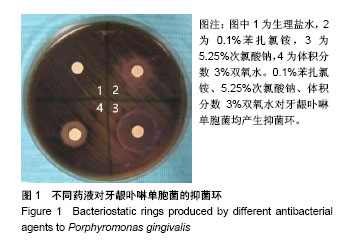
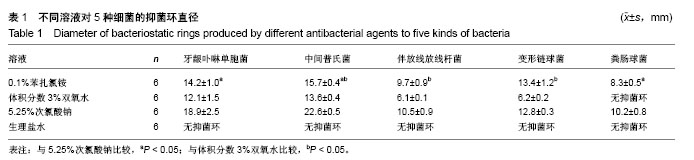
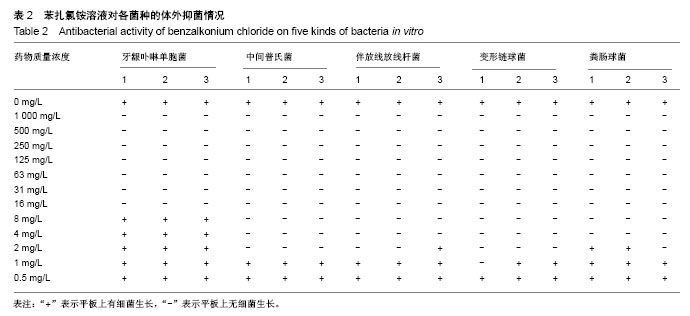
| [1] Rajaram A,Kotrashetti VS,Somannavar PD,et al.Culture-based identification of pigmented Porphyromonas and Prevotella species in primary endodontic infections.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects.2016;10(3):136-141.[2] Pan C,Liu J,Wang H,et al.Porphyromonas gingivalis can invade periodontal ligament stem cells. BMC Microbiol.2017; 17(1):38.[3] Choi EY,Bae SH,Ha MH,et al. Genistein suppresses Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in macrophages and attenuates alveolar bone loss in ligature- induced periodontitis.Arch Oral Biol.2016;62:70-79.[4] Nomura R,Ogaya Y,Nakano K.Contribution of the Collagen- Binding Proteins of Streptococcus mutans to Bacterial Colonization of Inflamed Dental Pulp.PLoS One.2016;11(7):e0159613.[5] Stojanovi? N,Kruni? J,Popovi? B,et al.Prevalence of Enterococcus faecalis and Porphyromonas gingivalis in infected root canals and their susceptibility to endodontic treatment procedures: a molecular study .Srp Arh Celok Lek.2014;142(9-10):535-541.[6] Raja M,Ummer F,Dhivakar CP.Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans—a tooth killer J Clin Diagn Res.2014;8(8):ZE13-16.[7] Priyank H,Pandey V,Bagul A,et al.Evaluation of 4% Sodium Hypochlorite in eliminating Enterococcus faecalis from the Root Canal when Used with Three Irrigation Methods: An in vitro Study.J Contemp Dent Pract.2017;18(3):214-217.[8] Kobayashi Y,Hayashi M,Yoshino F,et al.Bactericidal effect of hydroxyl radicals generated from a low concentration hydrogen peroxide with ultrasound in endodontic treatment.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2014;54:161-165.[9] Sahebjam AM,Moradi HJ,Khoshhal M,et al.Clinical Effect of Periodontal Pocket Irrigation with H2O2.Avicenna J Dent Res.2011;3(1):53-59.[10] Rashed HT.Evaluation of the effect of hydrogen peroxide as a mouthwash in comparison with chlorhexidine in chronic periodontitis patients: A clinical study.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent.2016;6(3):206-212.[11] Oguz Ahmet S,Mutluay MM,Seyfioglu Polat Z.Addition of benzalkonium chloride to self-adhesive resin-cements: some clinically relevant properties.Acta Odontol Scand.2014;72(8): 831-838.[12] Passariello C,Sannino G,Petti S.Intensity and duration of in-vitro antibacterial activity of different adhesives used in orthodontics.Eur J Oral Sci.2014;122(2):154-160.[13] Xu SY,Bian RL,Chen X.Methodology of Pharmacological Experiment.3rd. Beijing: People Hygiene Press, 2002:1657-1660.[14] Pataky L, Iványi I, Grigár A, et al. Antimicrobial efficacy of various root canal preparation techniques: an in vitro comparative study. J Endod,.2002;28(8):603-605.[15] Carrotte P. 21st century endodontics: part 3. Int Dent J. 2005; 55(4):247-253.[16] Pawar R,Alqaied A,Safavi K,et al.Influence of an apical negative pressure irrigation system on bacterial elimination during endodontic therapy: a prospective randomized clinical study.J Endod. 2012;38:1177-1181.[17] 樊明文.牙体牙髓病学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.[18] Fernandez y Mostajo M,van der Reijden WA,Buijs MJ,et al.Effect of an oxygenating agent on oral bacteria in vitro and on dental plaque composition in healthy young adults.Front Cell Infect Microbiol.2014;4:95.[19] Jhingta P,Bhardwaj A,Sharma D,et al.Effect of hydrogen peroxide mouthwash as an adjunct to chlorhexidine on stains and plaque.J Indian Soc Periodontol.2013;17(4):449-453.[20] 史宗道.口腔临床药物学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012:154-155.[21] Al-Ali M,Sathorn C,Parashos P.Root canal debridement efficacy of different final irrigation protocols.Int Endod J.2012;45(10): 898-906.[22] Metzger Z,Basrani B,Goodis HE.Instruments, materials,and devices. In:Hargreaves KM, Cohen S, Berman LH, eds.Pathways of the Pulp(10th ed).St.Louis: Mosby Elsevia (USA),2011:223-282.[23] Vajrabhaya LO,Sangalungkarn V,Srisatjaluk R,et al.Hypochlorite solution for root canal irrigation that lacks a chlorinated odor.Eur J Dent.2017;11(2):221-225. [24] Urano H,Fukuzaki S.The mode of action of sodium hypochlorite in the cleaing process.Biocontrol Sci.2005;10(1/2):21-29.[25] Fukuzaki S.Mechanisms of actions of sodium hypochlorite in cleaning and disinfection processes.Biocontrol Sci.2006;11(4):147-157.[26] Del Carpio-Perochena A,Bramante CM,de Andrade FB,et al.Antibacterial and dissolution ability of sodium hypochlorite in different pHs on multi-species biofilms.Clin Oral Investig.2015;19(8):2067-2073.[27] Ragnarsson KT,Rechenberg DK,Attin T,et al.Available chlorine consumption from NaOCl solutions passively placed in instrumented human root canals.Int Endod J.2015;48(5):435-440.[28] Gernhardt CR,Eppendorf K,Kozlowski A,et al.Toxicity of concentrated sodium hypochlorite used as an endodontic irrigant.Int Endod J.2004;37(4):272-280.[29] Pozarowska D,Pozarowski P.Benzalkonium chloride (BAK) induces apoptosis or necrosis, but has no major influence on the cell cycle of Jurkat cells.Folia Histochem Cytobiol.2011;49(2):225-230.[30] Wessels S,Ingmer H.Modes of action of three disinfectant active substances: a review.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.2013;67(3):456-467.[31] Jaramillo DE,Arriola A,Safavi K,et al. Decreased bacterial adherence and biofilm growth on surfaces coated with a solution of benzalkonium chloride.J Endod.2012;38(6):821-825.[32] da Costa LF,Amaral CD,Barbirato DD,et al.Chlorhexidine mouthwash as an adjunct to mechanical therapy in chronic periodontitis: A meta-analysis.J Am Dent Assoc. 2017;148(5): 308-318.[33] Lamont T.Lower concentration of chlorhexidine and cetyl-pyridinium chloride mouthwash demonstrates some efficacy.Evid Based Dent.2012;13(2):52-53.[34] Tarbox BB,Conroy BP,Malicky ES,et al. Benzalkonium chloride. A potential disinfecting irrigation solution for orthopaedic wounds].Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;(346):255-261.[35] Liebert MA.Final report on the safety assessment of benzalkonium chloride. J Am Coll Toxicol. 1989;8:589625. [36] Scannapieco FA.The oralmicrobiome: its role in health and in oral and systemic infections.Clin Microbiol Newsl. 2013;35(20): 163-169.[37] Larsen T, Fiehn NE. Dental biofilm infections - an update. APMIS. 2017;125(4):376-384.[38] [Awadalla HI, Ragab MH, Bassuoni MW, et al. A pilot study of the role of green tea use on oral health. Int J Dent Hygiene. 2011;9(2): 110-116.[39] George DE, Shetty R, Shetty PJ, et al . An In vitro Study to Compare the Effect of Different Types of Tea with Chlorhexidine on Streptococcusmutans.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(9): ZC05-ZC07.[40] Preshaw PM,Alba AL,Herrera D,et al.Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship.Diabetologia.2012;55(1):21-31.[41] Feng X, Zhu L, Xu L, et al. Distribution of 8 periodontal microorganisms in family members of Chinese patients with aggressive periodontitis.Arch Oral Biol.2015;60(3):400-407.[42] Akincibay H, Orsal SO, Sengün D, et al. Systemic administration of doxycycline versus metronidazole plus amoxicillin in the treatment of localized aggressive periodontitis: a clinical and microbiologic study.Quintessence Int.2008;39(2):e33-39.[43] Burgess DK, Huang H, Harrison P, et al. Non-Surgical Therapy Reduces Presence of JP2 Clone in Localized Aggressive Periodontitis.J Periodontol.2017;88(12):1263-1270.[44] Lima SM,Sousa MG,Freire Mde S,et al.Immune Response Profile against Persistent Endodontic Pathogens Candida albicans and Enterococcus faecalis In Vitro.J Endod.2015;41(7):1061-1065.[45] Cheng X,Chen B,Qiu J,et al.Bactericidal effect of Er:YAG laser combined with sodium hypochlorite irrigation against Enterococcus faecalis deep inside dentinal tubules in experimentally infected root canals.J Med Microbiol. 2016;65(2): 176-187.[46] Hiremath GS,Kulkarni RD,Naik BD.Evaluation of minimal inhibitory concentration of two new materials using tube dilution method: An in vitro study.J Conserv Dent.2015;18(2):159-162. [47] 邢飞鹏,孙立洲,王欣梅.苯扎氯铵溶液根管冲洗液抗菌效果研究[J].医药论坛杂志,2011,32(12):168-169.[48] Baron A,Lindsey K,Sidow SJ,et al.Effect of a Benzalkonium Chloride Surfactant-Sodium Hypochlorite Combination on Elimination of Enterococcus faecalis.J Endod. 2016;42(1): 145-149. |
.jpg)