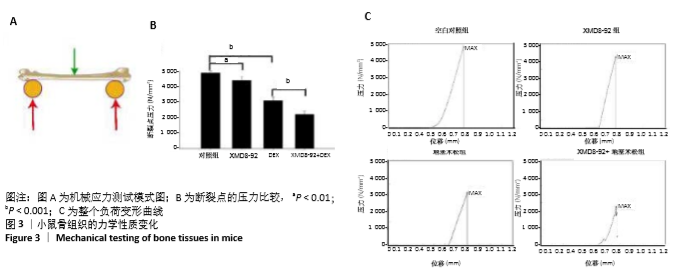
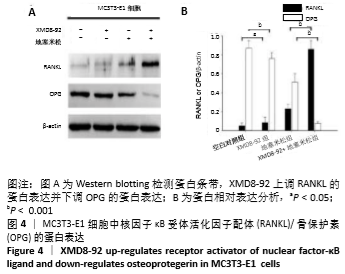
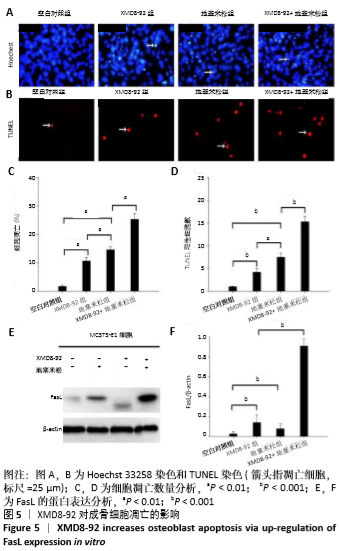
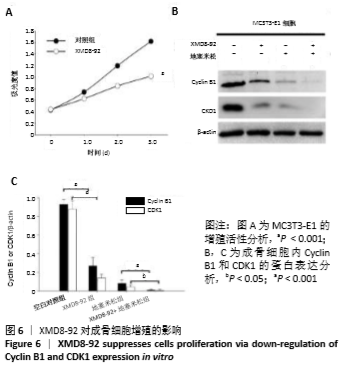
[1] MARUOTTI N, CORRADO A,ROTONDO C, et al. Janus kinase inhibitors role in bone remodeling. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(3): 915-1920.
[2] TOOSI S,BEHRAVAN J. Osteogenesis and bone remodeling: A focus on growth factors and bioactive peptides. Biofactors. 2019;3(9): e10213.
[3] KATSIMBRI P. The biology of normal bone remodelling. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2017;26(6). doi: 10.1111/ecc.12740.
[4] KHOSLA S, MONROE DG. Regulation of Bone Metabolism by Sex Steroids. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(1): pii: a031211.
[5] FRENKEL B, WHITE W, TUCKERMANN J. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;872:179-215.
[6] BUCKLEY L, HUMPHREY MB. Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(26): 2547-2556.
[7] WEINSTEIN RS, JILKA RL, PARFITT AM, et al. Inhibition of osteoblastogenesis and promotion of apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes by glucocorticoids. Potential mechanisms of their deleterious effects on bone. J Clin Invest. 1998;102(2): 274-282.
[8] JIA D, O’BRIEN CA, STEWART SA, et al. Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoclasts to increase their life span and reduce bone density. Endocrinology. 2006;147(12): 5592-5599.
[9] WEINSTEIN RS.Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012;41(3):595-611.
[10] BRIOT K. Bone and glucocorticoids. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2018;79(3): 115-118.
[11] DING N, GENG B, LI Z, et al. Fluid shear stress promotes osteoblast proliferation through the NFATc1-ERK5 pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;60(2): 107-116.
[12] BO Z,BIN G, JING W, et al. Fluid shear stress promotes osteoblast proliferation via the Gαq-ERK5 signaling pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2016;57(4): 299-306.
[13] JIANG J, ZHAO LG, TENG YJ, et al. ERK5 signalling pathway is essential for fluid shear stress-induced COX-2 gene expression in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;406(1-2): 237-243.
[14] BIN G, CUIFANG W, BO Z, et al. Fluid shear stress inhibits TNF-alpha-induced osteoblast apoptosis via ERK5 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;466(1):117-123.
[15] ZHOU G, BAO ZQ, DIXON JE. Components of a new human protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(21): 12665-12669.
[16] LEE JD, ULEVITCH RJ, HAN J. Primary structure of bmk1: A new mammalian map kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;213(2): 715-724.
[17] ABE J, KUSUHARA M, ULEVITCH RJ, et al. Big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (BMK1) is a redox-sensitive kinase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(28): 16586-16590.
[18] KATO Y, KRAVCHENKO VV, TAPPING RI, et al. BMK1/ERK5 regulates serum-induced early gene expression through transcription factor MEF2C. EMBO J. 1997;16 (23):7054-7066.
[19] FUKUHARA S, MARINISSEN MJ, CHIARIELLO M, et al. Signaling from G protein-coupled receptors to ERK5/Big MAPK 1 involves Galpha q and Galpha 12/13 families of heterotrimeric G proteins. Evidence for the existence of a novel Ras AND Rho-independent pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275 (28): 21730-21736.
[20] KIM EK, CHOI EJ. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1802 (4): 396-405.
[21] REGAN CP, LI W, BOUCHER DM, et al. Erk5 null mice display multiple extraembryonic vascular and embryonic cardiovascular defects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(14): 9248-9253.
[22] WANG X, MERRITT AJ, SEYFRIED J, et al. Targeted deletion of mek5 causes early embryonic death and defects in the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5/myocyte enhancer factor 2 cell survival pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(1): 336-345.
[23] YAN L, CARR J, ASHBY PR, et al. Knockout of ERK5 causes multiple defects in placental and embryonic development. BMC Dev Biol. 2003;3 (11).
[24] HAYASHI M, KIM SW, IMANAKA-YOSHIDA K, et al. Targeted deletion of BMK1/ERK5 in adult mice perturbs vascular integrity and leads to endothelial failure. J Clin Invest. 2004;113 (8): 1138-1148.
[25] SOHN SJ, SARVIS BK, CADO D, et al. ERK5 MAPK regulates embryonic angiogenesis and acts as a hypoxia-sensitive repressor of vascular endothelial growth factor expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277(45): 43344-43351.
[26] YANG Q, DENG X, LU B, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of BMK1 suppresses tumor growth through promyelocytic leukemia protein. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(3): 258-267.
[27] YANG Q, LEE JD. Targeting the BMK1 MAP kinase pathway in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(11): 3527-3532.
[28] SUREBAN SM,MAY R,WEYGANT N,et al.XMD8-92 inhibits pancreatic tumor xenograft growth via a DCLK1-dependent mechanism. Cancer Lett. 2014;351(1): 151-161.
[29] ROVIDA E, DI MAIRA G, TUSA I, et al. The mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK5 regulates the development and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2015;64(9): 1454-1465.
[30] KATO Y, TAPPING RI, HUANG S, et al. Bmk1/Erk5 is required for cell proliferation induced by epidermal growth factor. Nature. 1998;395(6703): 713-716.
[31] NAKAMURA H, AOKI K, MASUDA W, et al. Disruption of NF-kappaB1 prevents bone loss caused by mechanical unloading. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(6): 1457-1467.
[32] NAKAMURA K, JOHNSON GL. Activity assays for extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5. Methods Mol Biol 2010; 661:91-106.
[33] PELLETIER JP, FERNANDES JC, JOVANOVIC DV, et al. Chondrocyte death in experimental osteoarthritis is mediated by MEK 1/2 and p38 pathways: role of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(11): 2509-2519.
[34] PAWLIK TM, KEYOMARSI K. Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59(4): 928-942.
[35] THORNTON TM, RINCON M. Non-classical p38 map kinase functions: Cell cycle checkpoints and survival. Int J Biol Sci. 2009;5(1): 44-51.
[36] PELLETIER JP, MINEAU F, BOILEAU C, et al. Diacerein reduces the level of cartilage chondrocyte DNA fragmentation and death in experimental dog osteoarthritic cartilage at the same time that it inhibits caspase-3 and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21(2): 171-177.
[37] LOHBERGER B, LEITHNER A, STUENDL N, et al. Diacerein retards cell growth of chondrosarcoma cells at the G2/M cell cycle checkpoint via cyclin B1/CDK1 and CDK2 downregulation. BMC Cancer. 2015; 15:891.
[38] KANESHIRO S, OTSUKI D, YOSHIDA K, et al. MEK5 suppresses osteoblastic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015; 463(3): 241-247.
[39] ZHANG B, AN L, GENG B, et al. ERK5 negatively regulates Kruppel-like factor 4 and promotes osteogenic lineage cell proliferation in response to MEK5 overexpression or fluid shear stress. Connect Tissue Res. 2019;21: 1-12.
[40] MORIMOTO H, KONDOH K, NISHIMOTO S, et al. Activation of a C-terminal transcriptional activation domain of ERK5 by autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(49): 35449-35456.
[41] THOUVEREY C, CAVERZASIO J. Ablation of p38alpha MAPK signaling in osteoblast lineage cells protects mice from bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency. Endocrinology. 2015;156(12): 4377-4387.
[42] BOYLE DL, HAMMAKER D, EDGAR M, et al. Differential roles of MAPK kinases MKK3 and MKK6 in osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(1): e84818.
[43] EL KHASSAWNA T, BOCKER W, BRODSKY K, et al. Impaired extracellular matrix structure resulting from malnutrition in ovariectomized mature rats. Histochem Cell Biol. 2015;144(5): 491-507.
[44] ZHANG P, DAI Q, OUYANG N, et al. Mechanical Strain Promotes Osteogenesis of BMSCs from Ovariectomized Rats via the ERK1/2 but not p38 or JNK-MAPK Signaling Pathways. Curr Mol Med. 2015:15(8): 780-789.
[45] KRUM SA, CHANG J, MIRANDA-CARBONI G, et al.Novel functions for NFkappaB: inhibition of bone formation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010:6(10): 607-611.
|