中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (31): 5030-5035.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1338
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
中强度耐力运动与大蒜素对高脂饮食致脂肪肝模型大鼠具有协同抵抗效应
杨忠明1,蒋满意2,许思毛3
- (1桂林电子科技大学信息科技学院,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541004;2浙江经贸职业技术学院,浙江省杭州市 310018;3广西师范大学体育学院,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541004)
Synergistic resistance of moderate-intensity endurance exercise and allicin to rat models of fatty liver induced by high-fat diet
Yang Zhongming1, Jiang Manyi2, Xu Simao3
- (1College of Information Science and Technology, Guilin University of Electronic Science and Technology, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Zhejiang Vocational and Technical College of Economics and Trade, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China; 3College of Physical Education, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
大蒜素:存在于大蒜鳞茎中,是大蒜的主要活性物质,化学名为烯丙基硫代亚磺酯丙酯,具有降脂、抗氧化及防治心血管疾病、护肝、抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤等多种功效。
脂肪肝:是指由于各种原因引起的肝细胞内脂肪堆积过多的病变,是一种常见的肝脏病理改变,而非一种独立的疾病。脂肪性肝病正严重威胁国人的健康,成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病,发病率在不断升高,且发病年龄日趋年轻化。脂肪肝一般分为酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝两大类,此次研究中脂肪肝模型属于非酒精性脂肪肝。
文题释义:
大蒜素:存在于大蒜鳞茎中,是大蒜的主要活性物质,化学名为烯丙基硫代亚磺酯丙酯,具有降脂、抗氧化及防治心血管疾病、护肝、抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤等多种功效。
脂肪肝:是指由于各种原因引起的肝细胞内脂肪堆积过多的病变,是一种常见的肝脏病理改变,而非一种独立的疾病。脂肪性肝病正严重威胁国人的健康,成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病,发病率在不断升高,且发病年龄日趋年轻化。脂肪肝一般分为酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝两大类,此次研究中脂肪肝模型属于非酒精性脂肪肝。
.jpg) 文题释义:
大蒜素:存在于大蒜鳞茎中,是大蒜的主要活性物质,化学名为烯丙基硫代亚磺酯丙酯,具有降脂、抗氧化及防治心血管疾病、护肝、抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤等多种功效。
脂肪肝:是指由于各种原因引起的肝细胞内脂肪堆积过多的病变,是一种常见的肝脏病理改变,而非一种独立的疾病。脂肪性肝病正严重威胁国人的健康,成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病,发病率在不断升高,且发病年龄日趋年轻化。脂肪肝一般分为酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝两大类,此次研究中脂肪肝模型属于非酒精性脂肪肝。
文题释义:
大蒜素:存在于大蒜鳞茎中,是大蒜的主要活性物质,化学名为烯丙基硫代亚磺酯丙酯,具有降脂、抗氧化及防治心血管疾病、护肝、抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤等多种功效。
脂肪肝:是指由于各种原因引起的肝细胞内脂肪堆积过多的病变,是一种常见的肝脏病理改变,而非一种独立的疾病。脂肪性肝病正严重威胁国人的健康,成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病,发病率在不断升高,且发病年龄日趋年轻化。脂肪肝一般分为酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝两大类,此次研究中脂肪肝模型属于非酒精性脂肪肝。摘要
背景:近年来,高脂饮食及运动缺乏导致非酒精性脂肪肝发病率逐年上升。耐力运动和大蒜素均可改善血脂代谢,但有关耐力运动联合大蒜素抗高脂饮食大鼠脂肪肝形成作用方面的研究非常少见。
目的:探讨中强度耐力运动联合大蒜素抗高脂饮食大鼠脂肪肝形成作用。
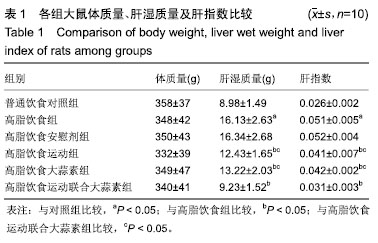
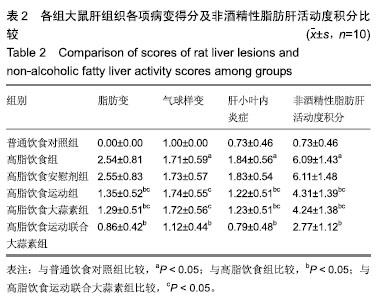
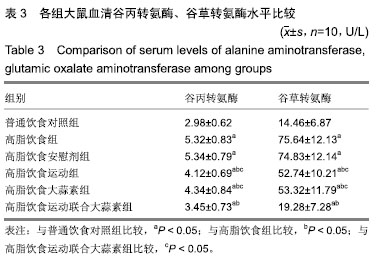
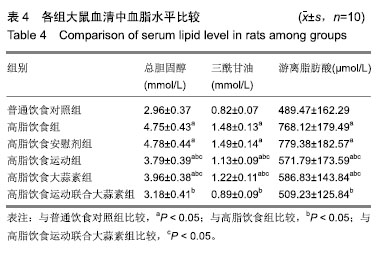
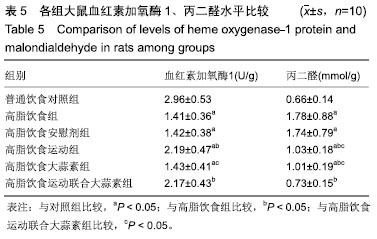
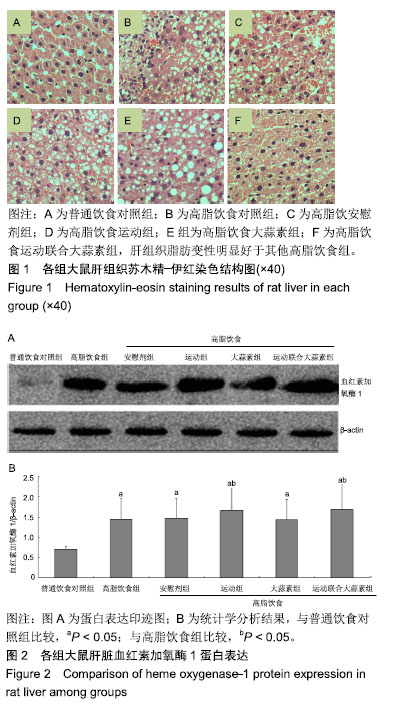
方法:实验方案经广西师范大学动物实验伦理委员会批准。选择成年雄性 SD 大鼠 60 只,随机分为普通饮食对照组、高脂饮食组、高脂饮食安慰剂组、高脂饮食运动组、高脂饮食大蒜素组及高脂饮食运动联合大蒜素组。普通饮食对照组大鼠采用普通饲料喂养,其余组大鼠采用高脂饲料喂养,均自由饮食;高脂饮食大蒜素组、高脂饮食运动联合大蒜素组大鼠给予大蒜素液灌胃;高脂饮食安慰剂组则用同等体积剂量的蒸馏水灌胃。此外,高脂饮食运动组、高脂饮食运动联合大蒜素组大鼠进行耐力跑锻炼,每天30 min、每天1次、每周 6 d。观察大鼠肝脏血红素加氧酶1 蛋白表达及其活性、丙二醛含量等的变化,观察血液谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶及三酰甘油、游离脂肪酸、总胆固醇等浓度变化;观察肝组织形态学变化并计算非酒精性脂肪肝活动度积分。
结果与结论:①高脂饮食引起大鼠血液三酰甘油、游离脂肪酸、总胆固醇及谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶等浓度显著升高(P < 0.05),导致肝脏血红素加氧酶1活性显著下降及丙二醛含量显著升高(P < 0.05),且肝脏出现明显脂肪变性、非酒精性脂肪肝活动度积分显著升高(P < 0.05);②与高脂饮食组相比,高脂饮食运动组、高脂饮食运动联合大蒜素组脂肝脏血红素加氧酶1蛋白表达及血红素加氧酶1活性显著升高(P < 0.05);③与高脂饮食组相比,高脂饮食运动组、高脂饮食大蒜素组、高脂饮食运动联合大蒜素组血液三酰甘油、游离脂肪酸、总胆固醇及谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶等浓度显著下降(P < 0.05),肝脏丙二醛含量显著下降(P < 0.05),肝组织脂肪变性得到明显改善且非酒精性脂肪肝活动度积分显著下降(P < 0.05);上述变化以高脂饮食运动联合大蒜素组最明显;④结果说明,中强度耐力运动与大蒜素对高脂饮食大鼠脂肪肝形成具协同抵抗效应,可能与二者对肝脏脂质过氧化反应及血液三酰甘油、游离脂肪酸、总胆固醇浓度升高等方面的协同控制作用有关。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
大蒜素:存在于大蒜鳞茎中,是大蒜的主要活性物质,化学名为烯丙基硫代亚磺酯丙酯,具有降脂、抗氧化及防治心血管疾病、护肝、抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤等多种功效。
脂肪肝:是指由于各种原因引起的肝细胞内脂肪堆积过多的病变,是一种常见的肝脏病理改变,而非一种独立的疾病。脂肪性肝病正严重威胁国人的健康,成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病,发病率在不断升高,且发病年龄日趋年轻化。脂肪肝一般分为酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝两大类,此次研究中脂肪肝模型属于非酒精性脂肪肝。
文题释义:
大蒜素:存在于大蒜鳞茎中,是大蒜的主要活性物质,化学名为烯丙基硫代亚磺酯丙酯,具有降脂、抗氧化及防治心血管疾病、护肝、抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤等多种功效。
脂肪肝:是指由于各种原因引起的肝细胞内脂肪堆积过多的病变,是一种常见的肝脏病理改变,而非一种独立的疾病。脂肪性肝病正严重威胁国人的健康,成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病,发病率在不断升高,且发病年龄日趋年轻化。脂肪肝一般分为酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝两大类,此次研究中脂肪肝模型属于非酒精性脂肪肝。