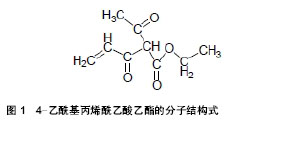
| [1] Luangphakdy V,Walker E,Shinohara K,et al.Evaluation of osteoconductive scaffolds in the canine femoral multi-defect model.Tissue Eng Part A.2013;19(5-6):634.
[2] Kreja L,Liedert A,Schlenker H,et al.Effects of mechanical strainon human mesenchymal stem cells and ligament fibroblasts in a texturedpoly(L-lactide) scaffold for ligament tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2012; 23(10): 2575.
[3] Han Q,Jin W,Xiao Z,et al.The promotion of neural regeneration in an extreme rat spinal cord injury model using a collagen scaffold containing a collagen binding neuroprotective protein and an EGFR neutralizing antibody. Biomaterials.2013;31(35):9212.
[4] Zhao Q,Wang S,Tian J,et al.Combination of bone marrow concentrate and PGA scaffolds enhance bone marrow stimulation in rabbit articular cartilage repair.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2013;24(3):793.
[5] Hong Y,Gong Y,Gao C,et al.Collagen-coated polylactide microcarriers/chitosan hydrogel composite: injectable scaffold for cartilageregeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008; 85(3): 628.
[6] 韩倩倩,何晨光,赵莉,等.组织工程支架材料聚乙醇酸的体外细胞贴壁性和降解性能研究[J].药物分析杂志,2013,33(8): 1331-1335.
[7] Ho E,Lowman A,Marcolongo M.Synthesis and characterization of an injectable hydrogel with tunable mechanical properties for soft tissue repair. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7(11):3223-3228.
[8] Shome A,Debnath S,Das PK.Head group modulated pH-responsive hydrogel of amino acid-based amphiphiles: entrapment and release of cytochrome c and vitamin B12. Langmuir.2008;24(8):4280-4288.
[9] Zhang XZ, Yang YY, Wang FJ, et al.Thermosensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels with expanded network structures and improved oscillating swelling-deswelling operties.Langmuir. 2002;18(6): 2013-2018.
[10] 林松柏,丛辉,柯爱茹,等.PVA增强P(AAEA-co-AA)温度敏感性水凝胶的合成及其性能研究[J].化学学,2011,69(22): 2710-2716.
[11] Ho J,Jin W,Hyung D,et al.Thermosensitive Chitosans as Novel Injectable Biomaterials. Macromol Symp. 2005;224(1): 275-286.
[12] Pochan DJ,Schneider JP,Kretsinger J,et al.Thermally reversible hydrogels via intramolecular folding and consequent self-assembly of a denovo designed peptide. JACS.2003;125(39):11802-11803.
[13] Tanaka T,Fillmore D,Sun S,et a1.Phasetransitions inionicgels.Phys Rev Lett.1980;45(20):1636-l639.
[14] 王芳平,牟琥珀,张珺瑛,等.pH响应性P(AA-co-C8PhEO10Mac) 水凝胶的制备及其对L-抗坏血酸的控释性能[J].精细化工,2013, 30(2):134-138.
[15] 陈旭日,陈学刚.新型P(NIPAAm-co-IA)pH敏感智能水凝胶的合成与性能研究[J].化学推进剂与高分子材料,2011,9(2):253.
[16] 郑施施,王增寿.pH敏感型羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶的制备及体外释药考察[J].中国药师,2013,16(4):535-536.
[17] Park BG,Kang HS,Lee W,et al.Reinforcement of pH-responsive γ-poly(glutamic acid)/chitosan hydrogel for orally administrable colon-targeted drug delivery.J Appl Polym Sci.2013;127(1):832-836.
[18] 张海璇.曲酸二棕榈酸酯光敏感性水凝胶智能给药系统的研究[D].兰州:兰州大学硕士学位论文,2009.
[19] Yamamoto H,Kitsuki T,Nishida A,et al.Photoresponsive peptide and polypeptide systems. 13. Photoinduced cross-linked gel and biodegradation properties of copoly(l-lysine) containing ε-7-Coumaryloxyacetyl-L-lysine Residues. Macromolecules.1999; 32(4):1055-1061.
[20] Ohkawa K,Shoumura K,Yamada M,et al.Photoresponsive Peptide and Polypeptide Systems, 14. Biodegradation of Photocrosslinkable Copolypeptide Hydrogels Containing L-Ornithine and δ-7-Coumaryloxyacetyl-L-ornithine Residues. Macromol Biosci.2001;1(4):149-156.
[21] 张书第,翟玉春,张振芳.PVA/Fe2O3磁敏感性水凝胶的制备及性能[J].过程工程学报,2010,10(2):405-408.
[22] Starkar NS,Hilt JZ.Magnetic hydrogel nanocomposites for remote controlled pulsatile drug release.J Control Release. 2008;130(3):246-251.
[23] Paulino AT,Guilhermea MR,de Almeida EAMS,et al. One- potsynthesis of achitosanbased hydrogel as a potential device for magnetic biomaterial.J Magnet Magnet Mater. 2009;321(17):2636-2642.
[24] Shim WS,Yoo JS,Lee DS,et al.Novel injectable pH and temperature sensitive block copolymer hydrogel.Biomacromolecules.2005;6(6):2930−2934..
[25] 陆遥遥,吴季怀,林建明,等.反应条件对海藻酸钠/聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺水凝胶温度及pH敏感性能的影响研究[J].材料导报,2010, 24(5):99-104.
[26] Sun GM,Zhang XZ,Chu CC.Formulation and characterization of chitosan-based hydrogel films having both temperature and pH sensitivity.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007;18(8):1563-1577.
[27] 余娟,刘守信,房喻,等.pH/温度双重敏感的PDMAEMA水凝胶的力学性质[J].陕西师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2010,38(3): 50-55.
[28] Khurma JR,Nand AV.Temperature and pH Sensitive Hydrogels Composed of Chitosan and Poly ( ethylene glycol).Polymer Bulletin.2008;59(6):805-812.
[29] Canter HI,Vargel I,Korkusuz P,et al.Effect of use of slow release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-Beta-2 in a chitosan gel matrix on cranial bone graft survival in experimental cranial critical size defect model.Ann Plastic Surg.2010;64(3):342-350.
[30] Gulati K,Ramakrishnan S,Aw MS,et al.Biocompatible polymer coating of titania nanotube arrays for improved drug elution and osteoblast adhesion.Acta Biomaterialia. 2011;8(1): 449-456.
[31] Coimbra P,Ferreira P,de Sousa HC,et al. Preparation and chemical and biological characterization of a pectin/chitosan polyelectrolyte complex scaffold for possible bone tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2011;48(1): 112-118.
[32] Anderson JM,Vines JB,Patterson JL,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells synergistically enhanced by biomimetic peptide amphiphiles combined with conditioned medium.Acta Biomater. 2010; 7(2):675-682.
[33] Miller RE,Grodzinsky AJ,Vanderploeg EJ,et al.Effect of self-assembling peptide,chondrogenic factors and bone marrow-derived stromal cells on osteochondral repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2010;18(12):1608-1619.
[34] 吴敏,宋鸿,陆永志,等.自组装短肽用于SD大鼠头顶骨损伤的修复[J].四川动物, 2010,29(3):386-388.
[35] 盛宇,陆永志,孙丽娟,等.新型纳米材料及与前成骨细胞联合培养的实验研究[J].北京生物医学工程,2009,28(1):55-60.
[36] Kim HK,Shim WS,Kim SE,et al.Injectable in situ- forming pH/ thermo- sensitive Hydrogel for bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(4):923-33.
[37] Koh MY,Ohtsuki C,Miyazaki T.Modification of polyglutamic acid with silanol groups and calcium salts to induce calcification in a simulated body fluid.J Biomater Appl. 2011; 25(6):581-594.
[38] Tan H,Chu CR,Payne KA,et al.Injectable in situ forming biodegradable chitosan-hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2009;30(13): 2499-2506.
[39] 郝彤,刘暾,吕双红,等.采用温敏性壳聚糖水凝胶体外构建组织工程化软骨的实验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2007,32(5):500-502.
[40] Cho JH.Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells using a thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and water-soluble chitosan copolymer.Biomaterials.2004;25(26):5743-5751.
[41] Chao PH,Yodmuang S,Wang X,et al. Silk of Hydrogel frcartilage Tissue Eng ineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2010;95(1):84-90.
[42] Tysseling-Mattiace VM,Sahni V,Niece KL,et al. Self-assembling nanofibers inhibit glial scar formation and promote axon elongation after spinal cord injury.J Neurosci. 2008;28(14):3831-3823.
[43] Sun J,Zheng Q,Wu Y,et al.Culture of nucleus pulposus cells from intervertebral disc on self-assembling KLD-12 peptide hydrogel scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C.2010;30(7):975-980. |