| [1] Kang L,Lin D,Ding Z,et al.Artificial disk replacement combined with midlevel ACDF versus multilevel fusion for cervical disk disease involving 3 levels. Orthopedics.2013;36(1):e88-94.
[2] 王逢贤,徐林,俞兴,等.新型国产颈椎间盘实验山羊模型的建立及初步研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,10(3):50-52.
[3] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[4] Tsuchiya S,Hara K,Ikeno M,et al.Rat bone marrow stromal cell-conditioned medium promotes early osseointegration of titanium implants.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2013;28(5): 1360-1369.
[5] Garai S,Sinha A.Biomimetic nanocomposites of carboxymethyl cellulose-hydroxyapatite: Novel three dimensional load bearing bone grafts.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2013;115C:182-190.
[6] Butcher A,Milner R,Ellis K,et al.Interaction of platelet-rich concentrate with bone graft materials: an in vitro study.J Orthop Trauma.2009;23(3):195-200.
[7] Bae SE,Bhang SH,Kim BS,et al.Self-assembled extracellular macromolecular matrices and their different osteogenic potential with preosteoblasts and rat bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.Biomacromolecules. 2012;13(9): 2811-2820.
[8] Phinney DG,Kopen Q,Isaacson RL,et al.Plastic adherent stromal cells from the bone marrow of commonly used strains of inbred mice:variations in yield,growth,and diferentiation.J Cell Biochem.1999;72:570-585.
[9] Zhang MM,Jia GQ,Cheng JQ,et al.In vitro analysis and in vivo tracing of BrdU-labeled rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.2012;43(2): 266-270.
[10] Djouad F,Bony C,Häupl T,et al.Transcriptional profiles discriminate bone marrow-derived and synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Arthritis Res Ther.2005;7(6): R1304-1315.
[11] Martin JY,Schwartz Z,Hummert TW,et al.Effect of titanium surface roughness on proliferation, differentiation and protein synthesis of human osteoblast-like cells(MG63).J Biomed Mater Res.1995;29:389-401.
[12] Chien CY,Tsai WB.Poly(dopamine)-assisted immobilization of Arg-Gly-Asp peptides,hydroxyapatite,and bone morphogenic protein-2 on titanium to improve the osteogenesis of bone marrow stem cells.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2013;5(15): 6975-6983.
[13] Malchau H,Herberts P,Ahnfelt L.Prognosis of total hip replacement in Sweden.Acta Orthop Scand.1993;64:497-506.
[14] 姜红江,王玉林.医用钛合金的表面改性[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2005,2(4):28-33.
[15] Hench LL.Bioceramics from concept to clinic.J Am Ceram Soc.1991;8(1):1487-1510.
[16] Mutsuzaki H,Sogo Y,Oyane A,et al.Improved bonding of partially osteomyelitic bone to titanium pins owing to biomimetic coating of apatite.Int J Mol Sci.2013;14(12): 24366-24379.
[17] Anselme K.Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials.Biomaterials. 2000;21:667-681.
[18] Nakashima Y,Sato T,Yamamoto T,et al.Results at a minimum of 10 years of follow-up for AMS and PerFix HA-coated cementless total hip arthroplasty: impact of cross-linked polyethylene on implant longevity.J Orthop Sci.2013;18(6): 962-968.
[19] Shin J,Lee K,Koh J,et al.Hydroxyapatite coatings on nanotubular titanium dioxide thin films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013;13(8):5807-5810.
[20] Lee TM,Yang CY,Chang E,et al.Comparison of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatitc coatings and zirconia-reinforced hydroxyapatite composite coatings: in vivo study.J Biomed Mater Res A.2004;71A(4):652-660.
[21] Antonov EN,Bagratashvili VN,Ball M,et al.Influence of target density on properties of laser deposited calcium phosphate coatings.Key Eng Mater.2001;192-195(22-26):107-110.
[22] Long LH,Kim HW,Lee SH,et al.Biocompatibility of titanium implants modified by microarc oxidation and hydraxyapatite coating.J Biomed Mater Res A.2005;73(1):48-54.
[23] Ma J,Wang C,Peng KM.Electrophoretic deposition of porous hydroxyapatite scaffold.Biomaterials.2003;24:(3)505-510.
[24] Lord G,Bancel P.Themadreporic cementless total hip arthroplasty.New experimental data and a seven-year clinical follow-up study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1983;176:67-76.
[25] Zreiqat H,Valenzuela SM,Nissan BB,et al.The effect of surface chemistry modification of titanium alloy on signalling pathways in human osteoblasts.Biomaterials.2005;26:7579-7586.
[26] Millet P,Girardin E,Braham C,et al.Stress influence on interface in plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium alloy.J Biomed Mater Res.2012;60(4):679-684.
[27] Li HW,Sun JY.Effects of dicalcium silicate coating ionic dissolution products on human mesenchymal stem-cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation.J Int Med Res. 2011; 39(1):112-128.
[28] Zeng XL,Li JF,Yang SH,et al.In Vivo Testing of Canine Prosthetic Femoral Components with HA-Ti Ladder-type Coating on Vacuum Plasma-sprayed Ti Substrate. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.2013;33(4):543-550.
[29] Heimann RB,Schurmann N,Muller RT.In vitro and in vivo performance of Ti6Al4V implants with plasma-sprayed osteoconductive hydroxylapatite-bioinert titania bond coat "duplex" systems: an experimental study in sheep.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2004;15(9):1045-1052.
[30] Ker ED,Chu B,Phillippi JA,et al.Engineering spatial control of multiple differentiation fates within a stem cell population. Biomaterials.2011;32(13):3413-3422. |
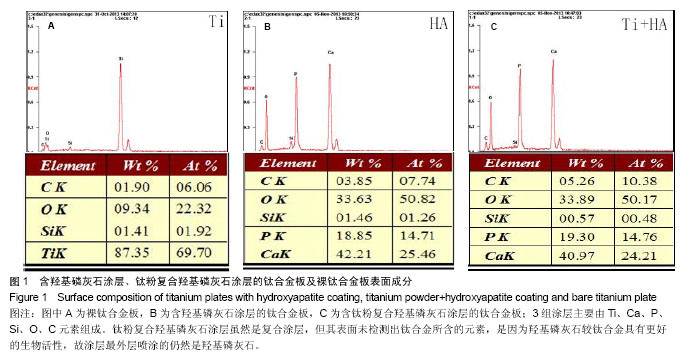
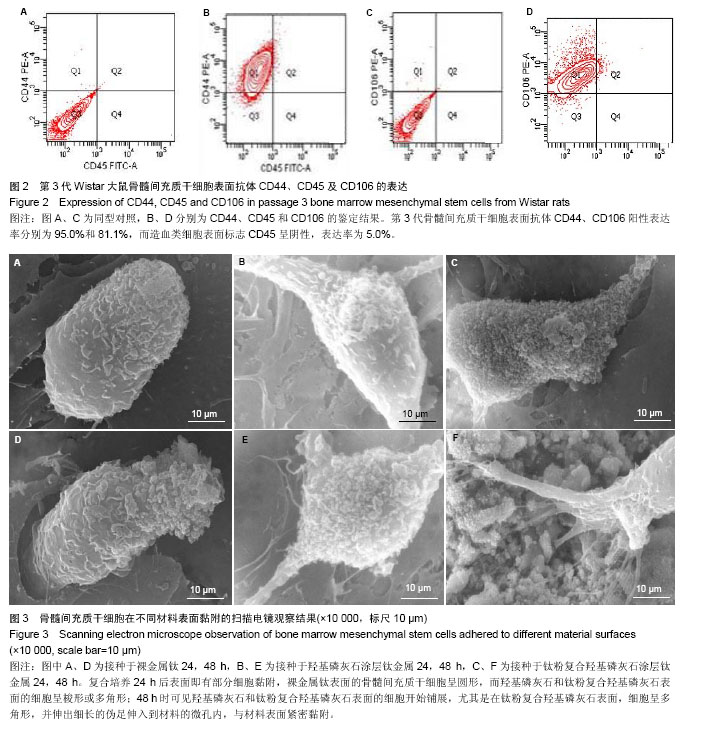
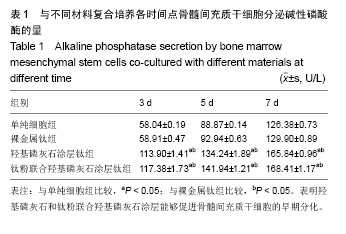
.jpg)