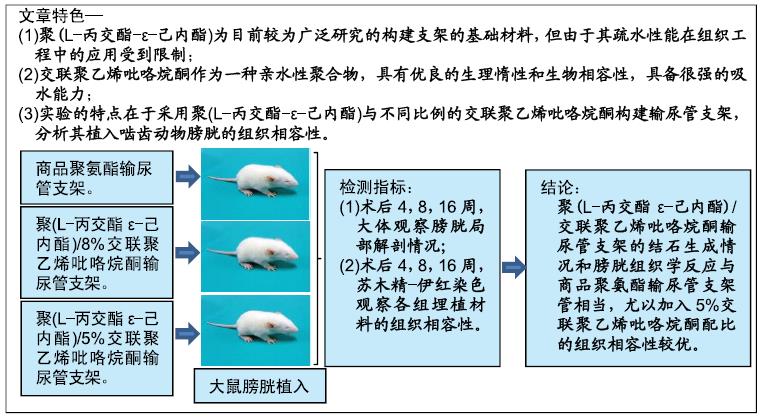
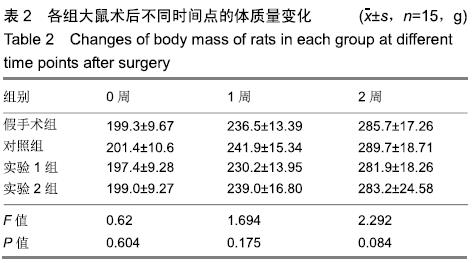
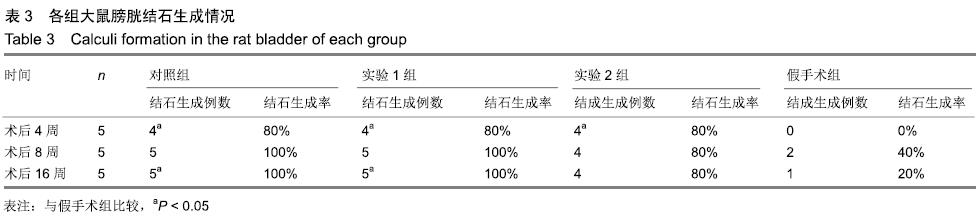
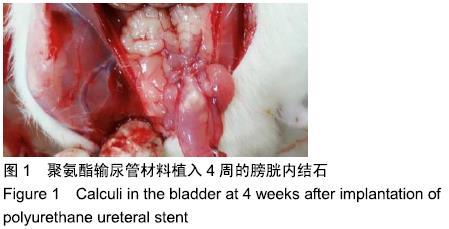
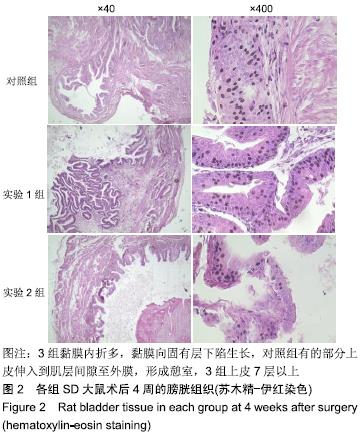
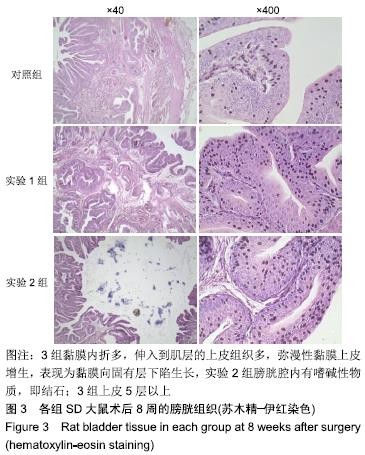
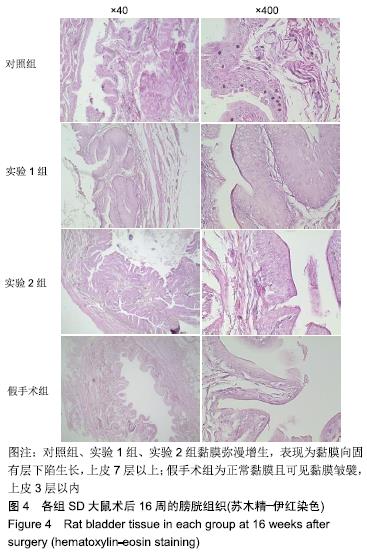
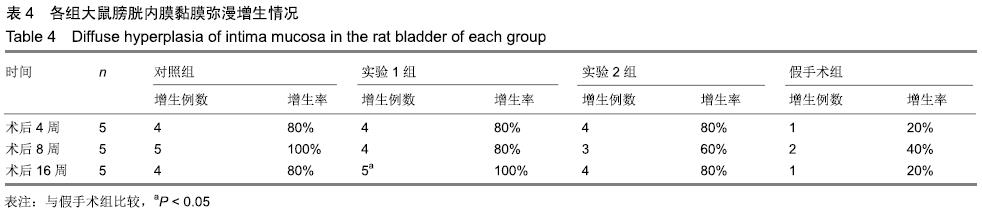
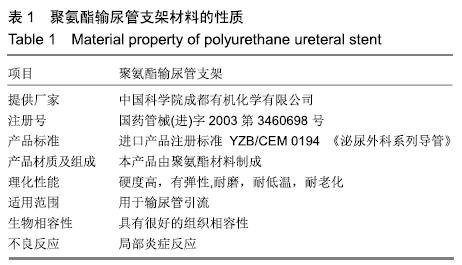
[1] 张昊,徐卫丽,张凯,等.输尿管内支架管在泌尿外科中的应用价值及并发症分析[J].中国卫生产业,2014,18(29):38.
[2] JACOBSEN S, KLEMETSEN Ø, BIRKELUND Y.Vesicoureteral reflux in young children: a study of radiometric thermometry as detection modality using an ex vivo porcine model.Phys Med biol.2012;57(17):5557.
[3] ZHANG MQ, ZOU T, HUANG YC, et al.Braided thin-walled biodegradable ureteral stent: Preliminary evaluation in a canine model. Int J Urol. 2014; 21(4):401.
[4] 王瑞庆,王艳波,陶森.多镜联合取出遗忘输尿管支架管合并结石1例[J].中国现代医学杂志,2016,26(9):131-133.
[5] BAUMGARTEN L, DESAI A, SHIPMAN S, et al.Spontaneous passage of ureteral stones in patients with indwelling ureteral stents.Can J Urol. 2017;24(5):9024-9029.
[6] 杨刚,沈天一,周昱霖,等.输尿管内支架管滞留后拔除困难的临床处理进展[J].医学研究生学报,2018,31(12):1314 .
[7] 施云峰,李维国,张捷等.双J管留置时间对输尿管结石并感染患者疗效的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2016,92(32):2588-2591.
[8] Taguchi M, Inoue T, Muguruma K, et al.Impact of loop-tail ureteral stents on ureteral stent-related symptoms immediately after ureteroscopic lithotripsy: Comparison with pigtail ureteral stents.Investig Clin Urol. 2017;58(6):440-446.
[9] AL-AWADI K, KEHINDE EO, AL-HUNAYAN A, et al.Iatrogenic Ureteric Injuries: Incidence, Aetiological Factors and the Effect of Early Management on Subsequent Outcome.Int Urol Nephrol.2005;37(2):235.
[10] GENTILE P, MCCOLGAN-BANNON K, GIANONE NC, et al. Biosynthetic PCL-graft-Collagen Bulk Material for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials.2017;10(7):693.
[11] CHUNG D, BRIGGS J, TURNEY BW, et al.Management of iatrogenic ureteric injury with retrograde ureteric stenting: an analysis of factors affecting technical success and long-term outcome.Acta Radiol.2017; 58(2):170.
[12] 赵立江.输尿管支架管在泌尿外科的临床实用价值[J].中西医结合心血管病杂志,2017,5(15):95.
[13] 周雪健,许华,姜昊文.可降解输尿管支架的研究现状及临床前景[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2017,32(12):979-984.
[14] BARROS AA, OLIVEIRA C, RIBEIRO AJ, et al.In vivo assessment of a novel biodegradable ureteral stent.World J Urol.2018;36(2):277.
[15] WOLTERS HH, HEISTERMANN HP, STÖPPELER S, et al.A New Technique for Ureteral Defect Lesion Reconstruction Using an Autologous Vein Graft and a Biodegradable Endoluminal Stent.J Urology.2010;184(3):1197.
[16] 钟华,刘建纯,郭乐斌,等.可吸收内固定PLLA材料制备及生物相容性评价[J].国际医药卫生导报,2018,24(8):1133.
[17] MOURE C, QASSEMYAR Q, DUNAUD O, et al.Skeletal stability and morbidity with self-reinforced P (l/dL) LA resorbable osteosynthesis in bimaxillary orthognathic surgery.J Cranio Maxill Surg.2012;40(1):55.
[18] JAYAKUMAR R, CHENNAZHI KP, SRINIVASAN S, et al.Chitin Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(3):1876.
[19] STERLING JA, GUELCHER SA.Biomaterial Scaffolds for Treating Osteoporotic Bone.Curr Osteoporos Rep.2014;12(1):48.
[20] FIORENTINO SM, CARFÌ PAVIA F, LA CARRUBBA V, et al. Characterization of PLLA scaffolds for biomedical applications.Int J Polym Mater.2017;66(9):469.
[21] 肖世伟,李亚楠,刘军.可降解输尿管支架管的研究进展[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2018,9(1):76-77.
[22] QI H, YE Z, REN H, et al.Bioactivity assessment of PLLA/PCL/HAP electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Life Sci. 2016;148:139.
[23] 韦茜茜,金嘉长,周密,等.PCL基聚合物的制备及其在生物医学工程中的应用[J].宁波大学学报(理工版), 2018,31(4):36.
[24] MALIKMAMMADOV E, TANIR TE, KIZILTAY A, et al.PCL and PCL-based materials in biomedical applications.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(7-9):863.
[25] SIDDIQUI N, ASAWA S, BIRRU B, et al.PCL-Based Composite Scaffold Matrices for Tissue Engineering Applications.Mol Biotechnol. 2018;60(7):506.
[26] ABEDALWAFA M, WANG F, LI W, et al.Biodegradable poly-epsilon- caprolactone (PCL) for tissue engineering applications: a review.Rev Adv Mater Sci.2013;34(2):123-140.
[27] 刘秀萍,臧恒昌,孙海龙.交联聚乙烯吡咯烷酮的生产应用与市场前景[J].食品与药品,2012,14(9):366-368.
[28] 叶佳佳,杨青芳,吴杨传,等.硅橡胶/PVPP水凝胶共混型吸水膨胀材料的制备及性能研究[J].橡胶工业,2008,55(6):325-328.
[29] 陈和春,张大宏,熊成东.等.一种用于可降解输尿管支架管的复合材料及可降解输尿管支架管:中国, 201210538575.X[P]. 2013-04-17
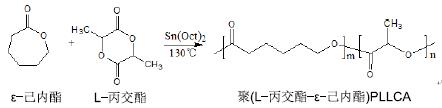
[30] 吴航,张丽芳,熊左春.等.酯交换反应条件对聚(L-丙交酯-co-Ɛ-己内酯)力学性能的影响[J].合成化学, 2011,19(5):590-594.
[31] 鲁越,熊左春,李庆,等.聚(L-丙交酯-co-Ɛ-己内酯)力学性能和降解性能研究[J].塑料工业,2012,38(8):34-38.
[32] CERCA N, PIER GB, VILANOVA M, et al.Quantitative analysis ofadhesion and biofilm formation on hydrophilic and hydrophobicsurfaces ofclinical isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis.ResMicrobiol. 2005;156(4):506-514.
[33] 熊富忠,赵小希,廖胤皓,等.材料表面特征对生物膜形成的影响及其应用[J].微生物学通报,2018,45(1):155-165.
[34] 尹卫民.治疗短鼻畸形的可控性膨胀材料的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学, 2008:32-40.
[35] FISCHER KM, LOUIE M, MUCKSAVAGE P.Ureteral Stent Discomfort and Its Management.Curr Urol Rep.2018;19(8):1-7.
[36] CHEW BH, LANGE D.Advances in ureteral stent development.Curr Opin Urol.2016;26(3):277.
[37] WANG L, YANG G, XIE H, et al.Prospects for the research and application of biodegradable ureteral stents: from bench to bedside.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2018;29(14):1657.
[38] QI H, YE Z, REN H, et al.Bioactivity assessment of PLLA/PCL/HAP electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Life Sci. 2016;148:139.
[39] 姚海军,赵阳,周哲,等.人脂肪来源干细胞与左旋聚乳酸/聚己内酯支架的体内外生物相容性研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2014,10(5):255-258.
[40] 姚丹,郝岱峰,赵帆,等.富血小板血浆联合聚乳酸/聚己内酯对小型猪破片伤深部软组织缺损愈合的影响[J].中华烧伤杂志,2019,35(1):31-39.
[41] 陈丽芬,吴建辉,黄冬妍,等.探讨微孔树脂应用于膀胱结石模型的可行性[C]. 2017年生殖毒理药理学理论与技术及科技产品研发学术交流会论文集, 2017.
[42] 张薇,陈苑,邹移海,等.不同剂量化学纯三聚氰胺诱发SD大鼠尿结石的比较[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(14):102-105.
[43] 曹建英,曲秀君,段晓勇.石淋消汤对大鼠膀胱结石的溶解作用[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(27):251-252.
[44] 白殿卿,范薇.医学实验动物等级划分及生物医学[J].青海医药杂志, 1993, 36(5):59.
[45] 王妍,王汉中,张英,等.生物骨组织立体培养分化和动物体内修复实验[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):836-842.
|