| [1] Kumar YS,Acharya S,Pentapati KC.Prevalence of dental pain and its relationship to caries experience in school children of Udupi district.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2014;15(6):371-375.
[2] Do LG,Miller J,Phelan C,et al.Dental caries and fluorosis experience of 8-12-year-old children by early-life exposure to fluoride.Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2014;42(6): 553-562.
[3] Rothen M,Cunha-Cruz J,Zhou L,et al.Oral hygiene behaviors and caries experience in Northwest PRECEDENT patients.Community Dent Oral Epidemiol.2014;42(6):526-535
[4] 王家良.循证医学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001:165-190.
[5] Prabhakar AR,Dhanraj K,Sugandhan S.Comparative evaluation in vitro of caries inhibition potential and microtensile bond strength of two fluoride releasing adhesive systems.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent.2014;15(6):385-391.
[6] Mei ML,Ito L,Chu CH,et al.Prevention of dentine caries using silver diamine fluoride application followed by Er:YAG laser irradiation: an in vitro study.Lasers Med Sci. 2014;29(6): 1785-1791.
[7] Soni S,Mehta M,M AD,et al.Root caries among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients visiting a hospital.Spec Care Dentist.2014;34(6):273-277.
[8] Makhija SK,Gilbert GH,Funkhouser E,et al.Twenty-month follow-up of occlusal caries lesions deemed questionable at baseline: findings from the National Dental Practice-Based Research Network.J Am Dent Assoc.2014;145(11): 1112-1118.
[9] Gaudilliere D,Thakur Y,Ku M,et al.Caries management by risk assessment in a cleft and craniofacial center.J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(6):e529-836.
[10] Fattori G,Saito N,Seregni M,et al.Commissioning of an integrated platform for time-resolved treatment delivery in scanned ion beam therapy by means of optical motion monitoring.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2014;13(6):517-528.
[11] Beil H,Rozier RG,Preisser JS,et al.Effects of early dental office visits on dental caries experience.Am J Public Health. 2014;104(10):1979-1985.
[12] Schwendicke F, Kern M, Blunck U,etal.Marginal integrity and secondary caries of selectively excavated teeth in vitro.J Dent.2014;42(10):12611268.
[13] Albert D,Barracks SZ,Bruzelius E,et al.Impact of a Web-based intervention on maternal caries transmission and prevention knowledge, and oral health attitudes.Matern Child Health J.2014;18(7):1765-1771.
[14] Liu X, Xu J.Treatment of advanced NSCLC with unknown EGFR gene status?--TKI or chemotherapy?Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi.2014;17(10):709-714.
[15] Loesche WJ.Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay.Microbiol Rev. 1986;50(4):353-380.
[16] Beighton D.The complex oral microflora of high-risk individuals and groups and its role in the caries process. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol.2005;33(4): 248-255.
[17] Byun R,Nadkarni MA,Chhour KL,et al.Quantitative analysis of diverse Lactobacillus species present in advanced dental caries.J Clin Microbiol.2004;42(7):3128-3136.
[18] Chhour KL, Nadkarni MA, Byun R,et al.Molecular analysis of microbial diversity in advanced caries.J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43(2):843-849.
[19] Palmer RJ Jr,Diaz PI,Kolenbrander PE.Rapid succession within the Veillonella population of a developing human oral biofilm in situ.J Bacteriol. 2006;188(11):4117-4124.
[20] Egland PG,Palmer RJ Jr,Kolenbrander PE.Interspecies communication in Streptococcus gordonii-Veillonella atypica biofilms: signaling in flow conditions requires juxtaposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2004;101(48): 16917-16922.
[21] Bradshaw DJ,Marsh PD.Analysis of pH-driven disruption of oral microbial communities in vitro. Caries Res,1998;32(6): 456-462.
[22] Noorda WD,Purdell-Lewis DJ,van Montfort AM,et al.Monobacterial and mixed bacterial plaques of Streptococcus mutans and Veillonella alcalescens in an artificial mouth: development, metabolism, and effect on human dental enamel.Caries Res.1988;22(6):342-347.
[23] Kvist T,Zedrén-Sunemo J,Graca E,et al.Is treatment under general anaesthesia associated with dental neglect and dental disability among caries active preschool children?Eur Arch Paediatr Dent.2014;15(5):327-332.
[24] Xin BC,Luo AH,Qin J,et al.Microbial diversity in the oral cavity of healthy Chinese Han children.Oral Dis.2013;19(4): 401-405.
[25] Luo AH,Yang DQ,Xin BC,et al.Microbial profiles in saliva from children with and without caries in mixed dentition.Oral Dis. 2012;18(6):595-601. |
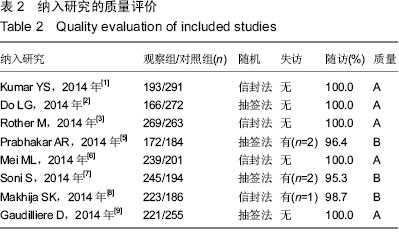
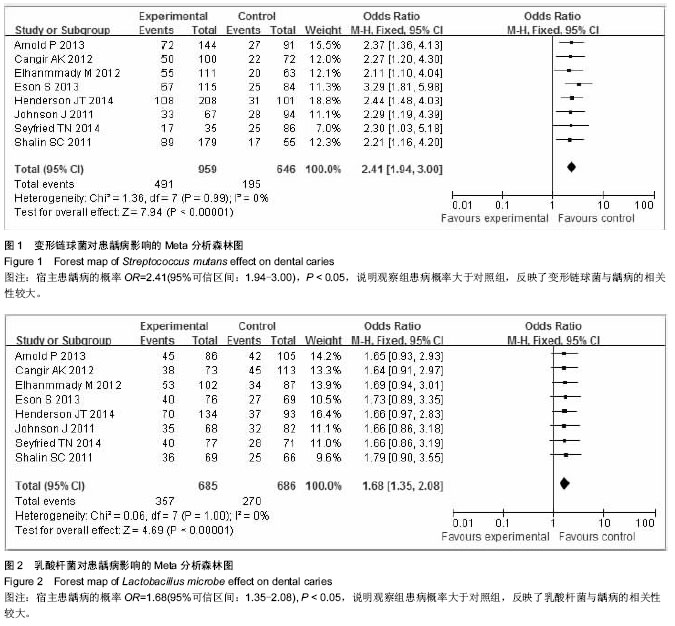
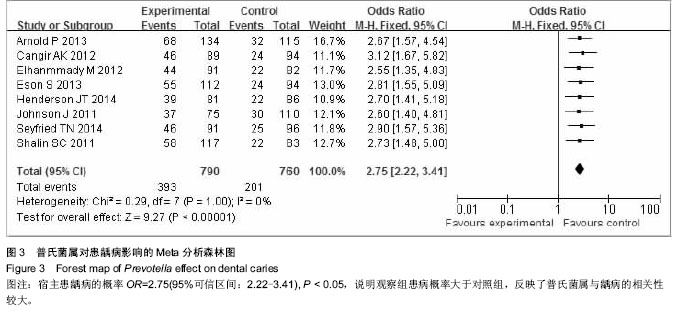
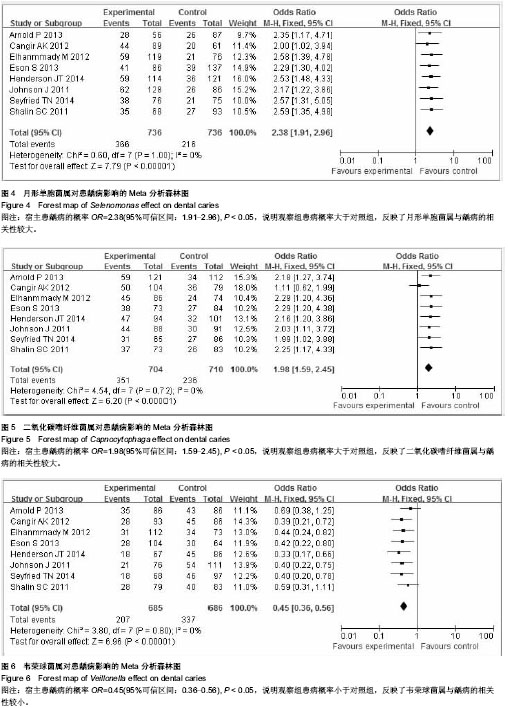
.jpg)