中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (14): 2231-2235.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3102
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
20 m折返跑推测20-29岁成年人的无氧阈强度
贾 潇1,薛晓婧2,孔振兴1,于晶晶1,孙婷婷1,张一民1
- 1北京体育大学运动与体质健康教育部重点实验室,北京市 100084;2中国高等教育学会,北京市 100191
Anaerobic threshold intensity of adults aged 20 to 29: a speculation based on a 20-meter shuttle run test
Jia Xiao1, Xue Xiaojing2, Kong Zhenxing1, Yu Jingjing1, Sun Tingting1, Zhang Yimin1
- 1Key Laboratory of Sports and Physical Health of the Ministry of Education, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China; 2China Association of Higher Education, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
 文题释义:
文题释义:
无氧阈强度:人体在逐渐增加运动强度的运动中会出现由有氧代谢供能开始大量动用无氧代谢供能的临界点,这一临界点所对应的运动强度为无氧阈强度。用无氧阈强度指导训练,能够在能量代谢上将无氧供能的比例减少到最低程度的情况下使呼吸、循环功能达到或接近其最大水平,因而无氧阈强度是发展有氧耐力的最佳强度。
20 m折返跑:是一种用于评定心肺耐力的间接测试方法。该方法能模拟非实验室环境下测试有氧能力的渐进性递增负荷状态,最大限度契合实验室测试的递增负荷模式的基本控制要素,具有简便易行、成本低、重复性好等优点,广泛应用于心肺耐力测试。
背景:适宜运动强度的选择是制定个性化精准指导方案的关键。无氧阈强度是发展有氧耐力的最佳强度,常用无氧阈的测定需要在实验室环境下进行,步骤复杂、成本偏高,并且需要专业的人员计算分析,存在一定的局限性。
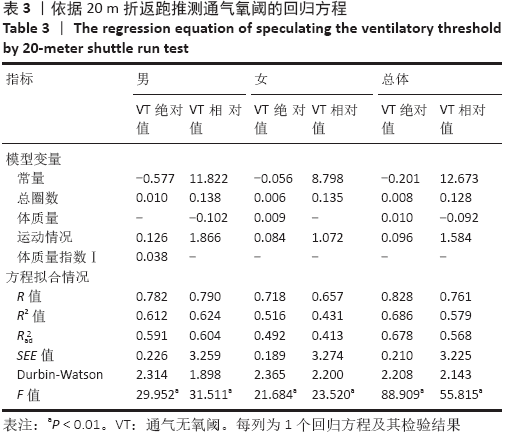
目的:探索用20 m折返跑测试成绩结合性别、年龄、身高、体质量、运动情况等指标推测无氧阈强度的可行性,建立推测20-29岁成年人无氧阈强度的回归方程。
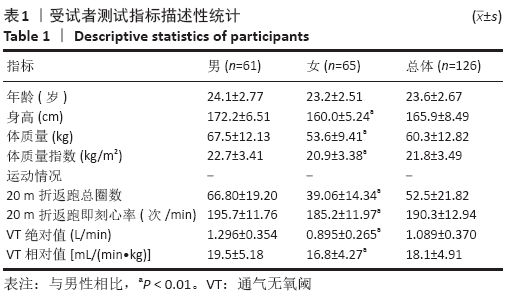
方法:招募20-29岁受试者共计126人,其中男性61人,女性65人。首先采集性别、年龄、身高、体质量、运动情况等指标,然后利用功率自行车进行递增负荷运动试验(GXT)采集气体代谢指标并计算通气无氧阈(VT),择日进行20 m折返跑测试。根据各指标相关性分析结果,将通气无氧阈作为因变量,20 m折返跑测试成绩和其他相关指标作为自变量,采用逐步回归的方法建立回归方程。
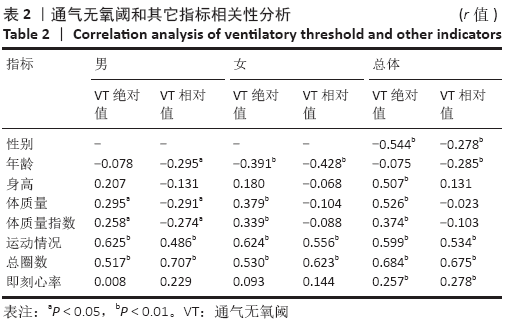
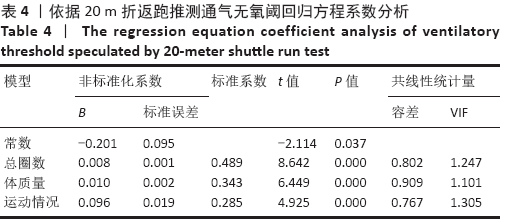
结果与结论:①20 m折返跑的总圈数与总样本的通气无氧阈绝对值中度相关,r=0.684(P < 0.01);②20 m折返跑推测20-29岁成年人无氧阈强度回归方程为:通气无氧阈(L/min)=-0.201+0.008*总圈数+0.01*体质量+0.096*运动情况(R=0.828,R2=0.686,SEE=0.210);③提示:20 m折返跑推测20-29岁成年人无氧阈强度的方法可行,可用于指导大众科学、安全、有效健身。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5198-2612 (贾潇)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: