| [1] Mitchell NS,Catenacci VA,Wyatt HR,et al.Obesity: overview of an epidemic.Psychiatr Clin North Am.2011;34(4): 717-732.[2] 倪国华,张璟,郑风田.中国肥胖流行的现状与趋势[J].中国食物与营养,2013,19(10):70-74.[3] Strasser B. Physical activity in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013;1281:141-159.[4] Matsunaga Y,Tamura Y,Sakata Y,et al.Comparison between pre–exercise casein peptide and intact casein supplementation on glucose tolerance in high–fat diet–fed mice. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab.2017;1. [5] Wang N,Liu Y,Ma Y,et al.High-intensity interval versus moderate-intensity continuous training: Superior metabolic benefits in diet-induced obesity mice.Life Sci. 2017;15(191): 122-131.[6] Bae JY,Woo J,Roh HT,et al.The effects of detraining and training on adipose tissue lipid droplet in obese mice after chronic high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis.2017;16(1):13.[7] Marques CM,Motta VF,Torres TS,et al. Beneficial effects of exercise training (treadmill) on insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat fed C57BL/6 mice.Braz J Med Biol Res.2010;43(5):467-475.[8] Chiu CH,Ko MC,Wu LS,et al.Benefits of different intensity of aerobic exercise in modulating body composition among obese young adults: a pilot randomized controlled trial.Health Qual Life Outcomes.2017;15(1):168.[9] Puigserver P,Wu Z,Park CW,et al.A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis.Cell. 998; 92:829-839.[10] Bostrom P,Wu J,Jedrychowski MP,et al.A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature.2012;481(7382):463-468.[11] Lira VA,Benton CR,Yan Z,et al.PGC-1α regulation by exercise training and its influences on muscle function and insulin sensitivity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2010;299:145-161.[12] Yan Z,Li P,Akimoto T.Transcriptional control of the Pgc-1α gene in skeletal muscle in vivo.Exerc Sport Sci Rev.2007;35(3):97-101.[13] Lopaschuk GD,Belke DD,Gamble J,et al.Regulation of fatty acid oxidation in the mammalian heart in health and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta.1994;1213(4):263-276.[14] Hondares E,Torra IP,Iglesias R,et al.PPARδ, but not PPARα, activates PGC-1α gene transcription in muscle. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2007;354: 1021-1027.[15] Luquet S,Lopez-Soriano J,Holst D,et al.Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ controls muscle development and oxydative capability.FASEB J.2003;17(15):2299-2301.[16] Wang Y,Lee CH,Tiep S,et al. Peroxisome-proliferator- activated receptor δ activates fat metabolism to prevent obesity.Cell. 2003;113(2):159-170.[17] Dressel U, Allen TL, Pippal JB, et al. The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor β/δ Agonist, GW501516, Regulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Catabolism and Energy Uncoupling in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17(12):2477-2493.[18] Roberts MD,Bayless DS,Company JM,et al.Elevated skeletal muscle irisin precursor FNDC5 mRNA in obese OLETF rats. Metabolism. 2013;62(8):1052-1056.[19] Swick AG,Orena S,O'Connor A.Irisin levels correlate with energy expenditure in a subgroup of humans with energy expenditure greater than predicted by fat free mass.Metabolism.2013;62(8): 1070-1073.[20] Handschin C,Chin S,Li P,et al.Skeletal muscle ?ber-type switching, exercise intolerance, and myopathy in PGC-1α muscle-speci?c knock-out animals.J Biol Chem.2007;282:30014-30021.[21] Camargo GL,de Souza RA,da Silva DB,et al.Raman spectral characteristics of neck and head of femur in low-density lipoprotein receptor gene knockout mice submitted to treadmill aerobic training.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;173:92-98.[22] 朱小烽,王茹,杨钦,等.不同强度急性有氧运动对肥胖小鼠PGC-1α及其下游因子的调控影响[J].体育科学, 2017,37(3):44-50.[23] Kus V,Prazak T,Brauner P,et al.Induction of muscle thermogenesis by high-fat diet in mice: association with obesity-resistance.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;295(2): E356-E367.[24] Wang B,Sun J,Ma Y,et al.Increased oxidative stress and the apoptosis of regulatory T cells in obese mice but not resistant mice in response to a high-fat diet.Cell Immunol. 2014;288(1-2): 39-46.[25] 王欢,李宛真,汪弋力,等.高脂饮食诱导的肥胖及肥胖抵抗小鼠肠道菌群元基因组的比较研究[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2014, 35(2):240-244.[26] Timmons JA,Baar K,Davidsen PK,et a1.Is irisin a human exercise gene? Nature.2012;488(7413):E9-E10.[27] Chen J,Huang Y,Gusdon AM,et al.Irisin: a new molecular marker and target in metabolic disorder. Lipids Health Dis.2015;14:2.[28] Huh JY,Panagiotou G,Mougios V,et al.FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise.Metabolism.2012;61(12): 1725-1738.[29] Stengel A,Hofmann T,Goebel-Stengel M,et al.Circulating levels of irisin in patients with anorexia nervosa and different stages of obesity-correlation with body mass index.Peptides.2013;39: 125-130.[30] Crujeiras AB,Pardo M,Arturo RR,et al.Longitudinal variation of circulating irisin after an energy restriction-induced weight loss and following weight regain in obese men and women.Am J Hum Biol. 2014;26(2):198-207.[31] Choi YK, Kim MK, Bae KH, et al. Serum irisin levels in new-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013;100(1):96-101.[32] Moreno-Navarrete JM,Ortega F,Serrano M,et al.Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(4):E769-778.[33] Lecker SH,Zavin A,Cao P,et al.Expression of the irisin precursor FNDC5 in skeletal muscle correlates with aerobic exercise performance in patients with heart failure.Circ Heart Fail. 2012; 5(6):812-818.[34] Mahmoodnia L,Sadoughi M,Ahmadi A,et al.Relationship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients.J Renal Inj Prev.2017;6(2):88-92.[35] Rohas LM,St-Pierre J,Uldry M,et al.A Fundamental System of Cellular Energy Homeostasis Regulated by PGC-1α.Proc Natl Acad Sci.U.S.A. 2007;104(19):7933-7938.[36] Arany Z.PGC-1 coactivators and skeletal muscle adaptations in health and disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008;18(5):426-434.[37] Wenz T,Rossi SG,Rotundo RL,et al.Increased muscle PGC-1α expression protects from sarcopenia and metabolic disease during aging.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(48): 20405-20410.[38] Choi CS,Befroy DE,Codella R,et al.Paradoxical effects of increased expression of PGC-1α on muscle mitochondrial function and insulin -stimulated muscle glucose metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(50):19926-19931.[39] Handschin C,Choi CS,Chin S,et al.Abnormal glucose homeostasis in skeletal muscle-specific PGC-1α knockout mice reveals skeletal muscle -pancreatic β cell crosstalk.J Clin Invest. 2007;117(11):3463-3474.[40] Mootha VK,Handschin C,Arlow D,et al.Errα and Gabpa/b Specify PGC-1α-Dependent Oxidative Phosphorylation Gene Expression That Is Altered in Diabetic Muscle.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(17):6570-6575.[41] de Macêdo SM,Lelis DF,Mendes KL,et a1.Effects of Dietary Macronutrient Composition on FNDC5 and Irisin in Mice Skeletal Muscle.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2017;15(4):161-169.[42] Wang Y,Zhang C,Yu R,et al.Regulation of muscle fiber type and running endurance by PPARδ.PLoS Biol.2004;2:1532-1538.[43] 邹毅,管晓峰,黄淑玉,等.运动对高脂饮食诱导肥胖大鼠过氧化物酶体增长因子活化受体-δ表达和胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2011,3(2):107-111.[44] Nygaard H,Slettaløkken G,Vegge G,et al.Irisin in blood increases transiently after single sessions of intense endurance exercise and heavy strength training.PLoS One.2015;10 (3):e0121367.[45] Lee P,Linderman JD,Smith S,et a1.Irisin and FGF21 are cold-induced endocrine activators of brown fat function in humans.Cell Metabolism.2014;19(2):302-309.[46] Saleem A, Safdar A,Haikalis M,et a1.Exercise-Induced Amelioration of Diet-Induced Obesity and Diabetes is Not Regulated by Irisin.The FASEB Journal.2015;29(1): 992.[47] Hecksteden A,Wegmann M,Steffen A,et al.Irisin and exercise training in humans-Results from a randomized controlled training trial.BMC Med.2013;11(1):235.[48] Ellefsen S,Vikmoen O,Slettalokken G,et al.Irisin and FNDC5: effects of 12-week strength training, and relations to muscle phenotype and body mass composition in untrained women.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2014;114(9):1875-1888.[49] Czarkowska-Paczek B,Zendzian-Piotrowska M,Gala K,et al.One session of exercise or endurance training does not influence serum levels of irisin in rats.J Physiol Pharmacol.2014;65(3): 449-454.[50] Seo DY,Kwak HB,Lee SR,et al.Effects of aged garlic extract and endurance exercise on skeletal muscle FNDC-5 and circulating irisin in high-fat-diet rat models.Nutr Res Pract.2014;8(2): 177-182.[51] Kim H,Lee HJ,So B,et a1.Effect of aerobic training and resistance training on circulating irisin level and their association with change of body composition in overweight/obese adults: a pilot study. Physiol Res.2016;65(2):271-279.[52] Tadaishi M,Miura S,Kai Y,et al.Effect of exercise intensity and AICAR on isoform-specific expressions of murine skeletal muscle PGC-1α mRNA: a role of β?-adrenergic receptor activation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2011;300(2):E341-E349.[53] Terada S, Tabata I. Effects of acute bouts of running and swimming exercise on PGC-1α protein expression in rat epitrochlearis and soleus muscle.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;286(14):208-216.[54] Kannisto K,Chibalin A,Glinghammar B,et al.Differential expression of peroxisomal proliferator activated receptors α and δ in skeletal muscle in response to changes in diet and exercise.Int J Mol Med.2006;17:45-52.[55] 苏丽,姜宁,张玥,等.有氧运动对C57BL/6小鼠骨骼肌PPARδ表达和肌纤维类型的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2008,27(1):27-31. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子α(PGC-1α):运动可以提高骨骼肌PGC-1α蛋白的表达,在生物学上具有促进肌肉纤维类型转化,促进葡萄糖代谢和脂肪酸氧化代谢等作用。
Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5(FNDC5):是Irisin的前体,由Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5基因编码的一种主要由肌肉分泌的膜蛋白,能促进能量消耗,促进白色脂肪细胞向棕色脂肪细胞的转化。
鸢尾素(Irisin):2012年发现的具有减肥作用的新激素,由骨骼肌分泌释放,与运动密切相关,是Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5蛋白经蛋白水解酶水解形成的约110个氨基酸大小的可分泌多肽分子。
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体δ(PPARδ):是调节骨骼肌糖类和脂肪酸代谢相关基因表达的核内受体,骨骼肌中PPARδ的表达受过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子1α调控。
文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子α(PGC-1α):运动可以提高骨骼肌PGC-1α蛋白的表达,在生物学上具有促进肌肉纤维类型转化,促进葡萄糖代谢和脂肪酸氧化代谢等作用。
Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5(FNDC5):是Irisin的前体,由Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5基因编码的一种主要由肌肉分泌的膜蛋白,能促进能量消耗,促进白色脂肪细胞向棕色脂肪细胞的转化。
鸢尾素(Irisin):2012年发现的具有减肥作用的新激素,由骨骼肌分泌释放,与运动密切相关,是Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5蛋白经蛋白水解酶水解形成的约110个氨基酸大小的可分泌多肽分子。
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体δ(PPARδ):是调节骨骼肌糖类和脂肪酸代谢相关基因表达的核内受体,骨骼肌中PPARδ的表达受过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子1α调控。.jpg) 文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子α(PGC-1α):运动可以提高骨骼肌PGC-1α蛋白的表达,在生物学上具有促进肌肉纤维类型转化,促进葡萄糖代谢和脂肪酸氧化代谢等作用。
Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5(FNDC5):是Irisin的前体,由Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5基因编码的一种主要由肌肉分泌的膜蛋白,能促进能量消耗,促进白色脂肪细胞向棕色脂肪细胞的转化。
鸢尾素(Irisin):2012年发现的具有减肥作用的新激素,由骨骼肌分泌释放,与运动密切相关,是Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5蛋白经蛋白水解酶水解形成的约110个氨基酸大小的可分泌多肽分子。
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体δ(PPARδ):是调节骨骼肌糖类和脂肪酸代谢相关基因表达的核内受体,骨骼肌中PPARδ的表达受过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子1α调控。
文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子α(PGC-1α):运动可以提高骨骼肌PGC-1α蛋白的表达,在生物学上具有促进肌肉纤维类型转化,促进葡萄糖代谢和脂肪酸氧化代谢等作用。
Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5(FNDC5):是Irisin的前体,由Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5基因编码的一种主要由肌肉分泌的膜蛋白,能促进能量消耗,促进白色脂肪细胞向棕色脂肪细胞的转化。
鸢尾素(Irisin):2012年发现的具有减肥作用的新激素,由骨骼肌分泌释放,与运动密切相关,是Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5蛋白经蛋白水解酶水解形成的约110个氨基酸大小的可分泌多肽分子。
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体δ(PPARδ):是调节骨骼肌糖类和脂肪酸代谢相关基因表达的核内受体,骨骼肌中PPARδ的表达受过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子1α调控。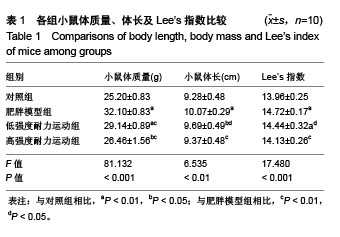
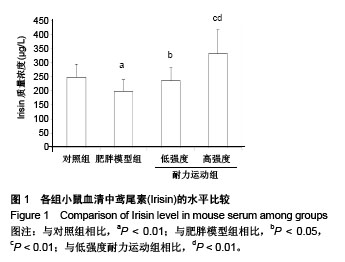
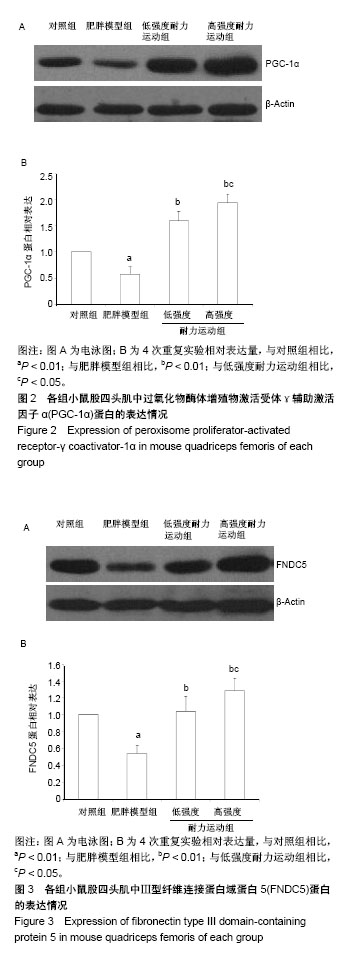
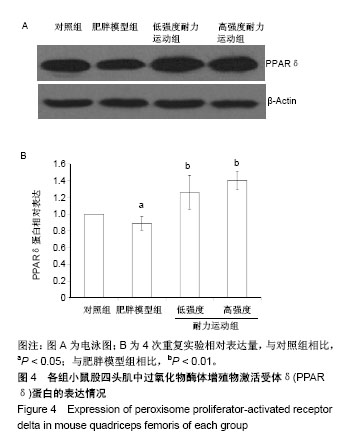
.jpg) 文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子α(PGC-1α):运动可以提高骨骼肌PGC-1α蛋白的表达,在生物学上具有促进肌肉纤维类型转化,促进葡萄糖代谢和脂肪酸氧化代谢等作用。
Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5(FNDC5):是Irisin的前体,由Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5基因编码的一种主要由肌肉分泌的膜蛋白,能促进能量消耗,促进白色脂肪细胞向棕色脂肪细胞的转化。
鸢尾素(Irisin):2012年发现的具有减肥作用的新激素,由骨骼肌分泌释放,与运动密切相关,是Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5蛋白经蛋白水解酶水解形成的约110个氨基酸大小的可分泌多肽分子。
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体δ(PPARδ):是调节骨骼肌糖类和脂肪酸代谢相关基因表达的核内受体,骨骼肌中PPARδ的表达受过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子1α调控。
文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子α(PGC-1α):运动可以提高骨骼肌PGC-1α蛋白的表达,在生物学上具有促进肌肉纤维类型转化,促进葡萄糖代谢和脂肪酸氧化代谢等作用。
Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5(FNDC5):是Irisin的前体,由Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5基因编码的一种主要由肌肉分泌的膜蛋白,能促进能量消耗,促进白色脂肪细胞向棕色脂肪细胞的转化。
鸢尾素(Irisin):2012年发现的具有减肥作用的新激素,由骨骼肌分泌释放,与运动密切相关,是Ⅲ型纤维连接蛋白域蛋白5蛋白经蛋白水解酶水解形成的约110个氨基酸大小的可分泌多肽分子。
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体δ(PPARδ):是调节骨骼肌糖类和脂肪酸代谢相关基因表达的核内受体,骨骼肌中PPARδ的表达受过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅助激活因子1α调控。