| [1]Chatterjee S, Khunti K, Davies MJ.Type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2017;389(10085):2239-2251.[2]Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.2018;138: 271-281.[3]Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, et al. Prevalence and Ethnic Pattern of Diabetes and Prediabetes in China in 2013.JAMA. 2017;317(24):2515-2523.[4]中华医学会糖尿病学分会, 国家基层糖尿病防治管理办公室 .国家基层糖尿病防治管理指南(2018)[J].中华内科杂志,2018, 57(12):885-893.[5]Morrow RM,Picard M,Derbeneva O,et al.Mitochondrial energy deficiency leads to hyperproliferation of skeletal muscle mitochondria and enhanced insulin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2017;114(10): 2705-2710.[6]Kim-Muller JY, Zhao S, Srivastava S, et al. Metabolic inflexibility impairs insulin secretion and results in MODY-like diabetes in triple FoxO-deficient mice. Cell Metab.2014; 20(4): 593-602.[7]Yonashiro R, Eguchi K, Wake M,et al. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase PDH-E1β Controls Tumor Progression by Altering the Metabolic Status of Cancer Cells. Cancer Res.2018;78(7): 1592-1603.[8]Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Hernández-Esquivel L, Marín-Hernández A, et al. Mitochondrial free fatty acid β-oxidation supports oxidative phosphorylation and proliferation in cancer cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2015; 65: 209-221.[9]Kaufman BA, Li C, Soleimanpour SA.Mitochondrial regulation of β-cell function: maintaining the momentum for insulin release.Mol Aspects Med.2015;42:91-104.[10]Park S, Jeon JH, Min BK, et al. Role of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex in Metabolic Remodeling: Differential Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Functions in Metabolism. Diabetes Metab J.2018; 42(4): 270-281.[11]Talchai C, Xuan S, Lin HV, Sussel L, Accili D. Pancreatic β cell dedifferentiation as a mechanism of diabetic β cell failure. Cell.2012;150(6): 1223-1234.[12]Requejo-Aguilar R,Lopez-Fabuel I,Fernandez E,et al.PINK1 deficiency sustains cell proliferation by reprogramming glucose metabolism through HIF1. Nat Commun.2014;5: 4514.[13]Whitley MJ, Arjunan P, Nemeria NS, et al.Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency is linked to regulatory loop disorder in the αV138M variant of human pyruvate dehydrogenase.J Biol Chem. 2018;293(34):13204-13213.[14]Zhang S, Hulver MW, McMillan RP, et al. The pivotal role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases in metabolic flexibility. Nutr Metab (Lond).2014;11(1):10.[15]Liu YQ, Moibi JA, Leahy JL. Chronic high glucose lowers pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in islets through enhanced production of long chain acyl-CoA: prevention of impaired glucose oxidation by enhanced pyruvate recycling through the malate-pyruvate shuttle. J Biol Chem.2004;279(9): 7470-7475.[16]Yang F, Liu C, Chen D, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-loxP-Mediated Gene Editing as a Novel Site-Specific Genetic Manipulation Tool. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.2017;7: 378-386.[17]Ma Y, Yu L, Pan S, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeting of the Rosa26 locus produces Cre reporter rat strains for monitoring Cre-loxP-mediated lineage tracing. FEBS J. 2017; 284(19): 3262-3277.[18]Mulder H. Transcribing β-cell mitochondria in health and disease. Mol Metab.2017;6(9): 1040-1051.[19]Sun W, Quan N, Wang L, et al. Cardiac-Specific Deletion of the Pdha1 Gene Sensitizes Heart to Toxicological Actions of Ischemic Stress. Toxicol Sci.2016;151(1): 193-203.[20]Lewis AJ, Neubauer S, Tyler DJ,et al. Pyruvate dehydrogenase as a therapeutic target for obesity cardiomyopathy. Expert Opin Ther Targets.2016; 20(6): 755-766.[21]Ussher JR, Wang W, Gandhi M, et al.Stimulation of glucose oxidation protects against acute myocardial infarction and reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;94(2): 359-369.[22]Gudiksen A, Bertholdt L, Vingborg MB,et al.Muscle interleukin-6 and fasting-induced PDH regulation in mouse skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2017;312(3): E204-E214.[23]Harrison BC, Bell ML, Allen DL, et al. Skeletal muscle adaptations in response to voluntary wheel running in myosin heavy chain null mice. J Appl Physiol (1985).2002; 92(1): 313-322.[24]Krus U,Kotova O,Spégel P,et al.Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 controls mitochondrial metabolism and insulin secretion in INS-1 832/13 clonal beta-cells. Biochem J. 2010; 429(1):205-213.[25]Bortesi L, Zhu C, Zischewski J, et al. Patterns of CRISPR/Cas9 activity in plants, animals and microbes. Plant Biotechnol J.2016;14(12): 2203-2216.[26]Valny M, Honsa P, Kirdajova D,et al.Tamoxifen in the Mouse Brain: Implications for Fate-Mapping Studies Using the Tamoxifen-Inducible Cre-loxP System. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10: 243.[27]Aguirre AJ, Meyers RM,Weir BA,et al.Genomic Copy Number Dictates a Gene-Independent Cell Response to CRISPR/Cas9 Targeting. Cancer Discov.2016;6(8): 914-929.[28]Cerniglia GJ, Dey S, Gallagher-Colombo SM,et al. The PI3K/Akt Pathway Regulates Oxygen Metabolism via Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH)-E1α Phosphorylation. Mol Cancer Ther.2015;14(8):1928-1938. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
Cre 重组酶:由大肠杆菌噬菌体P1中Cre基因编码表达的蛋白单体,可特异性识别细胞DNA序列上的loxP位点,根据loxP位点的排列方式介导标记基因的特异性重组反应。
loxP序列:由2个13 bp反向重复序列和中间间隔的8 bp序列共同组成,可与Cre重组酶特异性结合位点。当2个loxP序列位于同一条DNA链且方向相同时,Cre重组酶能够敲除2个loxP序列间的DNA片段。
文题释义:
Cre 重组酶:由大肠杆菌噬菌体P1中Cre基因编码表达的蛋白单体,可特异性识别细胞DNA序列上的loxP位点,根据loxP位点的排列方式介导标记基因的特异性重组反应。
loxP序列:由2个13 bp反向重复序列和中间间隔的8 bp序列共同组成,可与Cre重组酶特异性结合位点。当2个loxP序列位于同一条DNA链且方向相同时,Cre重组酶能够敲除2个loxP序列间的DNA片段。.jpg) 文题释义:
Cre 重组酶:由大肠杆菌噬菌体P1中Cre基因编码表达的蛋白单体,可特异性识别细胞DNA序列上的loxP位点,根据loxP位点的排列方式介导标记基因的特异性重组反应。
loxP序列:由2个13 bp反向重复序列和中间间隔的8 bp序列共同组成,可与Cre重组酶特异性结合位点。当2个loxP序列位于同一条DNA链且方向相同时,Cre重组酶能够敲除2个loxP序列间的DNA片段。
文题释义:
Cre 重组酶:由大肠杆菌噬菌体P1中Cre基因编码表达的蛋白单体,可特异性识别细胞DNA序列上的loxP位点,根据loxP位点的排列方式介导标记基因的特异性重组反应。
loxP序列:由2个13 bp反向重复序列和中间间隔的8 bp序列共同组成,可与Cre重组酶特异性结合位点。当2个loxP序列位于同一条DNA链且方向相同时,Cre重组酶能够敲除2个loxP序列间的DNA片段。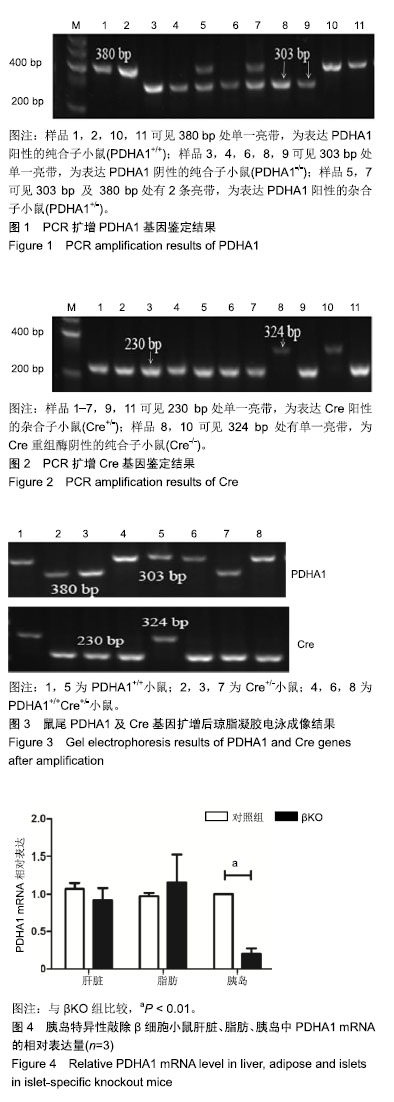
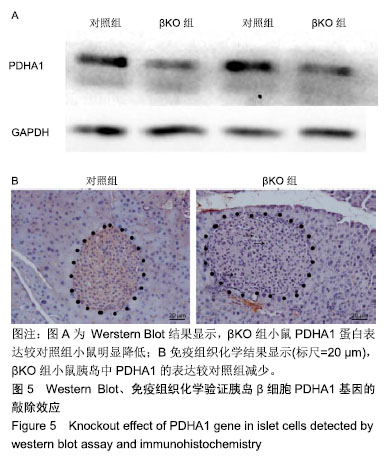
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
Cre 重组酶:由大肠杆菌噬菌体P1中Cre基因编码表达的蛋白单体,可特异性识别细胞DNA序列上的loxP位点,根据loxP位点的排列方式介导标记基因的特异性重组反应。
loxP序列:由2个13 bp反向重复序列和中间间隔的8 bp序列共同组成,可与Cre重组酶特异性结合位点。当2个loxP序列位于同一条DNA链且方向相同时,Cre重组酶能够敲除2个loxP序列间的DNA片段。
文题释义:
Cre 重组酶:由大肠杆菌噬菌体P1中Cre基因编码表达的蛋白单体,可特异性识别细胞DNA序列上的loxP位点,根据loxP位点的排列方式介导标记基因的特异性重组反应。
loxP序列:由2个13 bp反向重复序列和中间间隔的8 bp序列共同组成,可与Cre重组酶特异性结合位点。当2个loxP序列位于同一条DNA链且方向相同时,Cre重组酶能够敲除2个loxP序列间的DNA片段。